List接口继承了Collection接口和Iterable接口,即同样含有Collection和 Iterable的特性,还有方法,其基本方法有:
1)有关添加: boolean add(E e):添加元素 void add(int index,E element):在特定位置添加元素
boolean addAll(Collection extends E> c):添加集合中所有的元素 boolean addAll(int index,Collection extends E> c):在特定位置添加一组元素
2)有关清除:void clear(), E remove(int index),boolean remove(Object o),boolean remove(Collection> c)
3)有关检验:boolean contains(Object o),boolean containAll(Collection> c),boolean equals(Object o),boolean isEmpty()
4)有关获取:E get(int index),int hashCode(),int indexOf(Object o),int lastIndexOf(Object o),int size(),Lisy subList(int fromindex,int toindex)
5)有关设定:E set(int index, E element),boolean retainAll(Collection> c)
6)有关打印:Object[] toArray(), T[] toArray(T[] a)
7)有关迭代:Iterator iterator(),ListIterator listIterator(),ListIterator listIterator(int index)
8)其他:int hashcode()
AboutArrayList:
All Implemented Interfaces: Serializable, Cloneable, Iterable, Collection, List, RandomAccess extends AbstractList
实例代码:
class iphone{}
public void arraylist(){
//1)Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
/*
* 2)Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator
*/
ArrayList alist = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
//3)Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity
ArrayList alist1 = new ArrayList(10);
al.add(new iphone());
al.add(1);
al.add("a");
al.add(alist);
System.out.println(al.hashCode()); //int hashcode()
/*
* usage of methods that aren't mentioned within "List basic methods"
*/
//ensure that list can hold at least the number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument
alist1.ensureCapacity(30);
//Trims the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the list's current size
alist.trimToSize();
//Returns a shallow copy of this ArrayList instance(The elements themselves are not copied)
Object o = al.clone();
}
AboutLinkedList:
从上面可以知道,由于LinkedList实现的接口涉及到队列,所以它也会新增一些有关队列独有操作方法,还有pop(),push()等,下面举例:
public void linkedlist(){
LinkedList linklist = new LinkedList();
ArrayList a = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
LinkedList linklist2 = new LinkedList(a);
Iterator i = linklist2.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
System.out.println(i.next()); //1 2 3
}
Iterator ri = linklist2.descendingIterator();
while(ri.hasNext()){
System.out.println(ri.next()); //3 2 1
}
linklist.addFirst(1);
linklist.addLast("e");
System.out.println(linklist); //[1,e]
/*linklist.getFirst();
linklist.getLast();*/
//Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list
System.out.println(linklist.element()); //1
linklist.offer("x");
System.out.println(linklist);//[1,e,x]
linklist.offerFirst(0);
linklist.offerLast("y");
System.out.println(linklist);//[0,1,e,x,y]
//peek..()--->[Retrieves, but does not remove]
System.out.println(linklist.peek());//0
System.out.println(linklist.peekFirst());//0 ,list is empty,return "null"
System.out.println(linklist.peekLast());//y,list is empty, return "null"
//poll..()--->[Retrieves and removes]
System.out.println(linklist.poll()); //0
System.out.println(linklist.pollFirst());//1
System.out.println(linklist.pollLast()); //y
System.out.println(linklist);//[e,x]
/*linklist.removeFirst(); //return first element
linklist.removeFirstOccurrence(Object); //boolean
linklist.removeLast(); //return last element
linklist.removeLastOccurrence(Object); //boolean
*/
System.out.println(linklist2); //[1 2 3]
//Pops an element from the stack represented by this list
System.out.println(linklist2.pop()); //1
//Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list
linklist2.push("m");
System.out.println(linklist2);//[m,2,3]
}
ArrayList 和LinkedList的比较:
1.ArrayList是基于动态数组,LinkedList基于链表
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据
验证:
public void comparearraylistwithlinklist(){
SimpleDateFormat f = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
System.out.println(f.format(new Date()));
ArrayList a = new ArrayList();
long starttime = new Date().getTime();
for(int i = 0; i<10000; i++){
a.add(i);
}
long finishtime = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println(finishtime-starttime);
LinkedList l = new LinkedList();
long lstarttime = new Date().getTime();
for(int i = 0; i<10000; i++){
l.add(i);
}
long lfinishtime = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println(lfinishtime-lstarttime);
}
输出:
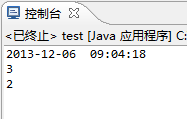
额外说明:以上验证代码是基于较大量数据的,输出也是不稳定的,即答案也不能确定,可能是我用错测试方法,也可能是因为数据量不够大,也可能是因为getTime()获得的是毫秒,程序可能需要更精确的时间单位,这样才有办法比较。另外,如果对于单个数据的插入或删除,是不是LinkedList还优于ArrayList呢?答案也很明显是不一定的,读者可以按照上面的实例验证一下
由于此博文可能有点长了,其他List的学习见“java集合类(三)List学习(续)”,尽请期待!!
### 学习从来都是一个过程,对对错错对对...若文中有错误,还望读者批评指出 ###





















 178
178











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








