1、硬件中断设计
关于中断,首先从其硬件结构说起,以下是一个典型的ARM soc的中断结构图。
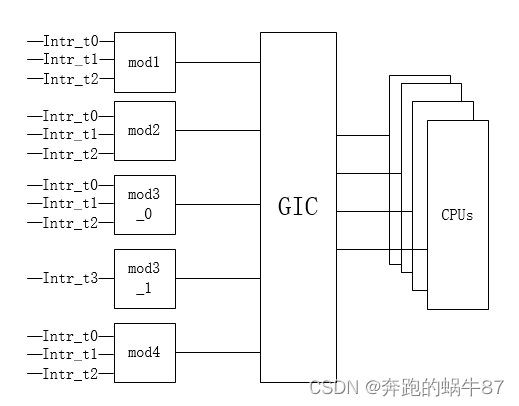
如图所示,所有模块的子中断都接入到GIC(Generic Interrupt Controller, arm公司推出),然后由GIC接入到各个CPU。不同的CPU架构,使用的中断控制器不一样,如Riscv的中断控制器为 LIC(Local Interrupt Controller)。
GIC主要的工作为仲裁,分发中断。不同的CPU的架构,也可支持不同安全级别的中断。具体的GIC功能,自行查看GIC的相关资料。GIC介绍及详细说明,可从arm官网上下载。参考《Arm Generic Interrupt Controller Architecture Specification》Documentation – Arm Developer
GIC中断可分为SPI(Shared Peripheral Interrupt),PPI(Private Peripheral Interrupts)以及SGI(Software Generated Interrupts)。其中PPI为core的私有外设中断,一般用于CPU core的私有timer等;SGI为软件出发中断,一般用于多核之间的消息通信;SPI为共享外设中断,也就是通常所说的中断,本篇重点介绍SPI。
如上图所示,每个外设模块,可能有多个事件源,如I2C 控制器,可能有start event, arbitrate,RX Fifo not empty, TX fifo empty等众多事件源。一般来说,这些事件源会在外设模块内部统一归集到一个中断出口,这个中断出口连接GIC的某个input端口。这个端口编号,即我们常说的硬中断号。
所以,一旦CPU接收到一个中断后,GIC的中断服务,会根据中断号,调用对应的外设中断服务。外设中断服务首先查询该模块的中断状态,然后根据状态做对应的处理。如i2c,查询TX fifo,RX fifo的状态,以便接收和发送数据,或者查询到其他错误状态,驱动进行相应的错误处理。
当然,在一些特例的外设设计中,也可以一个外设模块支持多个中断接入到GIC上(图中mod3),即一个外设模块支持多个中断。这样的设计通常出现在复杂的外设中,如GPU。也可以为了提高特定中断的处理速度,如上所述,外设中断服务会先获取模块的中断状态标志位,再执行中断处理。单独的一个中断号(图中mod3_1),可以省略读多个标志位的步骤,从而可以快速处理该中断业务。
2、linux 中断框架
- 2.1 linux 中断处理流程
下图为一个典型的ARMv8架构的中断处理流程。
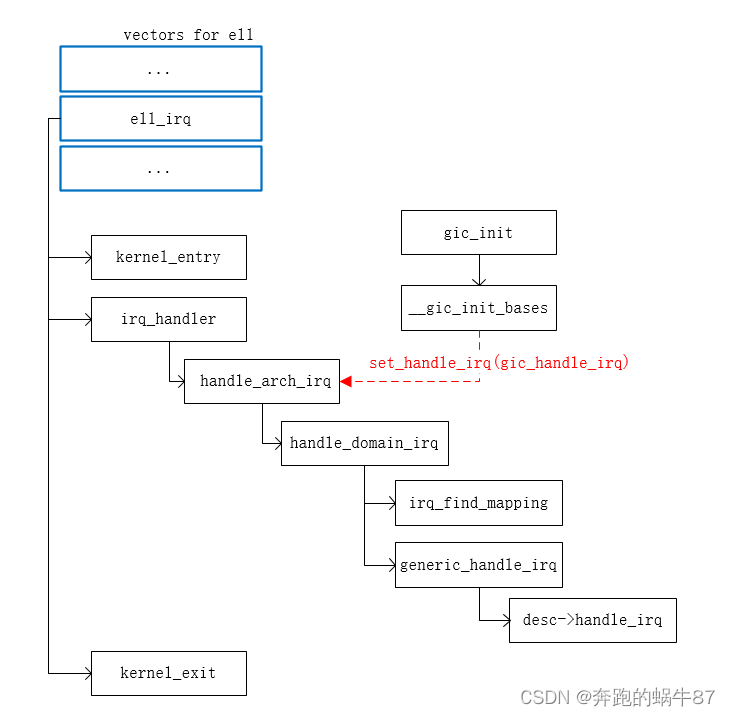
当有中断被GIC送到CPU时,CPU开始响应这个中断,CPU首先跳转至vertors的el1_irq处,这是因为linux运行在armv8的EL1级别,linux能响应的中断也在EL1处理。当然,部分中断可能只能在更高级别被处理,如安全认证的中断(此篇不介绍)。
el1_irq(汇编函数)首先会将当前CPU运行的上下文保存至中断运行栈中,中断处理完成后,再将CPU上下文恢复,此处用的汇编函数分别为kernel_entry,kernel_exit,感兴趣的可以自己研究相关源码。
irq_handler调用handle_arch_irq。根据CPU架构不同,其root中断控制器处理方法不同。所以在root中断控制器驱动初始化时,需要设置handle_arch_irq的函数地址。如上图,ARM的GIC控制器初始化时,设置root irq handle(set_handle_irq(gic_handle_irq))。
接下来的事务则由root中断控制器handle(gic_handle_irq)处理,此handle首先查询GIC寄存器,获取被rise的中断号。然后执行该中断号的handle,此处的接口为中断的上半部。关于下半部的调用,则由上半部决定。注意:部分中断request函数,只提供下半部的handle注册(接下来会分析原理)。
- 2.2结构框图
- 2.3 irq_domain
/**
* struct irq_domain - Hardware interrupt number translation object
* @link: Element in global irq_domain list.
* @name: Name of interrupt domain
* @ops: pointer to irq_domain methods
* @host_data: private data pointer for use by owner. Not touched by irq_domain
* core code.
* @flags: host per irq_domain flags
* @mapcount: The number of mapped interrupts
*
* Optional elements
* @fwnode: Pointer to firmware node associated with the irq_domain. Pretty easy
* to swap it for the of_node via the irq_domain_get_of_node accessor
* @gc: Pointer to a list of generic chips. There is a helper function for
* setting up one or more generic chips for interrupt controllers
* drivers using the generic chip library which uses this pointer.
* @parent: Pointer to parent irq_domain to support hierarchy irq_domains
* @debugfs_file: dentry for the domain debugfs file
*
* Revmap data, used internally by irq_domain
* @revmap_direct_max_irq: The largest hwirq that can be set for controllers that
* support direct mapping
* @revmap_size: Size of the linear map table @linear_revmap[]
* @revmap_tree: Radix map tree for hwirqs that don't fit in the linear map
* @linear_revmap: Linear table of hwirq->virq reverse mappings
*/
struct irq_domain {
struct list_head link;
const char *name;
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops;
void *host_data;
unsigned int flags;
