这次的合集是找到了几个论文... 一起来说下
- Fast Charging of Energy-dense Lithium-ion Batteries
- Real-time Short Video Recommendation on Mobile Devices
- Semantic interpretation for convolutional neural networks: What makes a cat a cat?
- Prompt-to-Prompt Image Editing with Cross Attention Control
- Poisson Flow Generative Models
- Creating a Dynamic Quadrupedal Robotic Goalkeeper with Reinforcement Learning
- Video-driven Neural Physically-based Facial Asset for Production
论文 1:Fast Charging of Energy-dense Lithium-ion Batteries
- 作者:Chao-Yang Wang 等
- 论文地址:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05281-0
摘要:电动汽车的电池材料有不同的选择,例如固态锂电池。今天介绍另一种特殊材料 —— 镍箔,通过在电池内部加入一层薄薄的镍,标准电动汽车电池可以在 10 分钟左右充满大部分电量。这可以为配备多个昂贵电池组的电动汽车提供一种更经济的替代品。
这项研究是由宾夕法尼亚州立大学材料与工程学杰出教授王朝阳等多位研究人员完成的,并发表在了 10 月 12 日的 Nature 上。王朝阳教授是燃料电池和二次电池领域的专家学者,并于 2019 年 12 月当选为美国国家发明家科学院院士。
推荐:11 分钟充电 70%,华人教授在锂电池中加镍箔登上 Nature。
论文 2:Real-time Short Video Recommendation on Mobile Devices
- 作者:Xudong Gong 等
- 论文地址:https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3511808.3557065
