标准差分进化算法matlab程序实现
自适应差分演化算法方面的Matlab和C++代码及论文
差分进化算法 DE-Differential Evolution
matlab练习程序(差异演化DE)
【DE算法】差分进化算法原理及matlab代码
差分进化算法
CEC2017 benchmark function调用接口
王勇:http://ist.csu.edu.cn/YongWang.htm http://www.escience.cn/people/yongwang1/index.html;jsessionid=7CE276B8D77C7CE70AE2C2D2F8DF1A7A-n1
Rammohan Mallipeddi Ponnuthurai N. Suganthan Quan-Ke Pan Mehmet Fatih Tasgetiren:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223921753_Differential_evolutionalgorithm_with_ensemble_of_parameters_and_mutation_trategies
- DE算法-作者网站: http://www1.icsi.berkeley.edu/~storn/code.html
- 维基百科资料库 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differential_evolution
终于开始了研究生阶段的学习生活,繁琐的入学相关事宜也处理得差不多了。在9月5号,我们实验室召开了第一次小组会议,导师也相继给我们指定了各自的研究方向,不出意外,我接下来将围绕智能优化算法在太阳能电池方面的应用展开学习和研究。
从6号到9号,我用三天时间看完了两篇关于标准差分进化算法的英文文献,虽然在完成本科毕业设计的时候也简单接触了差分进化算法,但是并没有自己动手实现,只是粗略地了解了算法流程,而这次则是仔细阅读了文献中的伪代码,参考了一些别人的代码。在这个过程中,我发现很多网上的代码有的没有进行封装,或者有的会出现或多或少的bug,所以最后自己尝试用matlab对别人的代码按照自己对差分进化算法的理解做了一定的修改实现,如果大家发现有不正确的地方,欢迎留言指正。下面给出两篇英文文献名以及具体的matlab代码。
差分进化算法英文文献:《Differential Evolution – A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces》、《Differential Evolution Algorithm With Strategy Adaptation for Global Numerical Optimization》
标准差分进化算法matlab程序实现:
一、主函数:DE_Std.m
%根据文章《Differential Evolution Algorithm With Strategy Adaptation for Global Numerical Optimization》的算法:ALGORITHMIC DESCRIPTION OF DE
%@written by Zhan Qian,2015-5-24
%测试函数求值用函数testFun(x,FunIndex)
%变异向量用函数mutation(X,bestX,F,mutationStrategy)
%交叉向量用函数crossover(X,V,CR,crossStrategy)
%mutation
%mutationStrategy=1:DE/rand/1,
%mutationStrategy=2:DE/best/1,
%mutationStrategy=3:DE/rand-to-best/1,
%mutationStrategy=4:DE/best/2,
%mutationStrategy=5:DE/rand/2.
%crossover
%crossStrategy=1:binomial crossover
%crossStrategy=2:Exponential crossover
clear
maxIteration=1000;%最大迭代次数
Generation=0;%进化代数,或者当前迭代代数
Xmax=30;%搜索上界,可以根据需要改为向量形式
Xmin=-30;%搜索下界
Dim=30;%个体维数
NP=50;%population size,种群规模
F=0.5;%scaling factor 缩放因子
CR=0.3;%crossover rate 交叉概率
FunIndex=3;%测试方程索引,不同值对应不同的测试函数
mutationStrategy=1;%变异策略
crossStrategy=2;%交叉策略
%%
%step1 初始化
%X represent population
%Generation=0;
X=(Xmax-Xmin)*rand(NP,Dim)+Xmin;%X行代表个体i,列代表个体i的维度j
%%
%step2 mutation,crossover,selection
while Generation<maxIteration
%求bestX
for i=1:NP
fitnessX(i)=testFun(X(i,:),FunIndex);%fitnessX表示X的适应值
end
[fitnessbestX,indexbestX]=min(fitnessX);
bestX=X(indexbestX,:);%bestX表示最优值对应的位置
%%
%step2.1 mutation
%mutationStrategy=1:DE/rand/1,
%mutationStrategy=2:DE/best/1,
%mutationStrategy=3:DE/rand-to-best/1,
%mutationStrategy=4:DE/best/2,
%mutationStrategy=5:DE/rand/2,
%产生为每一个个体Xi,G 产生一个变异向量Vi,G。 G代表进化代数
V=mutation(X,bestX,F,mutationStrategy);
%%
%step2.2 crossover
%crossStrategy=1:binomial crossover
%crossStrategy=2:Exponential crossover
%产生为每一个个体Xi,G 产生一个交叉向量Ui,G。 G代表进化代数
U=crossover(X,V,CR,crossStrategy);
%%
%step2.3 selection
for i=1:NP
fitnessU(i)=testFun(U(i,:),FunIndex);