unsigned int mapcount;
/* Optional data */
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token;
struct irq_domain_chip_generic *gc;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
struct irq_domain *parent;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
#endif
/* reverse map data. The linear map gets appended to the irq_domain */
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max;
unsigned int revmap_direct_max_irq;
unsigned int revmap_size;
struct radix_tree_root revmap_tree;
struct mutex revmap_tree_mutex;
unsigned int linear_revmap[];
};
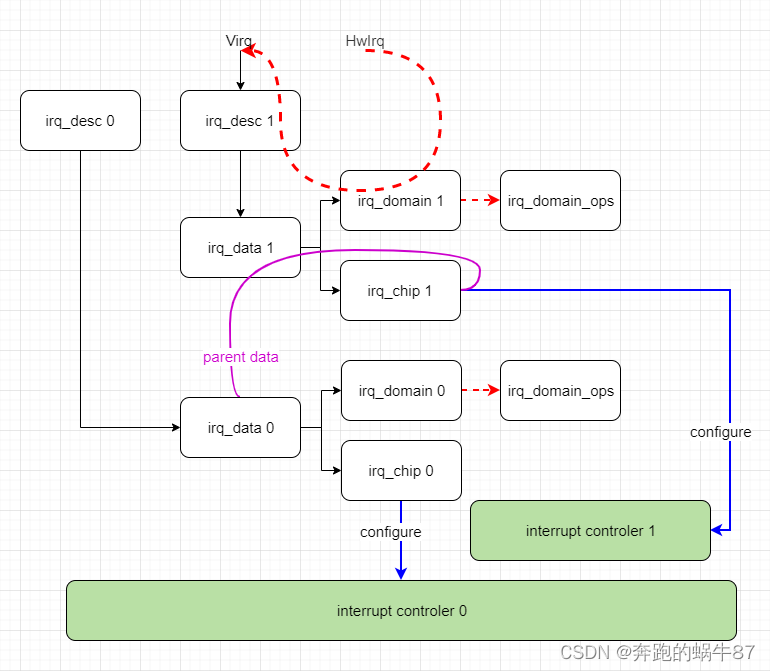
irq_domain是一个中断集合器的描述结构体,它可以描述gic,也可以描述其他中断集合器,如GPIO控制器的中断。
所以在注册中断时,需要提供中断所在的irq domain和编号,如果irq_domain为NULL,则指向default irq_domain 即root domain(Arm架构为gic驱动的irq_domain)。
中断编号则很好理解,如某外设接口的中断在GIC的偏移为87,则request irq时,irq domain为NULL,irq编号为87。如GPIO-B_25的中断注册,irq domain为GPIO-B控制器对应的irq_domain,irq为25。所以在dts配置gpio中断时,通常需要三个参数,interrupt parent,interrupt offset以及中断类型(电平/边沿中断)。如下举例
interrupt-parent = <&gpioB>;
interrupts = <25 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
irq_domian被创建时,需要提供其子中断的数目。针对中断数目大小以及预估的使用方式,可以提前将所有子中断的资源全部申请,也可在子中断申请分配时再alloc子中断的资源。子中断资源指每个中断对应的irq_desc(下文有描述)。
irq_domain申请,内核接口为__irq_domain_add();根据不同的入参,演变成上文说的几种方式。
/**
* __irq_domain_add() - Allocate a new irq_domain data structure
* @fwnode: firmware node for the interrupt controller
* @size: Size of linear map; 0 for radix mapping only
* @hwirq_max: Maximum number of interrupts supported by controller
* @direct_max: Maximum value of direct maps; Use ~0 for no limit; 0 for no
* direct mapping
* @ops: domain callbacks
* @host_data: Controller private data pointer
*
* Allocates and initializes an irq_domain structure.
* Returns pointer to IRQ domain, or NULL on failure.
*/
struct irq_domain *__irq_domain_add(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode, int size,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max, int direct_max,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_linear(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int size,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), size, size, 0, ops, host_data);
}
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_nomap(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int max_irq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, max_irq, max_irq, ops, host_data);
}
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_legacy_isa(
struct device_node *of_node,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return irq_domain_add_legacy(of_node, NUM_ISA_INTERRUPTS, 0, 0, ops,
host_data);
}
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_tree(struct device_node *of_node,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, ~0, 0, ops, host_data);
}
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_create_linear(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode,
unsigned int size,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(fwnode, size, size, 0, ops, host_data);
}
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_create_tree(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(fwnode, 0, ~0, 0, ops, host_data);
}