摘要:本文针对短视频推荐场景,传统服务端部署的推荐系统在决策时机和实时特征利用方面的不足问题,通过在移动客户端部署推荐系统来实时响应用户反馈,提高推荐结果的精准度,提升用户体验。论文提出的方案 100% 流量部署到了快手短视频推荐生产环境,影响了日均超过 3.4 亿用户的体验。
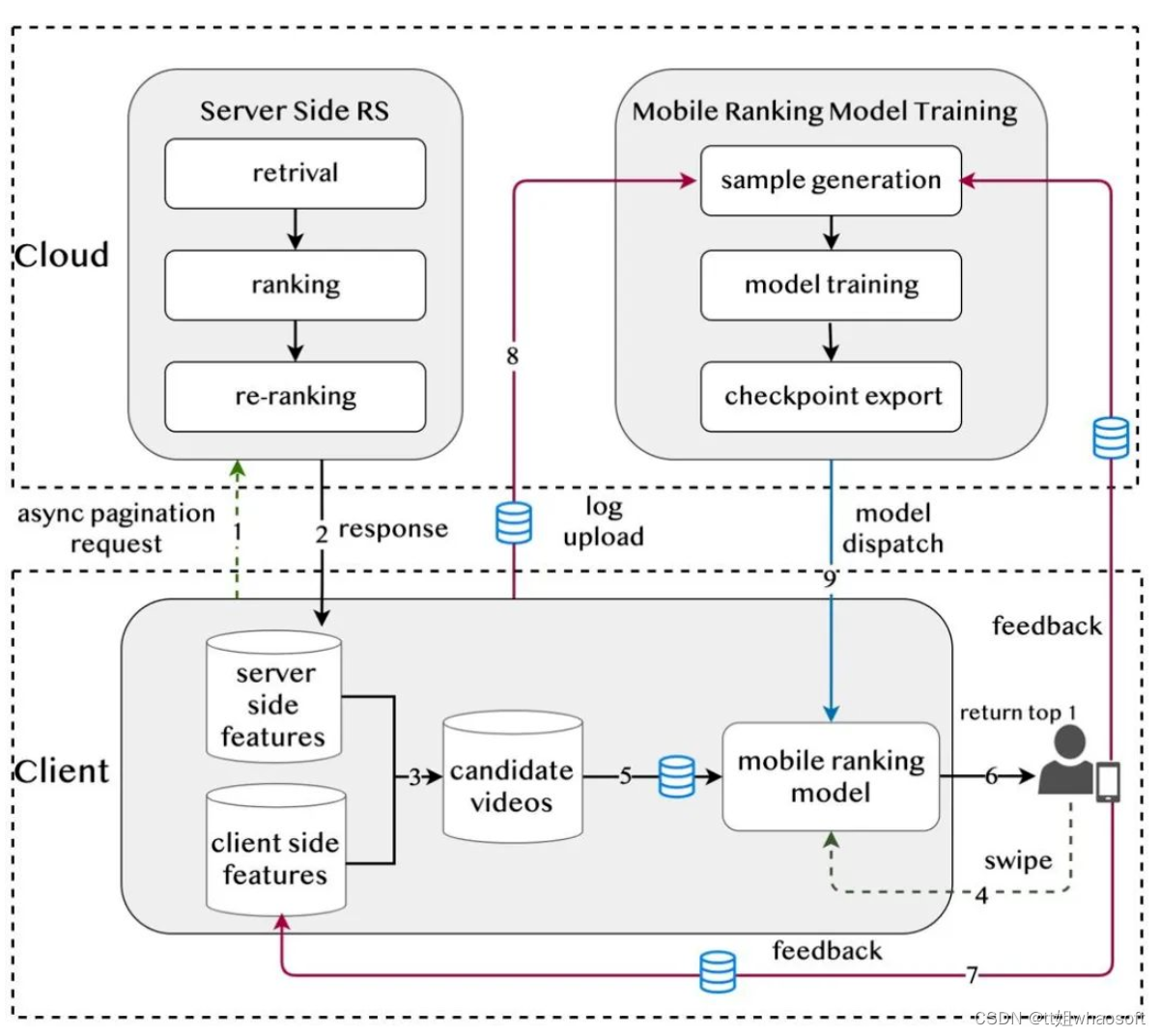
端上重排系统。
推荐:移动端部署推荐系统:快手获数据挖掘顶会 CIKM 2022 最佳论文。
论文 3:Semantic interpretation for convolutional neural networks: What makes a cat a cat?
- 作者:Hao Xu 等
- 论文地址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202204723
摘要:近年来,CNN 因其优异性能,在计算机视觉、自然语言处理等各个领域受到了研究者们的青睐。但是,CNN 是一个 「黑盒」 模型,即模型的学习内容和决策过程很难用人类能够理解的方式提取和表达,这限制了它的预测可信度和实际应用。
因此,CNN 的可解释性受到了越来越多的关注,研究者们试图采用特征可视化,网络诊断和网络架构调整等方式辅助解释 CNN 的学习机制,将这一 「黑盒」 透明化,使人类更容易理解、检测和改进其决策过程。
近日,北京大学,东方理工,南方科技大学和鹏城实验室等机构的研究团队提出了一种语义可解释人工智能 (semantic explainable AI, S-XAI)的研究框架,从语义层面解释了 CNN 的学习机制,并以猫狗二分类问题为例,形象地揭示了模型是如何学习类别意义上的猫的概念,即「何以为猫」。
推荐:何以为猫?可解释 AI 从语义层面理解 CNN 的识别机制
论文 4:Prompt-to-Prompt Image Editing with Cross Attention Control
- 作者:Amir Hertz 等
- 论文地址:https://prompt-to-prompt.github.io/ptp_files/Prompt-to-Prompt_preprint.pdf
摘要:动动嘴皮子就能把图改好是甲方和乙方的共同愿望,但通常只有乙方才知道其中的酸楚。如今 AI 却向这个高难度问题发起了挑战。
在一篇 10 月 17 日上传到 arXiv 的论文中,来自谷歌研究院、以色列理工学院、以色列魏茨曼科学研究所介绍了一种基于扩散模型的真实图像编辑方法——Imagic,只用文字就能实现真实照片的 PS,比如让一个人竖起大拇指、让两只鹦鹉亲吻。
