算法流程
关于BP神经网络的公式推导,上一篇博文《BP神经网络原理简单介绍以及公式推导(矩阵形式和分量形式) 》已经做了详细的说明。接下来,我们利用MATLAB对BP神经网络进行实现。我们直接上代码,并进行解释。
MATLAB 代码
整个代码是基于BP神经网络矩阵形式编写的,对公式有疑惑的同学可以参考下上篇博文。
sigmoid.m
function [ out ] = sigmoid( in )
%SIGMOID Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
out = 1./(1+exp(-in));
end。Sigmoid的函数一般形式有:
它们导数都是自相关的。我们的激活函数就选择最简单的Sigmoid的函数, f(x)=11+e−x ,其导数为: f′(x)=f(x)(1−f(x))
create_w.m
function [ W ] = create_w( n_levels )
%CREATE_W Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
n_level = numel(n_levels) - 1;
W = cell(n_level,1);
for i=1:n_level
W{i} = ones(n_levels(i+1), n_levels(i));
end
end创建权值矩阵,初始值都是1。其中n_levels是一个向量,描述了神经网络的结构,比如
n_levels = [2 6 1]描述了一个2-6-1的网络,也就是输入层2个神经元,隐藏层6个神经元,输出层1个神经元。上篇推导公式博文中的网络可以被描述为6-4-2-2网络。
每一层的权值矩阵与上一层的输入个数和这一层的输出个数有关。
create_theta.m
function [ theta ] = create_theta( levels )
%CREATE_THETA Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
n_level = numel(levels) - 1;
theta = cell(n_level, 1);
for i=1:n_level
theta{i} = ones(levels(i+1),1);
end
end创建偏移量矩阵,初始值为1。
BP_predict.m
function [ output, Y ] = BP_predict( input, W, theta)
%BP_ Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
f = @sigmoid;
n_w = numel(W);
Y = cell(n_w+1, 1);
Y{1} = input';
for i=1:n_w
net = W{i}*Y{i} + theta{i};
Y{i+1} = f(net);
end
output = Y{end};
end在训练中,需要对目前的
W
和
BP_predict2.m
function [ output] = BP_predict2( input, W, theta)
%BP_ Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
f = @sigmoid;
n_w = numel(W);
y = input';
for i=1:n_w
net = bsxfun(@plus,W{i}*y,theta{i});
y = f(net);
end
output = y;
endBP_predict2用于预测,可以对一个数据矩阵进行预测。
BP_tranning.m
function [ W,theta ] = BP_tranning( X, levels, step )
%BP_TRANNING Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
if nargin < 3
step = 0.001;
end
n_levels = size(levels, 2) - 1;
n_input = levels(1);
W = create_w(levels);
theta = create_theta(levels);
[n_data,col] = size(X);
n_label = col - n_input;
tranning_data = X(:,1:n_input); %Y0 is input
label = X(:,n_input+1:end)';
f = @sigmoid;
eps = 10e-7;
old_error = 0;
while true
for k=1:n_data
[output, Y] = BP_predict(tranning_data(k,:), W, theta);
delta = label(:,k) - output;
% update the W, from the last layer to the first layer
for l=n_levels:-1:1
net = W{l}*Y{l} + theta{l};
