boost库中的filesystem中有关路径的操作十分的方便特别是path重载的/,看起来就像对普通路径的书写一样,你再也不用担心为组合路径时少写‘/’而导致找不到文件或者程序直接崩溃烦恼啦,因为当你缺少时path会自动的给你添加上啦。而在C++14以上的版本这块正式成了C++的标准啦。废话不说啦,直接上代码,下面只演示了一些常用的,更多方法可以直接go到源码中去看看。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost::filesystem;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
string filePath = "/work/test/testPath";
string fileName = "test_path.txt";
//path("/work/test/testPath/test_path.txt");
boost::filesystem::path testFilePath(filePath);
// 使用'/'追加路径,并把路径转化成字符串
string fullFilePath = (testFilePath/fileName).string();
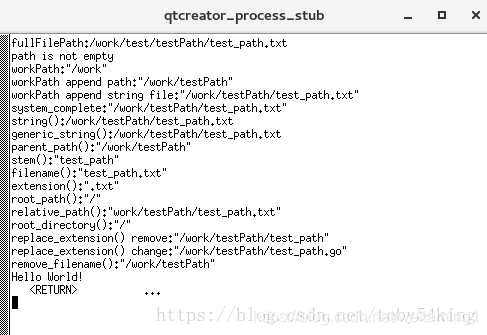
cout << "fullFilePath:" << fullFilePath << endl;
if(!testFilePath.empty())
cout << "path is not empty" << endl;
// 取fullFilePath中的部分路径
boost::filesystem::path workPath(fullFilePath.begin(),fullFilePath.begin()+5);
cout << "workPath:" << workPath << endl;
// 追加路径'/='
workPath /= "testPath";
cout << "workPath append path:" << workPath << endl;
// 追加字符序列append
workPath.append(fileName.begin(),fileName.end());
cout << "workPath append string file:" << workPath << endl;
// 返回当前文件系统下的绝对路径system_complete
cout << "system_complete:" << system_complete(workPath) << endl;
// 返回标准格式的文件路径string()
cout << "string():" << workPath.string() << endl;
// 返回文件通用路径
if(workPath.is_absolute())
cout << "generic_string():" << workPath.generic_string() << endl;
// 返回路径中的父路径
if(workPath.has_parent_path())
cout << "parent_path():" << workPath.parent_path() << endl;
// 不含扩展名的全路径
if(workPath.has_stem())
cout << "stem():" << workPath.stem() << endl;
// 返回文件名
if(workPath.has_filename())
cout << "filename():" << workPath.filename() << endl;
// 返回文件扩展名
cout << "extension():" << workPath.extension() << endl;
// 返回路径根目录
if(workPath.has_root_path())
cout << "root_path():" << workPath.root_path() << endl;
// 返回根名称
if(workPath.has_root_name())
cout << "root_name():" << workPath.root_name() << endl;
// 返回相对路径
if(workPath.has_relative_path())
cout << "relative_path():" << workPath.relative_path() << endl;
// 返回root文件夹目录
if(workPath.has_root_directory())
cout << "root_directory():" << workPath.root_directory() << endl;
// 变更文件扩展名(只是看起来像更改了,实际的文件名字并没有发生变化)
cout << "replace_extension() remove:" << workPath.replace_extension() << endl; // 删除扩展名
cout << "replace_extension() change:" << workPath.replace_extension("go") << endl; // 更改扩展名
// 删除文件名
cout << "remove_filename():" << workPath.remove_filename() << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
补充:
头文件
#include “boost/filesystem/path.hpp”
#include “boost/filesystem/operations.hpp”
获取当前绝对路径
string fullpath = boost::filesystem::initial_pathboost::filesystem::path().string();
fullpath.generic_string() vs fullpath.string() 的区别。
std::string getAbsolutePath()
{
boost::filesystem::path fullpath;
fullpath = boost::filesystem::initial_path<boost::filesystem::path>();
std::cout << "dir system_complete : " << fullpath << endl;
std::cout << "dir generic_string : " << fullpath.generic_string() << endl;
return fullpath.generic_string();
}
bool createDir(const string sDir)
{
boost::filesystem::path dir(sDir);
return boost::filesystem::create_directory(dir);
//if (boost::filesystem::create_directory(dir)) {
// //std::cout << "Success" << "\n";
//}
}
创建文件路径
create_directories() vs create_directory() 的区别
create_directory() : 只能用于boost::filesystem::path dir("./web_static"); 在已经存在的路径下,添加单层的文件夹,不能是多层文件夹路径的。
create_directories(): 可以用于多层文件夹或单层文件夹路径。
boost::filesystem::path dir("./web_static/pcd");
if (boost::filesystem::create_directories(dir)) {
std::cout << "Success create pcd dir" << "\n";
}
boost::filesystem::path dir("./web_static);
if (boost::filesystem::create_directory(dir)) {
std::cout << "Success create pcd dir" << "\n";
}
创建多级目录boost::filesystem::create_directories
是否是目录 boost::filesystem::is_directory
文件是不是存在 boost::filesystem::exists(strPath)
返回文件修改时间 boost::filesystem::last_write_time























 778
778

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