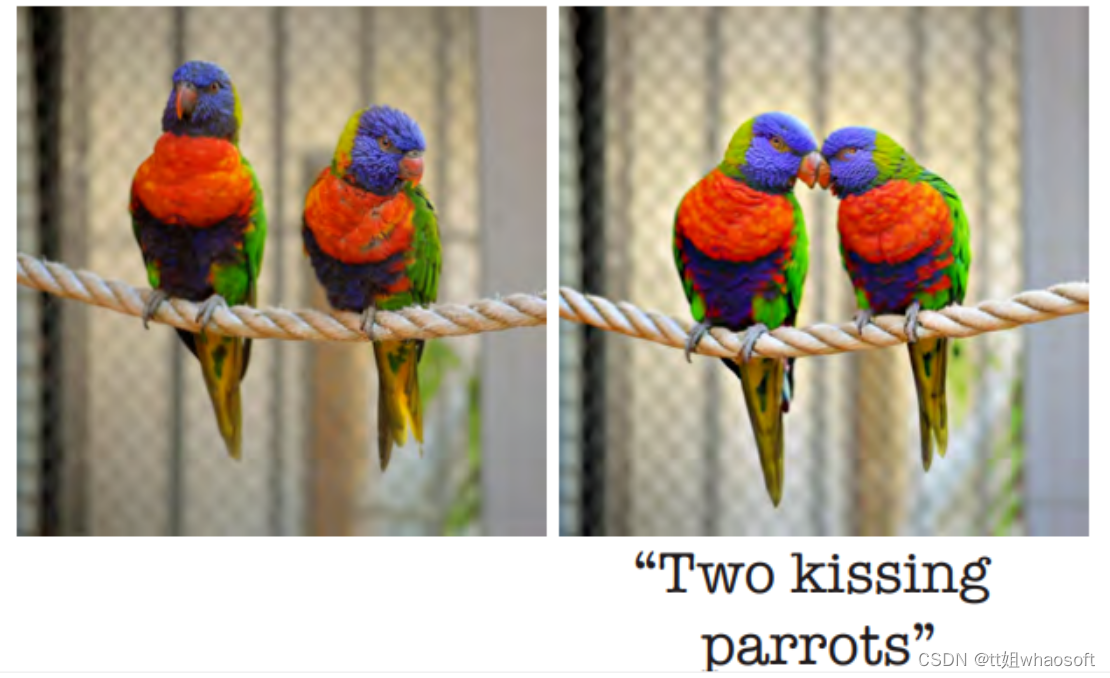


推荐:挡不住了!扩散模型只用文字就能 PS 照片了。
论文 5:Poisson Flow Generative Models
- 作者:Yilun Xu 等
- 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.11178.pdf
摘要:扩散模型最早来源于物理中的热力学,最近却在人工智能领域大放异彩。还有什么物理理论可以推动生成模型研究的发展呢?
最近,来自 MIT 的研究者受到高维电磁理论的启发,提出了一种称作泊松流(Poisson Flow)的生成模型。理论上,这种模型具有直观的图像和严谨的理论;实验上,它在生成质量、生成速度和鲁棒性上往往比扩散模型更好。本文已被 NeurIPS 2022 接收。
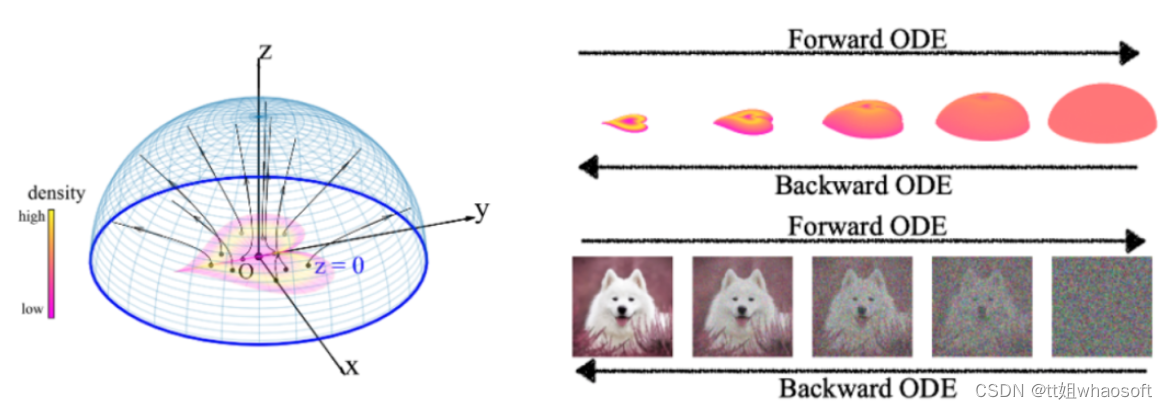
左图:泊松场在三维中的轨迹;右图:在图像上使用 PFGM 的前向 ODE 和反向 ODE。
推荐:卷!MIT 泊松流生成模型击败扩散模型,兼顾质量与速度。
论文 6:Creating a Dynamic Quadrupedal Robotic Goalkeeper with Reinforcement Learning
- 作者:Xiaoyu Huang 等
- 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.04435.pdf
摘要:机器狗不仅能跑能跳,踢足球、当守门员也都很在行。这款机器狗是 MIT 在 2019 年研发的 Mini Cheetah,现在来自加州大学伯克利分校等机构的研究者为 Mini Cheetah 部署了一个新的强化学习框架,让它完成足球守门任务,守门成功率高达 87.5%。
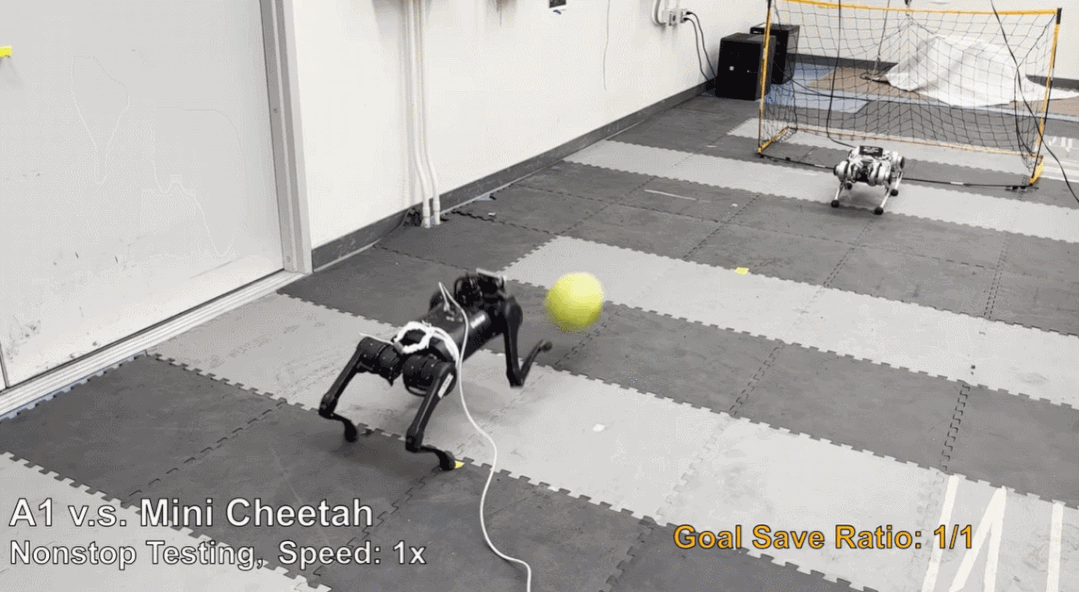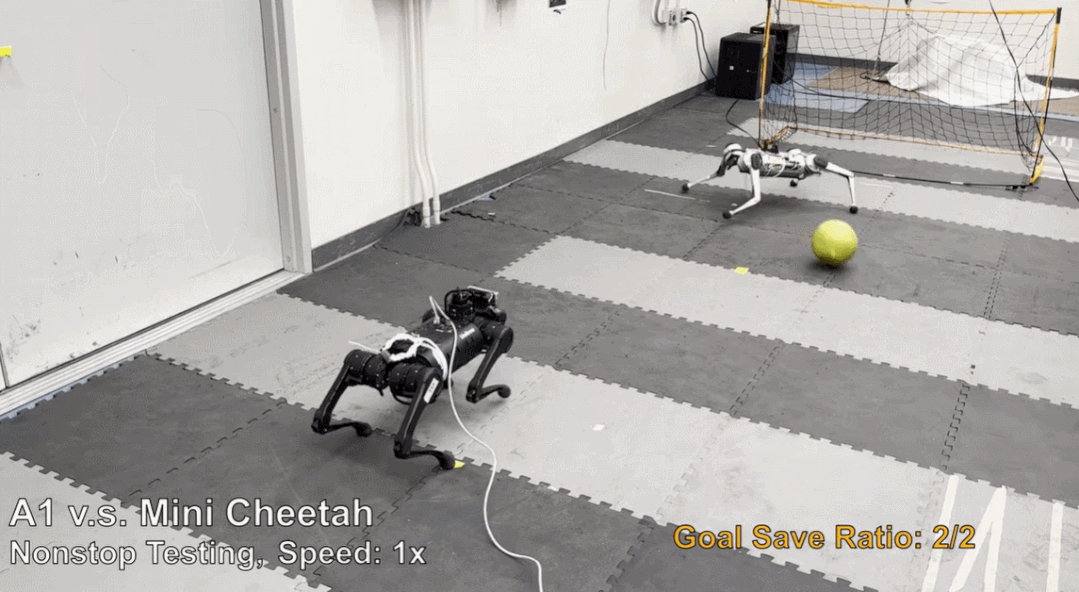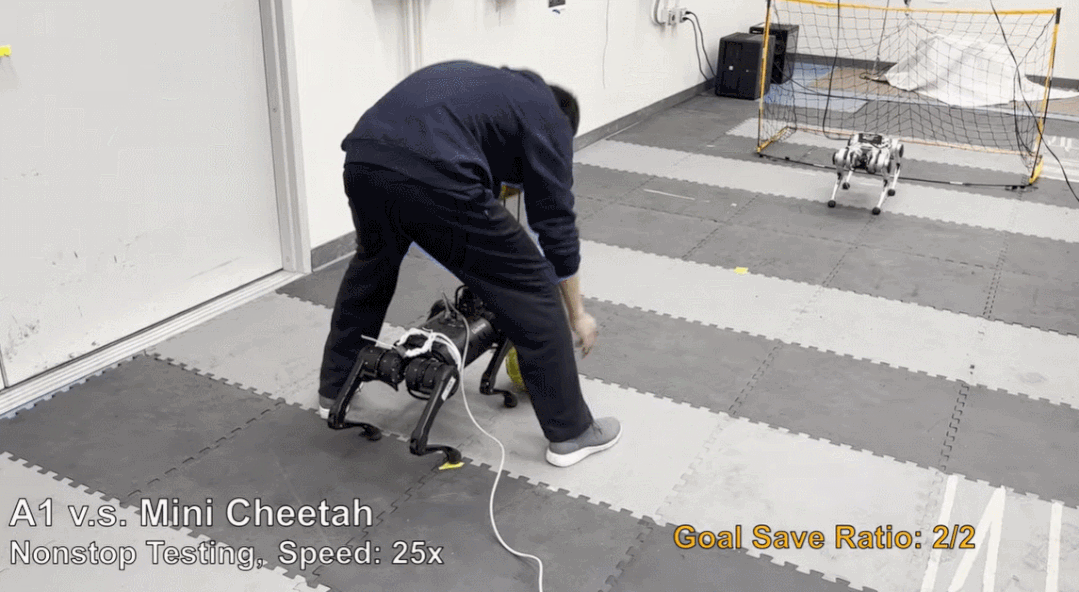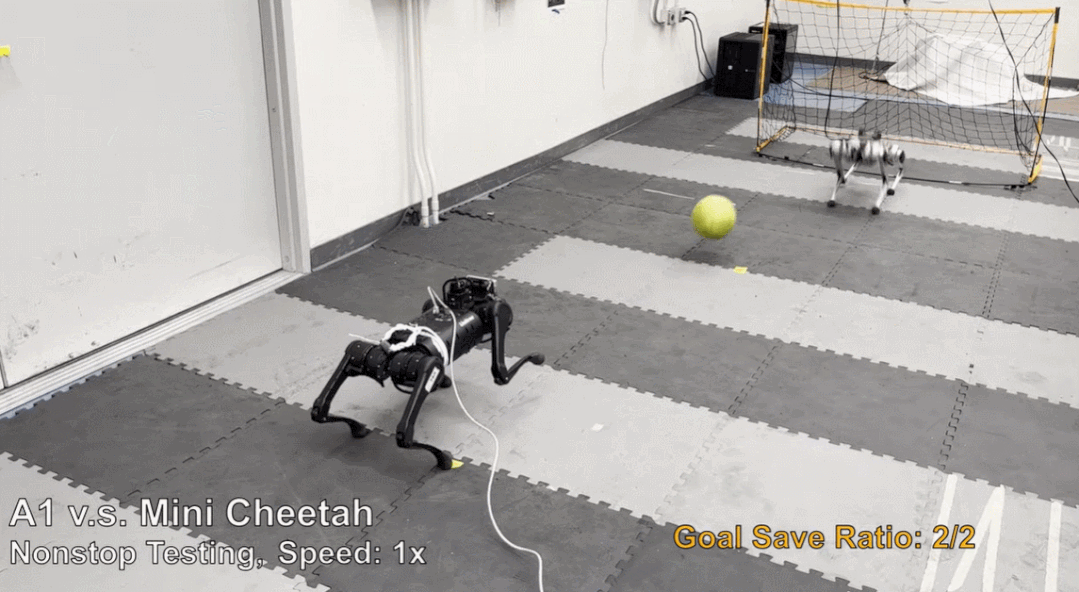
推荐:认真的吗?让机器狗当守门员,还发了篇论文。
论文 7:Video-driven Neural Physically-based Facial Asset for Production
- 作者:Longwen Zhang 等
- 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.05592.pdf