irq_domain 作为中断集合器描述体,其提供了中断的分配与释放方法,在irq domain创建时,需要设置irq_domain_ops的操作接口。如下是struct irq_domain_ops结构体定义:
/**
* struct irq_domain_ops - Methods for irq_domain objects
* @match: Match an interrupt controller device node to a host, returns
* 1 on a match
* @map: Create or update a mapping between a virtual irq number and a hw
* irq number. This is called only once for a given mapping.
* @unmap: Dispose of such a mapping
* @xlate: Given a device tree node and interrupt specifier, decode
* the hardware irq number and linux irq type value.
*
* Functions below are provided by the driver and called whenever a new mapping
* is created or an old mapping is disposed. The driver can then proceed to
* whatever internal data structures management is required. It also needs
* to setup the irq_desc when returning from map().
*/
struct irq_domain_ops {
int (*match)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token);
int (*select)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token);
int (*map)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq, irq_hw_number_t hw);
void (*unmap)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq);
int (*xlate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node,
const u32 *intspec, unsigned int intsize,
unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type);
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
/* extended V2 interfaces to support hierarchy irq_domains */
int (*alloc)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq,
unsigned int nr_irqs, void *arg);
void (*free)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq,
unsigned int nr_irqs);
int (*activate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irqd, bool reserve);
void (*deactivate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irq_data);
int (*translate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
void (*debug_show)(struct seq_file *m, struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_data *irqd, int ind);
#endif
};
通常map,unmap,xlate为一组,map负责将一个子中断映射成virq即linux可直接使用的中断编号,unmap功能与map相反;xlate则是将一组配置参数,转换成hwirq和irq type。然后map这些hwirq。
alloc,free,translate为一组,其功能与上面三个功能相似,通常只需要适配一组即可。
- 2.4 struct irq_chip
irq_chip是用来描述硬件中断控制器的描述符,其实现的是中断使能,mask等操作。irq_domain用来描述中断集合,irq_chip用来描述硬件相关操作。
/**
* struct irq_chip - hardware interrupt chip descriptor
*
* @parent_device: pointer to parent device for irqchip
* @name: name for /proc/interrupts
* @irq_startup: start up the interrupt (defaults to ->enable if NULL)
* @irq_shutdown: shut down the interrupt (defaults to ->disable if NULL)
* @irq_enable: enable the interrupt (defaults to chip->unmask if NULL)
* @irq_disable: disable the interrupt
* @irq_ack: start of a new interrupt
* @irq_mask: mask an interrupt source
* @irq_mask_ack: ack and mask an interrupt source
* @irq_unmask: unmask an interrupt source
* @irq_eoi: end of interrupt
* @irq_set_affinity: Set the CPU affinity on SMP machines. If the force
* argument is true, it tells the driver to
* unconditionally apply the affinity setting. Sanity
* checks against the supplied affinity mask are not
* required. This is used for CPU hotplug where the
* target CPU is not yet set in the cpu_online_mask.