if fitnessU(i)<=fitnessX(i)
X(i,:)=U(i,:);
fitnessX(i)=fitnessU(i);
if fitnessU(i)<fitnessbestX
bestX=U(i,:);
fitnessbestX=fitnessU(i);
end
end
end
%%
Generation=Generation+1;
bestfitnessG(Generation)=fitnessbestX;
end
%%
%画图
%plot(bestfitnessG);
optValue=num2str(fitnessbestX);
Location=num2str(bestX);
disp(strcat('the optimal value','=',optValue));
disp(strcat('the best location','=',Location));
二、变异:mutation.m
%为了保证多样性,在产生新的种群个体的过程中,产生的nrandI个互不相等的随机数,与i皆不相等;
%即:每产生的第 i 个新个体所用的随机选到的nrandI个旧个体不能是第 i 个旧个体。
function V=mutation(X,bestX,F,mutationStrategy)
NP=length(X);
for i=1:NP
%在[1 NP]中产生nrandI个互不相等的随机数,且与i皆不相等
nrandI=5;
r=randi([1,NP],1,nrandI);
for j=1:nrandI
equalr(j)=sum(r==r(j));
end
equali=sum(r==i);
equalval=sum(equalr)+equali;
while(equalval>nrandI) %若产生的随机数有相等的或与i相等的——需要重新生成随机数
r=randi([1,NP],1,nrandI);
for j=1:nrandI
equalr(j)=sum(r==r(j));
end
equali=sum(r==i);
equalval=sum(equalr)+equali;
end
switch mutationStrategy
case 1
%mutationStrategy=1:DE/rand/1;
V(i,:)=X(r(1),:)+F*(X(r(2),:)-X(r(3),:));
case 2
%mutationStrategy=2:DE/best/1;
V(i,:)=bestX+F*(X(r(1),:)-X(r(2),:));
case 3
%mutationStrategy=3:DE/rand-to-best/1;
V(i,:)=X(i,:)+F*(bestX-X(i,:))+F*(X(r(1),:)-X(r(2),:));
case 4
%mutationStrategy=4:DE/best/2;
V(i,:)=bestX+F*(X(r(1),:)-X(r(2),:))+F*(X(r(3),:)-X(r(4),:));
case 5
%mutationStrategy=5:DE/rand/2;
V(i,:)=X(r(1),:)+F*(X(r(2),:)-X(r(3),:))+F*(X(r(4),:)-X(r(5),:));
otherwise
error('没有所指定的变异策略,请重新设定mutationStrategy的值');
end
end
三、交叉:crossover.m
function U=crossover(X,V,CR,crossStrategy)
[NP,Dim]=size(X);
switch crossStrategy
%crossStrategy=1:binomial crossover
case 1
for i=1:NP
jRand=randi([1,Dim]);%jRand∈[1,Dim]
for j=1:Dim
k=rand;
if k<=CR||j==jRand %j==jRand是为了确保至少有一个U(i,j)=V(i,j)
U(i,j)=V(i,j);
else
U(i,j)=X(i,j);
end
end
end
%crossStrategy=2:Exponential crossover
case 2
for i=1:NP
j=randi([1,Dim]);%j∈[1,Dim]
L=0;
U(i,:)=X(i,:);
k=rand;
while(k<CR && L<Dim)
U(i,j)=V(i,j);
j=j+1;
if(j>Dim)
j=1;
end
L=L+1;
end
end
otherwise
error('没有所指定的交叉策略,请重新设定crossStrategy的值');
end
四、测试函数:testFun.m
function y=testFun(x,index)
%x代表参数,index代表测试的函数的选择
%该测试函数为通用测试函数,可以移植
%目录
% 函数名 位置 最优值
%1.Sphere 0 0
%2.Camel 多个
%3.Rosenbrock
switch index
case 1 %Sphere函数
y=sum(x.^2);
case 2 %Camel函数,Dim只能取2
if length(x)>2
error('x的维度超出了2');
end
xx=x(1);yy=x(2);y=(4-2.1*xx^2+xx^4/3)*xx^2+xx*yy+(-4+4*yy^2)*yy^2;
case 3 %Rosenbrock函数
y=0;
for i=2:length(x)
y=y+100*(x(i)-x(i-1)^2)^2+(x(i-1)-1)^2;
end
otherwise
disp('no such function, please choose another');
end
第一个网页(共2个)
点击打开链接 http://www1.osu.cz/~tvrdik/?page_id=18
Algorithms of global optimization and their applications (English)
Global Optimization, Evolutionary Algorithms and their Application to Computational Statistics
Stochastic algorithms of global optimization