摘要:上海科技大学科研团队联合数字人底层技术公司影眸科技,将首创的 4D PBR 扫描技术与神经网络表达相结合,训练多 VAE 的网络结构,跳过了传统的绑定与动态贴图制作流程。这项工作已经被计算机图形学顶会 SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 接收为 Technical Paper - Journal Track 并受邀作报告分享。

最后在推荐一些链接哦
10 篇 NLP 精选论文
1. EnTDA: Entity-to-Text based Data Augmentation Approach for Named Entity Recognition Tasks. (from Philip S. Yu)
2. Doc2Bot: Accessing Heterogeneous Documents via Conversational Bots. (from Jian Sun)
3. Prompt Conditioned VAE: Enhancing Generative Replay for Lifelong Learning in Task-Oriented Dialogue. (from Jian Sun)
4. Deep Bidirectional Language-Knowledge Graph Pretraining. (from Jure Leskovec)
5. Transcending Scaling Laws with 0.1% Extra Compute. (from Quoc V. Le)
6. Extracting Cultural Commonsense Knowledge at Scale. (from Gerhard Weikum)
7. Entity-Focused Dense Passage Retrieval for Outside-Knowledge Visual Question Answering. (from Raymond J. Mooney)
8. Multilingual Word Sense Disambiguation with Unified Sense Representation. (from Hongming Zhang, Tong Zhang)
9. MICO: A Multi-alternative Contrastive Learning Framework for Commonsense Knowledge Representation. (from Hongming Zhang, Tong Zhang)