* @irq_retrigger: resend an IRQ to the CPU
* @irq_set_type: set the flow type (IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL/etc.) of an IRQ
* @irq_set_wake: enable/disable power-management wake-on of an IRQ
* @irq_bus_lock: function to lock access to slow bus (i2c) chips
* @irq_bus_sync_unlock:function to sync and unlock slow bus (i2c) chips
* @irq_cpu_online: configure an interrupt source for a secondary CPU
* @irq_cpu_offline: un-configure an interrupt source for a secondary CPU
* @irq_suspend: function called from core code on suspend once per
* chip, when one or more interrupts are installed
* @irq_resume: function called from core code on resume once per chip,
* when one ore more interrupts are installed
* @irq_pm_shutdown: function called from core code on shutdown once per chip
* @irq_calc_mask: Optional function to set irq_data.mask for special cases
* @irq_print_chip: optional to print special chip info in show_interrupts
* @irq_request_resources: optional to request resources before calling
* any other callback related to this irq
* @irq_release_resources: optional to release resources acquired with
* irq_request_resources
* @irq_compose_msi_msg: optional to compose message content for MSI
* @irq_write_msi_msg: optional to write message content for MSI
* @irq_get_irqchip_state: return the internal state of an interrupt
* @irq_set_irqchip_state: set the internal state of a interrupt
* @irq_set_vcpu_affinity: optional to target a vCPU in a virtual machine
* @ipi_send_single: send a single IPI to destination cpus
* @ipi_send_mask: send an IPI to destination cpus in cpumask
* @irq_nmi_setup: function called from core code before enabling an NMI
* @irq_nmi_teardown: function called from core code after disabling an NMI
* @flags: chip specific flags
*/
struct irq_chip {
struct device *parent_device;
const char *name;
unsigned int (*irq_startup)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_enable)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_disable)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_ack)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_mask)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_mask_ack)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_unmask)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_eoi)(struct irq_data *data);
int (*irq_set_affinity)(struct irq_data *data, const struct cpumask *dest, bool force);
int (*irq_retrigger)(struct irq_data *data);
int (*irq_set_type)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int flow_type);
int (*irq_set_wake)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int on);
void (*irq_bus_lock)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_bus_sync_unlock)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_cpu_online)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_cpu_offline)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_suspend)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_resume)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_pm_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_calc_mask)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_print_chip)(struct irq_data *data, struct seq_file *p);
int (*irq_request_resources)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_release_resources)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_compose_msi_msg)(struct irq_data *data, struct msi_msg *msg);
void (*irq_write_msi_msg)(struct irq_data *data, struct msi_msg *msg);
int (*irq_get_irqchip_state)(struct irq_data *data, enum irqchip_irq_state which, bool *state);
int (*irq_set_irqchip_state)(struct irq_data *data, enum irqchip_irq_state which, bool state);
int (*irq_set_vcpu_affinity)(struct irq_data *data, void *vcpu_info);
void (*ipi_send_single)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int cpu);
void (*ipi_send_mask)(struct irq_data *data, const struct cpumask *dest);
int (*irq_nmi_setup)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_nmi_teardown)(struct irq_data *data);
unsigned long flags;
};struct irq_chip主要实现IRQ的配置接口:
irq_enable/irq_disable: 中断的使能与反使能;
irq_mask/irq_unmask:中断屏蔽与反屏蔽;与irq_enable和irq_disable类似,他们都可以开关中断。但是又不一样的是,mask/unmask通常是配置于源端,enable/disable配置于接收端,参考中断架构图,mask/unmask配置 mod0的intr_t0,1,2...;enable/disable配置gic的mod0,1,2...。
irq_ack:开始处理irq时调用该接口,可以用来清除irq的中断状态。ack一般用于外设中断响应,中断上半部记录该中断的状态,然后调用下半部。
irq_eoi:处理完irq时调用该接口,可以用来清除irq的中断状态。与irq_ack不同的是,一个在刚开始处理irq时调用,一个在处理完irq后调用。eoi通常在irq_chip端实现,如GIC有专门的EOI寄存器去清除中断状态。
irq_set_affinity:设置irq绑定,通常用于绑定irq到某个核。如果force == false,则会绑定到所有online的core上。当拔插CPU core时,系统也会调用这个接口去更新CPU core响应irq的映射map。
