TensorFlow is a highly-known open-source software library meant to process dataflow and make predictions based on machine learning models. However, for the longest time, TensorFlow has been restricted as a “python-oriented” software, limiting the use of the library for websites. This has caused many developers to resort to creating machine learning algorithms from scratch for web-pages, until their voices have been heard and thus TensorFlowJS was born.
TensorFlow是一个著名的开源软件库,用于处理数据流并基于机器学习模型进行预测。 但是,在最长的时间内,TensorFlow被限制为“ 面向python的”软件,从而限制了网站库的使用。 这导致许多开发人员不得不从头开始为网页创建机器学习算法,直到听到他们的声音并由此诞生了TensorFlowJS 。
Today I’ll be covering Part 1 of a brand new series dedicated to the ins and outs of TensorFlowJS, and creating machine learning models in the web environment. In this blog we will be covering the basics of machine learning and give a brief introduction to TensorflowJS itself, as well as resources that can be used to further understand the library. Let’s get started.
今天,我将介绍一个全新系列的第1部分 ,该系列专门介绍TensorFlowJS的来龙去脉,并在Web环境中创建机器学习模型。 在此博客中,我们将介绍机器学习的基础知识,并简要介绍TensorflowJS本身,以及可用于进一步理解该库的资源。 让我们开始吧。
什么是TensorflowJS? (What is TensorflowJS?)
Before we dive too deep, let’s first understand what TensorflowJS actually is:
在我们深入探讨之前,让我们首先了解TensorflowJS实际上是什么:
TensorflowJS, like Tensorflow, is a library that is able to build, train, and makes predictions from machine learning models, but in a Javascript environment. TensorflowJS has the ability to bring Python-built ML algorithms to function in a web-app by using Tensorflow Sequential, which acts similar to Keras, but built for Node.
与Tensorflow一样, TensorflowJS是一个库,它可以在Javascript环境中从机器学习模型构建,训练和做出预测。 TensorflowJS有可能带来的Python内置ML算法功能的web应用程序使用Tensorflow顺序 ,其作用类似于Keras,但专为节点的能力。
了解TensorflowJS: (Understanding TensorflowJS:)
数据集: (Datasets:)
When it comes to training a machine learning model, one of the first steps is to find a set of examples to guide the model on what the expectation may be. These examples are normally contained in what is known as CSV files, which you could think of as a built-in table containing columns and rows of sample data, which is called a dataset.
当谈到训练机器学习模型, 第一步骤之一是找到一组例子来指导怎样的预期可能是模型。 这些示例通常包含在所谓的CSV文件中 ,您可以将其视为包含样本数据的列和行的内置表,称为数据集 。

Some datasets like XGBoost (which is used to predict malicious websites) require a CSV format since most data is compared based on statistics, while other datasets such as Mnist (dataset used to predict hand written integers) are stored in its most compressed form as a png file.
某些数据集(例如XGBoost (用于预测恶意网站))需要CSV格式,因为大多数数据是根据统计数据进行比较的,而其他数据集(例如Mnist (用于预测手写整数的数据集))则以其最压缩的形式存储为png文件。