In 1993 we started to deal with stochastic algorithms of global optimization. We modified the Controlled Random Search algorithm (Price 1976) by randomizing the reflection in simplex. The modified CRS algorithm was applied to estimating parameters of non-linear regression models and also in the shape optimization problem. For the testing of the stochastic algorithms a set of fourteen difficult non-linear regression tasks was collected. This collection can be downloaded here, the description of the tasks and references are in the file nlmod14.pdf (zip), data in text format are in the file models.zip.
Differential Evolution:
Competitive Diferential Evolution for Constrained Problems – CEC 2010
Source code in Matlab download readme.txt (source code zip)
Adaptive Diferential Evolution Algorithms, Handbook of Optimization, 2012
Source code in Matlab or C download readmeHO.txt (source code zip)
Hybrid DE for Optimal Clustering 2015
Manuscript of paper download asoc2014sub_tvkr
Matlab source code readmeClust download clustan_b6e6rl_source
Matlab Program Library for Box-constrained Continuous Problems (including a new adaptive stochastic algorithm for the estimation of parameters
in nonlinear regression models) here
Selected papers:
Tvrdík, J., Estimation of Regression Parameters by Controlled Random Search Algorithm (in Czech), In: Antoch, J. and Dohnal, G. (eds), Proceedings of ROBUST 94, 153-159, JČMF Praha, 1994, ISBN 80-7015-492-6
Křivý, I., Tvrdík, J., The Controlled Random Search Algorithm in Optimizing of Regression Models, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 20, 229-234, 1995
Haslinger J., Jedelský D., Kozubek T., Tvrdík J., Genetic and Random Search Methods in Optimal Shape Design Problems, Journal of Global Optimizations 16, 109-131, 2000
Křivý I., Tvrdík J., Stochastic Algorithms in Estimating Regression Models, COMPSTAT 1996, Proceedings in Computational Statistics (ed. A. Prat), 325-330, Physica Verlag, 1996
Tvrdík, J., Křivý, I., Simple Evolutionary Heuristics for Global Optimization, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 30, 345-352, 1999
download allmut99.pdf (zip)
Křivý I., Tvrdík J., Krpec R.: Stochastic Algorithms in Nonlinear Regression, Comput. Statist, Data Anal. 33, 278-290, 2000
Mišík, L., Tvrdík, J., Křivý, I. : On Convergence of a Class of Stochastic Algorithms, In: Proceedings of ROBUST 2000 (J.Antoch a G. Dohnal eds), 198-209, JČMF Praha, 2001, ISBN 80-7015-792-5
download rob00new.pdf (zip)
Tvrdík, J., Křivý, I., Mišík, L., Evolutionary Algorithm with Competing Heuristics, In: Ošmera, P. (ed.) Proceedings of MENDEL 2001, 7th International Conference on Soft Computing, 58-64, Technical University, Brno, 2001,
download mendel01.pdf (zip)
Tvrdík, J., Mišík, L., Křivý, I., Competing Heuristics in Evolutionary Algorithms, 2nd Euro-International Symposium on Computational Intelligence June 16 – 19, 2002, Košice, Slovakia, published In SINCAK et al. Intelligent Technologies-Theory and Applications. Amsterdam, The Nethelands: IOS Press, 2002. 159-165.