irq_set_type:设置中断类型,如上升下降沿,电平中断等。
irq_set_wake:设置中断唤醒能力,用于休眠后,中断唤醒CPU。
irq_request_resources/irq_release_resources:请求配置为中断,通常用于GPIO的配置,request时,锁定GPIO的用途为中断类型,且使能该GPIO的中断配置(如设置为input,且使能其中断功能);release解锁定中断配置。
- 2.5 struct irq_desc
/**
* struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor
* @irq_common_data: per irq and chip data passed down to chip functions
* @kstat_irqs: irq stats per cpu
* @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler
* @preflow_handler: handler called before the flow handler (currently used by sparc)
* @action: the irq action chain
* @status: status information
* @core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it: core internal status information
* @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls
* @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple irq_set_irq_wake() callers
* @tot_count: stats field for non-percpu irqs
* @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs
* @last_unhandled: aging timer for unhandled count
* @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts
* @threads_handled: stats field for deferred spurious detection of threaded handlers
* @threads_handled_last: comparator field for deferred spurious detection of theraded handlers
* @lock: locking for SMP
* @affinity_hint: hint to user space for preferred irq affinity
* @affinity_notify: context for notification of affinity changes
* @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts
* @threads_oneshot: bitfield to handle shared oneshot threads
* @threads_active: number of irqaction threads currently running
* @wait_for_threads: wait queue for sync_irq to wait for threaded handlers
* @nr_actions: number of installed actions on this descriptor
* @no_suspend_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with
* IRQF_NO_SUSPEND set
* @force_resume_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with
* IRQF_FORCE_RESUME set
* @rcu: rcu head for delayed free
* @kobj: kobject used to represent this struct in sysfs
* @request_mutex: mutex to protect request/free before locking desc->lock
* @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry
* @debugfs_file: dentry for the debugfs file
* @name: flow handler name for /proc/interrupts output
*/
struct irq_desc {
struct irq_common_data irq_common_data;
struct irq_data irq_data;
unsigned int __percpu *kstat_irqs;
irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_PREFLOW_FASTEOI
irq_preflow_handler_t preflow_handler;
#endif
struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */
unsigned int status_use_accessors;
unsigned int core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it;
unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */
unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */
unsigned int tot_count;
unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */
unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */
unsigned int irqs_unhandled;
atomic_t threads_handled;
int threads_handled_last;
raw_spinlock_t lock;
struct cpumask *percpu_enabled;
const struct cpumask *percpu_affinity;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
const struct cpumask *affinity_hint;
struct irq_affinity_notify *affinity_notify;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
cpumask_var_t pending_mask;
#endif
#endif
unsigned long threads_oneshot;
atomic_t threads_active;
wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads;
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
unsigned int nr_actions;
unsigned int no_suspend_depth;
unsigned int cond_suspend_depth;
unsigned int force_resume_depth;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
const char *dev_name;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
struct mutex request_mutex;
int parent_irq;
struct module *owner;
const char *name;
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;irq_desc是内核描述中断的句柄,当用户操作一个中断时,kernel都会将中断号转换成对应的irq_desc,然后执行具体的操作流程。内核统一管理irq_desc 池。
struct irq_desc *irq_to_desc(unsigned int irq)即将irq 编号转换成irq_desc。
如常见的操作enable_irq,便是转换为desc,然后调用__enable_irq(desc)执行具体的enable步骤:
void enable_irq(unsigned int irq)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_get_desc_buslock(irq, &flags, IRQ_GET_DESC_CHECK_GLOBAL);
if (!desc)
return;
if (WARN(!desc->irq_data.chip,
KERN_ERR "enable_irq before setup/request_irq: irq %u\n", irq))
goto out;
__enable_irq(desc);
out:
irq_put_desc_busunlock(desc, flags);
}























 1812
1812











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










