我们将从零实现整个方法,包括数据流水线、模型、损失函数和小批量随机梯度下降优化器
导入包:
import random
import torch
根据带有噪声的线性模型构造一个人造数据集,我们使用线性模型参数w=[2,-3.4]和b=4.2和噪声项c生成数据集及其标签:
y=wx+b+c
添加训练样本:
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):
x = torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w)))
y = torch.mul(x,w)+b
#加入随机噪音
y += torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape)
#列向量返回
return x,y.reshape((-1,1))
true_w = torch.tensor([2,-3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features,labels = synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,1000)
查看样本:
print("features:",features[0],'\nlabels',labels[0])
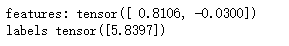
导入d2l包
先下载d2lzh_pytorch.zip文件,解压后将其放在anaconda对应目录:
from d2lzh_pytorch import torch as d2l
查看数据(散点图)
set_figsize()
plt.scatter(features[:, 1].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy()[0:1000], 1)

定义一个函数,该函数接收批量大小、特征矩阵和标签向量作为输入,生成大小为batch_size的小批量
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
#随机读取样本
#打乱下标
random.shuffle(indices)
#从0开始到num_exanples,每次跳batch_size大小
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
#min判断是否超出样本数目
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
batch_size = 10
for x,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
print(x,'\n',y)
break

定义初始化模型参数
w = torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(2,1),requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1,requires_grad=True)
定义模型
def linreg(x,w,b):
return torch.matmul(x,w)+b
定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat,y):
return (y_hat-y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2/2
定义优化算法
def sgd(params,lr,batch_size):
#小批量随机梯度下降
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
#求均值
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
训练网络
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) # `X`和`y`的小批量损失
# 因为`l`形状是(`batch_size`, 1),而不是一个标量。`l`中的所有元素被加到一起,
# 并以此计算关于[`w`, `b`]的梯度
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 使用参数的梯度更新参数
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
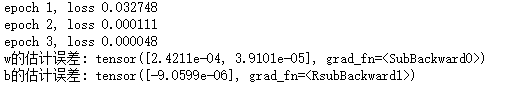
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')
print(f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b}')
























 1169
1169











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