download kos02cln.pdf (zip)
Tvrdík, J., Křivý, I., Mišík, L., Evolutionary Algorithms with Competing Heuristics in Computational Statistics, COMPSTAT 2002, Proceedings in Computational Statistics (ed. Haerdle W., Roenz B.), 349-354, Physica Verlag, Heidelberg
download comp02.pdf (zip)
Tvrdík, J., Generalized controlled random search and competing heuristics. In MENDEL 2004, 10th Internetional Conference on Soft Computing (Matoušek R. and Ošmera P. eds). University of Technology, Brno, 2004. 228-233.
download mendel04.pdf
Tvrdík, J. Competition and Cooperation in Evolutionary Algorithms: A Comparative Study. In MENDEL 2005, 11th International Coference on Soft Computing. Brno : University of Technology, Brno, 2005. 108-113.
download mendel05.pdf extended CD version men05_CD.pdf
Tvrdík, J., Křivý, I., Mišík, L., Adaptive population-based search: application to estimation of nonlinear regression parameters. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 52(2), 713-724 (2007)
download preprint CSDA-06SAS03e.pdf
Tvrdík, J. Competitive Differential Evolution. In MENDEL 2006, 12th International Coference on Soft Computing. Brno : University of Technology, Brno, 2006. 7-12.
download mendel06.pdf extended CD version mendel06_CD.pdf
Tvrdík, J. Differential Evolution with Competitive Setting of its Control Parameters. TASK Quarterly 11, 169-179 (2007)
download reprint task07.pdf
Tvrdík, J. Adaptation in Differential Evolution: A Numerical Comparison. APPL SOFT COMPUT. 2009, 9, 1149-1155. ASOC2009_reprint.pdf
Tvrdík, J. Self-adaptive Variants of Differential Evolution with Exponential Crossover. Analele Universitatii de Vest, Timisoara.Seria Matematica-Informatica. 2009, 47, 151-168.
download reprint analele09.pdf
TVRDÍK, J., POLÁKOVÁ, R. Competitive Differential Evolution for Constrained Problems. 2010 IEEE CONGRESS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION (CEC). IEEE, 2010. s. 1632-1639.
POLÁKOVÁ, R., TVRDÍK, J. Various Mutation Strategies in Enhanced Competitive Differential Evolution for Constrained Optimization. 2011 IEEE Symposium on Differential Evolution. IEEE, 2011. s. 17-24. [2011-04-11]. ISBN 978-1-61284-070-3
TVRDÍK, J., KŘIVÝ, I. Hybrid Adaptive Differential Evolution in Partitional Clustering. MENDEL 2011 17th International Conference on Soft Computing. Brno: University of Technology, 2011. s. 1-8. [2011-06-15]. ISBN 978-80-214-4302-0 download preprint mendel11tvkr.pdf
第二个网页(共2个)
Self-adaptive Algorithms for Global Optimization – MATLAB and C++ Library Including Parallel Implementation for Many Processors
Introduction
The Matlab program library has been established in the frame of the project201/05/0284 of the Czech Grant Agency at University of Ostrava in 2006.The extension by C++ version comes from next period and the parallel versionof C++ library is the result of the project supported by the European RegionalDevelopment Fund in the IT4Innovations Centre of Excellence project(CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0070)
Project team:
- Josef Tvrdík, Department of Comp. Science, University of Ostrava,
- Viktor Pavliska, Institute for Research and Applications of Fuzzy Modeling,University of Ostrava,
- Radek Valášek, Institute for Research and Applications of Fuzzy Modeling,University of Ostrava,
- Radka Poláková, Institute for Research and Applications of Fuzzy Modeling,University of Ostrava,
- Hashim Habiballa, Department of Comp. Science, University of Ostrava,
The aim of this library is to make new self-adaptive stochastic algorithmsaccessible for potential users and facilitate the use of the self-adaptivealgorithms in practical problems. The self-adaptation of the algorithms meansthat the user need not set up their control parameters by preliminarytrial-and-error numerical experiment.
