One can argue that composing functions is the most important idea in programming and functional programming in particular. The idea of compositionality is of monumental importance in human thinking. Creating systems by composing smaller systems that are easier to implement and design can be found in all levels of programming. Staring from the Syntax of the language, to Design patterns, architectural patterns, larger System design etc.
可以说,在编程中,尤其是在函数编程中,组成函数是最重要的想法。 组合性思想在人类思维中具有极其重要的意义。 在各个级别的编程中都可以找到通过组成更易于实现和设计的较小系统来创建系统的信息。 从语言的语法开始,一直到设计模式,建筑模式,更大的系统设计等。
In this section we are going to take a brief look at one of the most basic ones; Function composition.
在本节中,我们将简要介绍最基本的方法之一。 功能组成。

In mathematics, function composition is the application of one function to the result of another to produce a third function. For instance, the functions f : T→ R and g : R→ U can be composed to yield a function h: g(f(x)) which maps T→ U we usually represent that as g ○ f and we read that as “g after f ” the symbol ○ usually represents “after”.
在数学中,函数合成是将一个函数应用于另一个函数的结果以产生第三个函数。 例如,可以将函数f:T→R和g:R→U组合成函数h:g(f(x)) ,它映射T→U,我们通常将其表示为g○f,而我们将其读为“ g 在 f 之后 ”,符号○通常表示“ after ”。
Programmatically for the functional interfaces there are two ways called .andThen() and .compose() to make this composition. If you have a Function<T, R> you can:
对于功能接口,以编程方式有两种方法可以使.andThen()和.compose()进行组合。 如果您具有Function <T,R>,则可以:
Either post-compose
.andThen(Function<R, U>)another function后
.andThen(Function<R, U>)另一个函数Or you can start with Function<R, U> and pre-compose compose
.compose(Function<T, R>)或者您可以从Function <R,U>开始并预撰写compose
.compose(Function<T, R>)
Now we are now going to take a brief look at the most common java util Functional interface
现在,我们将简要介绍最常见的Java util Functional接口
功能<,>组成 (Function<,> composition)
Since the most usual functional interface is Function<T, R> it provides a default method .andThen (docs.oracle) that takes another Function<R, U> and returns a Function<T, U>
由于最常用的功能接口是Function <T,R>,因此它提供了默认方法.andThen( docs.oracle ),该方法采用另一个Function <R,U>并返回Function <T,U>
run this : Fiddle
运行此: 小提琴
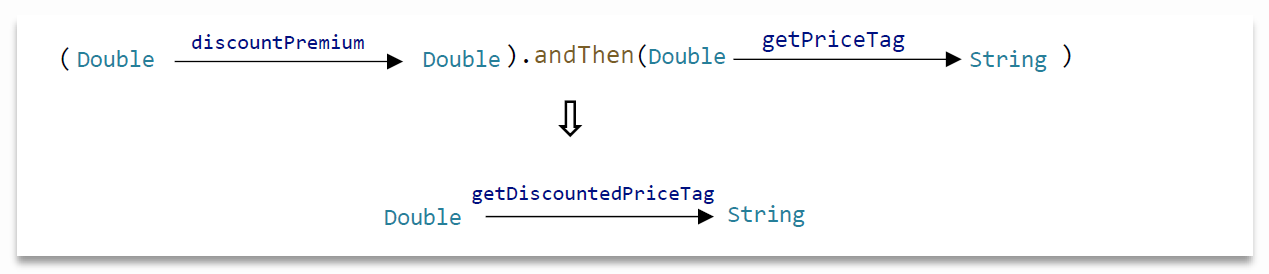
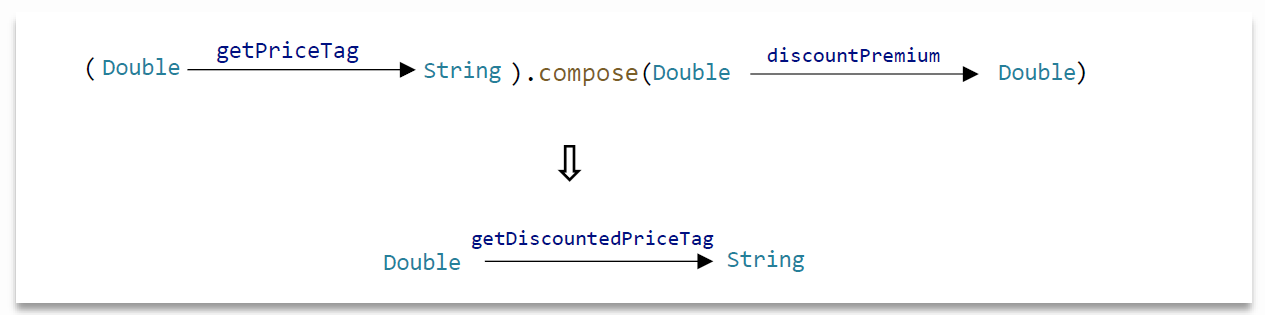
we can write the composition in the opposite direction using the compose method
我们可以使用compose方法以相反的方向编写构图
BiFunction <>组成 (BiFunction<> Composition)
BiFunction<U, V, R> also provides an andThen method
BiFunction <U,V,R>还提供了andThen方法

Take a look at the following function composition :
看一下下面的函数组成:
Run This: Fiddle
运行此: 小提琴

Excerpt from the book:
摘录:

翻译自: https://medium.com/@dimpapadim3/function-composition-in-java-beaf39426f52





















 1829
1829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