if l == n_levels
S = diag(f(net).*(1-f(net)))*delta;
else
S = diag((f(net).*(1-f(net))))*W{l+1}'*S;
end
%dW = -S*Y{l}';
new_W{l} = W{l} + step*S*Y{l}';
new_theta{l} = theta{l} + step*S;
end % end update
W = new_W;
theta = new_theta;
end % end for
y = BP_predict2(tranning_data, W, theta);
delta = y - label;
error = sum(sum(delta.^2));
if abs(error - old_error) < eps;
break;
else
old_error = error;
end
end
end训练的中止条件,个人觉得很难确定。不得已,写了一个不那么合理的:就是通过比较前后两次的错误率,错误率变化很小很小,说明错误率很难降低了,模型趋于稳定了。
其中
测试
demo_3class.m
%% Build a tranning set of three class
c_1 = [0 0];
c_2 = [0 1];
c_3 = [1 0];
c_4 = [1 1];
n_L1 = 20; % number of label 1
n_L2 = 20; % number of label 2
n_L3 = 20; % number of label 3
A = zeros(n_L1, 4);
A(:,3) = 0; A(:,4) = 0;
for i=1:n_L1
A(i,1:2) = c_1 + rand(1,2)/2;
end
B = zeros(n_L2, 4);
B(:,3) = 0; B(:,4) = 1;
for i=1:n_L2
B(i,1:2) = c_2 + rand(1,2)/2;
end
C = zeros(n_L3, 4);
C(:,3) = 1; C(:,4) = 0;
for i=1:n_L3
C(i,1:2) = c_3 + rand(1,2)/2;
end
D = zeros(n_L3, 4);
D(:,3) = 1; D(:,4) = 0;
for i=1:n_L3
D(i,1:2) = c_4 + rand(1,2)/2;
end
scatter(A(:,1), A(:,2),[],'r');
hold on
scatter(B(:,1), B(:,2),[],'g');
hold on
scatter(C(:,1), C(:,2),[],'k');
hold on
scatter(D(:,1), D(:,2),[],'k');
X = [A;B;C;D];
%% Trainning the BP network
dbstop if error
n_label = 2;
% create the weight matrix
n_input = size(X,2) - n_label;% number of feature of each data, here is 2, only x-axis and y-axis
levels = [n_input 7 n_label];
step = 0.1;
[W,theta] = BP_tranning(X, levels, step);
save three_class W theta
%% show the result
input = X(:,1:n_input);
label = X(:,n_input+1:end);
y = BP_predict2(input, W, theta);
Y = y';
Y(find(Y>0.5)) = 1;
Y(find(Y<=0.5)) = 0;
T = sum(label - Y, 2);
error_index = find(T ~= 0);
figure;
scatter(X(:,1), X(:,2), [], 'g');
hold on
scatter(X(error_index,1), X(error_index,2), [], 'r');
演示了一个三类分类器。对于多类分类,神经网络应该有多个输出,每个输出为0或者1,组合得到结果。比如这个例子,00表示第一类,01表示第二类,10表示第三类。
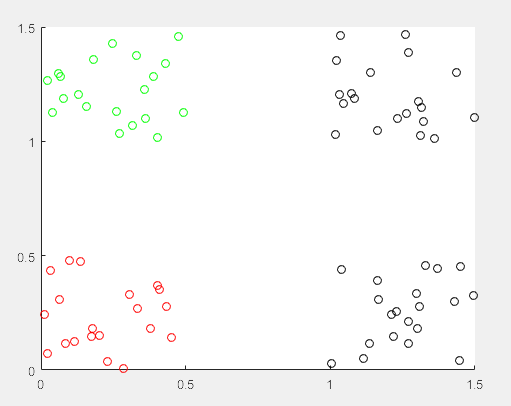
上图是初始训练数据,每种颜色代表一类。
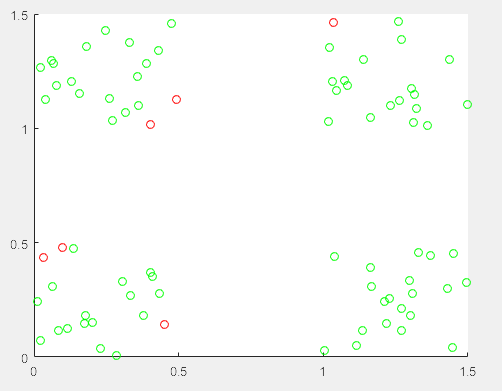
上图是训练之后,对训练集进行预测的结果,其中红色表示错误,绿色表示正确。
总结
整体来说,实现BP算法不难,但是在实验部分却发现模型的选择、step的选择、终止条件的选择都很麻烦。已经隐约感受到调参民工的辛苦了。所有代码可以在这里下载






















 422
422











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








