概述:
最近要学习写网络爬虫,所以把图的深度和广度搜索都再温习一下。
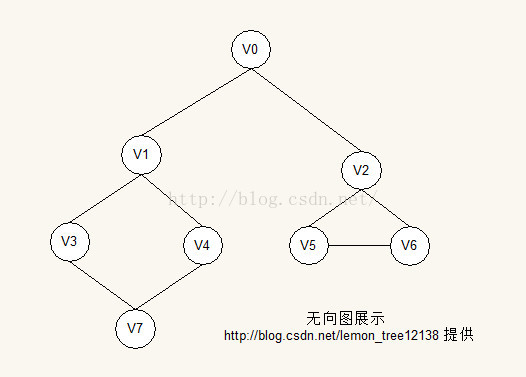
图结构展示:
实现过程:
首先,我们来看看图结构在代码中的实现。有三块逻辑:1.图中的节点:
public class GraphNode {
public List<GraphEdge> edgeList = null;
private String label = "";
public GraphNode(String label) {
this.label = label;
if (edgeList == null) {
edgeList = new ArrayList<GraphEdge>();
}
}
/**
* 给当前节点添加一条边
* GraphNode
* @param edge
* 添加的边
*/
public void addEdgeList(GraphEdge edge) {
edgeList.add(edge);
}
public String getLabel() {
return label;
}
}2.图中的边:
public class GraphEdge {
private GraphNode nodeLeft;
private GraphNode nodeRight;
/**
* @param nodeLeft
* 边的左端
* @param nodeRight
* 边的右端
*/
public GraphEdge(GraphNode nodeLeft, GraphNode nodeRight) {
this.nodeLeft = nodeLeft;
this.nodeRight = nodeRight;
}
public GraphNode getNodeLeft() {
return nodeLeft;
}
public GraphNode getNodeRight() {
return nodeRight;
}
}3.把节点和边组合成一个图结构:
public class MyGraph {
private List<GraphNode> nodes = null;
public void initGraph(int n) {
if (nodes == null) {
nodes = new ArrayList<GraphNode>();
}
GraphNode node = null;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
node = new GraphNode(String.valueOf(i));
nodes.add(node);
}
}
public void initGraph(int n, boolean b) {
initGraph(n);
GraphEdge edge01 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(0), nodes.get(1));
GraphEdge edge02 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(0), nodes.get(2));
GraphEdge edge13 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(1), nodes.get(3));
GraphEdge edge14 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(1), nodes.get(4));
GraphEdge edge25 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(2), nodes.get(5));
GraphEdge edge26 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(2), nodes.get(6));
GraphEdge edge37 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(3), nodes.get(7));
GraphEdge edge47 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(4), nodes.get(7));
GraphEdge edge56 = new GraphEdge(nodes.get(5), nodes.get(6));
nodes.get(0).addEdgeList(edge01);
nodes.get(0).addEdgeList(edge02);
nodes.get(1).addEdgeList(edge13);
nodes.get(1).addEdgeList(edge14);
nodes.get(2).addEdgeList(edge25);
nodes.get(2).addEdgeList(edge26);
nodes.get(3).addEdgeList(edge37);
nodes.get(4).addEdgeList(edge47);
nodes.get(5).addEdgeList(edge56);
}
public void initGraph() {
initGraph(8, false);
}
public List<GraphNode> getGraphNodes() {
return nodes;
}
}有了图的结构,我们就可以进行一些实际的操作了。
深度优先搜索:
public class DFSearch {
/**
* 深度遍历
* DFSearch
* @param node
* 当前节点
* @param visited
* 被访问过的节点列表
*/
public void searchTraversing(GraphNode node, List<GraphNode> visited) {
// 判断是否遍历过
if (visited.contains(node)) {
return;
}
visited.add(node);
System.out.println("节点:" + node.getLabel());
for (int i = 0; i < node.edgeList.size(); i++) {
searchTraversing(node.edgeList.get(i).getNodeRight(), visited);
}
}
}广度优先搜索:
public class BFSearch {
/**
* 广度优先搜索
* BFSearch
* @param node
* 搜索的入口节点
*/
public void searchTraversing(GraphNode node) {
List<GraphNode> visited = new ArrayList<GraphNode>(); // 已经被访问过的元素
Queue<GraphNode> q = new LinkedList<GraphNode>(); // 用队列存放依次要遍历的元素
q.offer(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
GraphNode currNode = q.poll();
if (!visited.contains(currNode)) {
visited.add(currNode);
System.out.println("节点:" + currNode.getLabel());
for (int i = 0; i < currNode.edgeList.size(); i++) {
q.offer(currNode.edgeList.get(i).getNodeRight());
}
}
}
}
}






















 226
226











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