The library includes source codes of algorithms:
- adaptive controlled random search (CRS) for the estimation of non-linear regression parameters (Matlab, non-parallel)
- competitive-adaptive differential evolution (DE) for boundary-constrained global optimization (Matlab, non-parallel)
- competitive-adaptive differential evolution (DE) for boundary-constrained global optimization (C++, non-parallel and/or parallel)
These programs are free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify itunder the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the FreeSoftware Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) anylater version. The programs are distributed in the hope that they will beuseful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General PublicLicense for more details, http://www.fsf.org/.
If you use a routine of this library, please, cite in your paper or report thisreference:
Tvrdík J., Pavliska V., Valášek, R., Poláková, R., Habiballa, H.(2014) Self-adaptive Algorithms forGlobal Optimization – MATLAB and C++ Library Including Parallel Implementationfor Many Processors, irafm.osu.cz/sago
Contact address for Matlab routines: josef.tvrdik@osu.cz, radka.polakova@osu.cz
Contact address for C++ routines: viktor.pavliska@osu.cz, radek.valasek@osu.cz
差分进化算法DE与遗传算法GA非常类似,下面是差分进化算法的步骤。
算法步骤如下:
-
初始化
-
变异
-
交叉
d.选择
测试函数:
Rastrigr函数
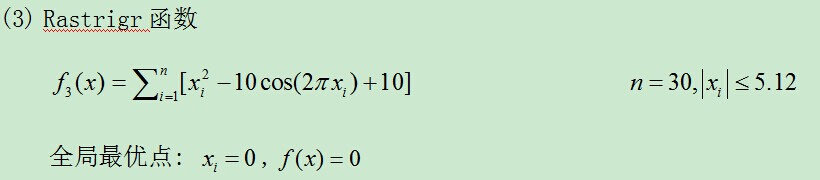
全局最优点: ,
matlab代码如下:
- function DE(Gm,F0)
- t0 = cputime;
- %差分进化算法程序
- %F0是变异率 %Gm 最大迭代次数
- Gm = 10000;
- F0 = 0.5;
- Np = 100;
- CR = 0.9; %交叉概率
- G= 1; %初始化代数
- D = 10; %所求问题的维数
- Gmin = zeros(1,Gm); %各代的最优值
- best_x = zeros(Gm,D); %各代的最优解
- value = zeros(1,Np);
- %产生初始种群
- %xmin = -10; xmax = 100;%带负数的下界
- xmin = -5.12;
- xmax = 5.12;
- function y = f(v)
- %Rastrigr 函数
- y = sum(v.^2 - 10.*cos(2.*pi.*v) + 10);
- end
- X0 = (xmax-xmin)*rand(Np,D) + xmin; %产生Np个D维向量
- XG = X0;
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%----这里未做评价,不判断终止条件----%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- XG_next_1= zeros(Np,D); %初始化
- XG_next_2 = zeros(Np,D);
- XG_next = zeros(Np,D);
- while G <= Gm
- G