10. A Survey of Active Learning for Natural Language Processing. (from Eduard Hovy)
10 篇 CV 精选论文
1. A Tri-Layer Plugin to Improve Occluded Detection. (from Andrew Zisserman)
2. Using Language to Extend to Unseen Domains. (from Trevor Darrell)
3. Large-batch Optimization for Dense Visual Predictions. (from Liang Chen)
4. Towards Sustainable Self-supervised Learning. (from Ming-Ming Cheng, Shuicheng Yan)
5. Learning Dual Memory Dictionaries for Blind Face Restoration. (from Lei Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo)
6. Multi-view Tracking Using Weakly Supervised Human Motion Prediction. (from Pascal Fua)
7. Two-level Data Augmentation for Calibrated Multi-view Detection. (from Pascal Fua)
8. Perceptual Grouping in Vision-Language Models. (from Jonathon Shlens)
9. Consistency and Accuracy of CelebA Attribute Values. (from Kevin W. Bowyer)
10. Is synthetic data from generative models ready for image recognition?. (from Philip Torr)
10 篇 ML 精选论文
1. A Reinforcement Learning Approach in Multi-Phase Second-Price Auction Design. (from Michael I. Jordan)
2. Spatiotemporal Classification with limited labels using Constrained Clustering for large datasets. (from Vipin Kumar)
3. Off-policy evaluation for learning-to-rank via interpolating the item-position model and the position-based model. (from Thorsten Joachims)
4. Mutual Information Regularized Offline Reinforcement Learning. (from Shuicheng Yan)
5. Uncertainty Disentanglement with Non-stationary Heteroscedastic Gaussian Processes for Active Learning. (from Kevin Murphy)
6. Deep conditional transformation models for survival analysis. (from Torsten Hothorn)
7. G-Augment: Searching For The Meta-Structure Of Data Augmentation Policies For ASR. (from Quoc V. Le)
8. A Pareto-optimal compositional energy-based model for sampling and optimization of protein sequences. (from Kyunghyun Cho)
9. Planning for Sample Efficient Imitation Learning. (from Yang Gao)
10. FedFM: Anchor-based Feature Matching for Data Heterogeneity in Federated Learning. (from Yonina C. Eldar)





















 2277
2277

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