卷积: (Convolutionals:)
Let’s say that the sample data we are going to use for our machine learning model is going to require the Mnist dataset, what we will need for our model to do next is read our sample data, but how can our model see the image? Everything a computer can see is made up of integers, so if the model were to break down each pixel of the image into integers, then the model will be able to read the image based on the values of each pixel. This process is known as a convolutional, where pixel units of an image are the sum of n by n slots.
假设我们要用于机器学习模型的样本数据将需要Mnist数据集 ,接下来我们需要模型做的是读取样本数据,但是我们的模型如何看到图像? 一切电脑可以看到由整数 ,因此,如果该模型被分解图像成整数的每个像素,那么模型将能够基于每个像素值读取图像。 此过程称为卷积 ,其中图像的像素单位是n x n槽之和。
Let’s break down this visual depicting a convolutional taking place:
让我们分解一下描述卷积发生的视觉效果:
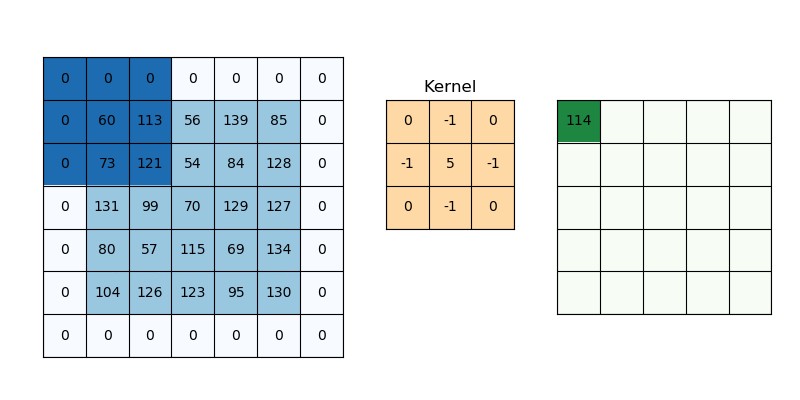
Let’s narrow down and focus on the process of the first selected units of 9. Notice how in the center there is a 9 unit square known as a “kernel”. If we were to do the math for the first 9 slots in the first square, the kernel will multiply the values of all units and then sum up the results. So automatically 121 will be negated since you get nothing when multiplying it by zero while 73 and 113 will be -186 because the kernel multiplies them by -1, and finally 60 will be multiplied by 5 to get 300, and if we were to get the sum, we will have 114, which is the result value placed in the last square. That’s how convolutionals work!
让我们缩小范围并关注9的第一个选定单位的过程。请注意,在中心如何有一个9单位的正方形,称为“ 内核 ”。 如果我们要对第一个正方形中的前9个插槽进行数学运算,则内核将乘以 所有单位的值,然后对结果求和 。 因此自动将121取反,因为当您将其乘以零时一无所获,而73和113将为-186,因为内核将其乘以-1,最后将60与5乘以得到300,如果我们要得到总和,我们将得到114,这是放在最后一个平方中的结果值。 卷积就是这样工作的!
神经网络: (Neural Networks:)
Now that we know what datasets are and how the model will read the sample data using convolutions, let’s take a look at the training phase a machine learning model will take. If we were to analyze the visual depiction below, we will notice how all pixel instances read will be plugged into one of the circles to the very right. This is what is known as the “hidden layer”, which is where the convolutionals take place.
现在我们知道什么是数据集,以及模型如何使用卷积读取样本数据,让我们看一下机器学习模型将要进行的训练阶段。 如果要分析下面的视觉描绘,我们将注意到如何读取所有像素实例,将它们插入最右边的圆圈之一。 这就是所谓的“ 隐藏层 ”,即发生卷积的位置。
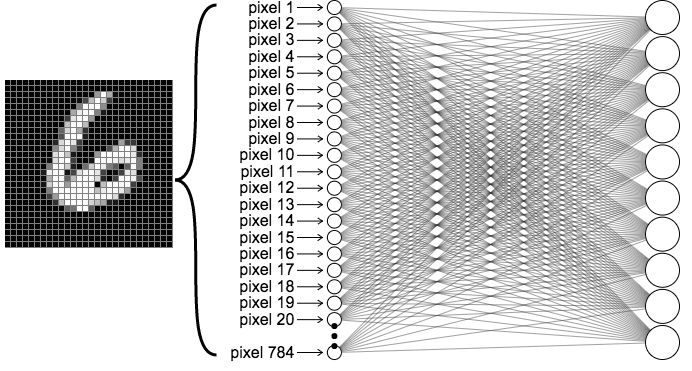
The structure of a neural network can also often vary. There are numerous varieties based on either what datasets the model is training for, how advanced the model is going to be, if the model will be comparing from a built in database, or maybe it’s just the developer’s preference.
神经网络的结构也经常会变化。 基于模型正在训练的数据集,模型的发展程度,是否要从内置数据库中进行比较,或者基于开发人员的偏爱,有很多不同的选择。
损失: (Losses:)
For the machine learning model to understand the do-s and don’t-s, the model must first compare input values and determine if the prediction is good or bad based on a decimal grade. Depending on how far or close the value is to the whole number 1 will determine if the prediction is either good or bad. If the grade is considered bad, then the model will be penalized and scrap the instance entirely, but if the grade is good, then the grade will be recorded for future training instances. This is how the model learns and adapts per epoch (number of training instances set).