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%----变异操作----%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- for i = 1:Np
- %产生j,k,p三个不同的数
- a = 1;
- b = Np;
- dx = randperm(b-a+1) + a- 1;
- j = dx(1);
- k = dx(2);
- p = dx(3);
- %要保证与i不同
- if j == i
- j = dx(4);
- else if k == i
- k = dx(4);
- else if p == i
- p = dx(4);
- end
- end
- end
- %变异算子
- suanzi = exp(1-Gm/(Gm + 1-G));
- F = F0*2.^suanzi;
- %变异的个体来自三个随机父代
- son = XG(p,:) + F*(XG(j,:) - XG(k,:));
- for j = 1: D
- if son(1,j) >xmin & son(1,j) < xmax %防止变异超出边界
- XG_next_1(i,j) = son(1,j);
- else
- XG_next_1(i,j) = (xmax - xmin)*rand(1) + xmin;
- end
- end
- end
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%---交叉操作----%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- for i = 1: Np
- randx = randperm(D);% [1,2,3,...D]的随机序列
- for j = 1: D
- if rand > CR & randx(1) ~= j % CR = 0.9
- XG_next_2(i,j) = XG(i,j);
- else
- XG_next_2(i,j) = XG_next_1(i,j);
- end
- end
- end
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%----选择操作---%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- for i = 1:Np
- if f(XG_next_2(i,:)) < f(XG(i,:))
- XG_next(i,:) = XG_next_2(i,:);
- else
- XG_next(i,:) = XG(i,:);
- end
- end
- %找出最小值
- for i = 1:Np
- value(i) = f(XG_next(i,:));
- end
- [value_min,pos_min] = min(value);
- %第G代中的目标函数的最小值
- Gmin(G) = value_min;
- %保存最优的个体
- best_x(G,:) = XG_next(pos_min,:);
- XG = XG_next;
- trace(G,1) = G;
- trace(G,2) = value_min;
- G = G + 1;
- end
- [value_min,pos_min] = min(Gmin);
- best_value = value_min
- best_vector = best_x(pos_min,:)
- fprintf('DE所耗的时间为:%f \n',cputime - t0);
- %画出代数跟最优函数值之间的关系图
- plot(trace(:,1),trace(:,2));
- end
结果:
以上转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/hehainan_86/article/details/38685231
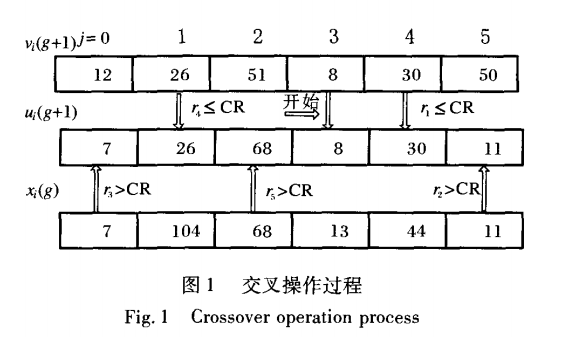
DE算法的求解步骤:
(1)基本参数的设置,包括NP, F, CR
(2)初始化种群
(3)计算种群适应度值
(4)终止条件不满足时,进行循环,依次执行变异、交叉、选择运算,直到终止运算。
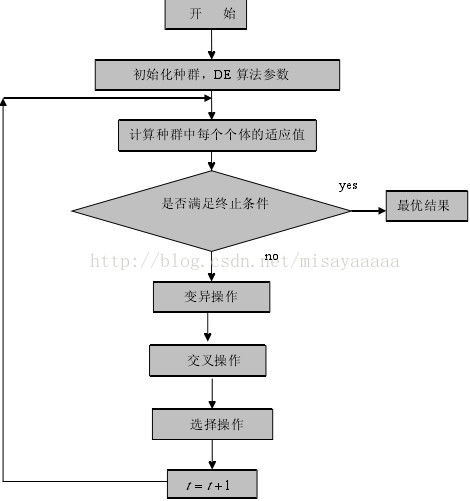
DE算法的流程图:
以上转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/misayaaaaa/article/details/54407548




























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