为了使机器学习模型能够理解应该做和不应该做的事情,该模型必须首先比较输入值,并根据十进制等级确定预测的好坏。 根据价值多远或接近对整个1号将确定预测是好是坏 。 如果认为成绩不好,则将对该模型进行惩罚并完全废弃该实例,但是如果该成绩很好,则将记录该成绩以供将来的训练实例使用。 这就是模型如何学习和适应每个时期 (设置的训练实例数) 。
优化器: (Optimizers:)
Once each instance in the hidden layer resolves its convolutionals, the model moves onto the next phase in training; learning between what is considered right and what is wrong, and balances the weight and learning rate of your model. This method is known as an optimizer, which is used to find the cross entropy (the comparison between two probable outcomes and gathers loss sum) and the generalization (the process of creating correct predictions for new data) based on the type of optimizer used (such as adam or adagrad), and the conditions of previous losses to prevent future losses from occurring.
一旦隐藏层中的每个实例解决了其卷积问题,模型就会进入训练的下一个阶段。 在正确与错误之间学习,并平衡模型的权重和学习率。 这种方法被称为优化器 ,其被用于查找基于所使用优化的类型的交叉熵和泛化 (创建新的数据正确预测的方法)(2 个可能的结果和褶裥损失总和之间的比较)( (例如 adam 或 adagrad )以及先前损失的条件,以防止将来发生损失。
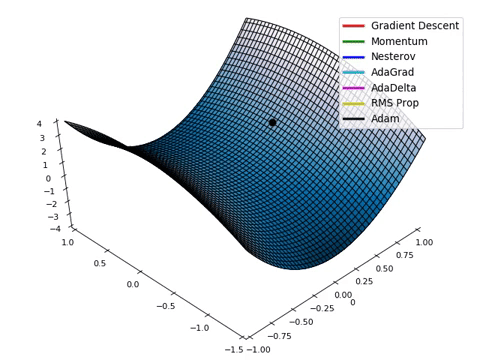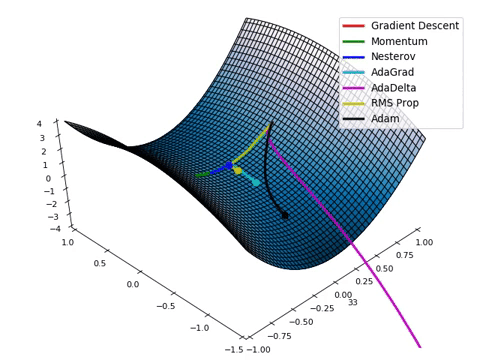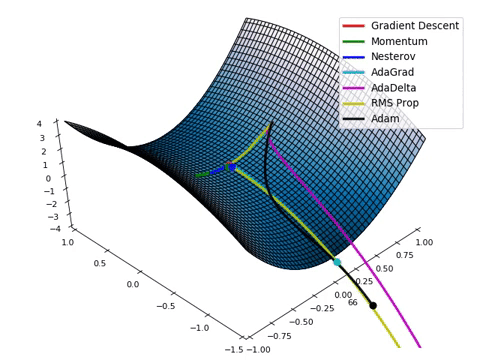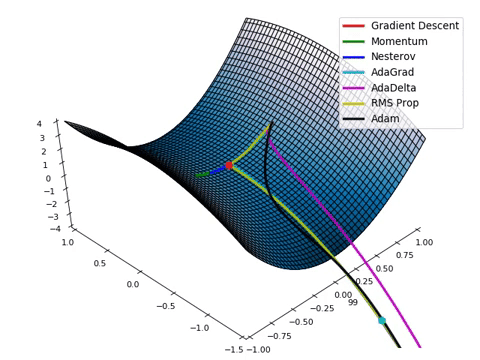
梯度下降: (Gradient Descent:)
Lastly, after the Optimizer finishes its course, the model’s final stage of training phase is to map the results from the optimized instances and finds the local minima (lowest projected value) in the graph of instances. This is known as a Gradient Descent, which is used to automatically tweak the weights and biases of the model. This is how the model checks for accuracy between all instances and reaches the most viable result.
最后,在优化程序完成课程之后,模型的训练阶段的最后阶段是映射优化实例的结果,并在实例图中找到局部最小值 (最小投影值) 。 这称为梯度下降 ,用于自动调整模型的权重和偏差 。 这是模型检查所有实例之间的准确性并达到最可行结果的方式。
结论: (Conclusion:)
Within the course of this blog we have covered exactly what TensorFlowJS is, what a dataset is and how to read visual data using convolutionals, what neural networks are and how they compare results and losses, what optimizers are and how they can gather the sum of losses to prevent future losses, and what gradient descent is and how it’s used to map the results of training and testing data from a model. Hopefully you learned more about machine learning and TensorFlowJS when leaving this blog than entering, and be sure to follow the next part whenever it is released to see how we can use what we taught here in this blog to create an app using TensorFlowJS.
在本博客的过程中,我们确切地介绍了TensorFlowJS是什么,数据集是什么以及如何使用卷积读取视觉数据,什么是神经网络以及它们如何比较结果和损失,什么是优化器以及如何收集和。损失以防止未来损失,以及什么是梯度下降以及如何将其用于映射模型的训练和测试数据的结果。 希望您在离开本博客时能比进入时学到更多有关机器学习和TensorFlowJS的知识,并且一定要在发布每篇文章时都遵循下一部分,以了解如何使用本博客中的教导来使用TensorFlowJS创建应用。
Kaggle: For open-source datasets.
Kaggle :适用于开源数据集。







 本文深入浅出地介绍了TensorFlowJS,从数据集读取、卷积操作到神经网络、损失函数、优化器和梯度下降。通过实际案例,带你理解如何在JavaScript环境中利用TensorFlowJS进行Web应用的机器学习开发。
本文深入浅出地介绍了TensorFlowJS,从数据集读取、卷积操作到神经网络、损失函数、优化器和梯度下降。通过实际案例,带你理解如何在JavaScript环境中利用TensorFlowJS进行Web应用的机器学习开发。














 2180
2180

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








