图像处理之基于采样距离变换算法
算法是别人提出来的,感兴趣可以搜索《Distance Transforms of Sampled Functions》
这篇论文,网上也有很多实现的代码,但是结构不是很好,而且很分散不是一个完整的
算法。所以我整理了一下,写成一个单独的类,只要简单调用一下即可出结果图片。
至于算法原理什么的,我真很难解释清楚,大致的思想是基于能量最小化的,分别
进行行与列的1D距离变变换采样。
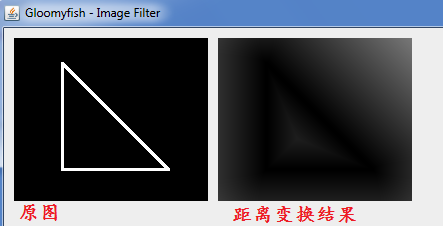
运行结果:
算法代码:
package com.gloomyfish.image.transform; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import com.gloomyfish.filter.study.GrayFilter; /** * * @author gloomyfish * */ public class FastDistanceTransformAlg extends GrayFilter { public final static double INF = 1E20; private int backgroundColor = 0; // default black public int getBackgroundColor() { return backgroundColor; } public void setBackgroundColor(int backgroundColor) { this.backgroundColor = backgroundColor; } @Override public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) { int width = src.getWidth(); int height = src.getHeight(); dest = super.filter(src, null); // int[] inPixels = new int[width*height]; float[] outPixels = new float[width*height]; getRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels ); int index = 0; for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { int tr = 0; for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { index = row * width + col; tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff; if(tr == backgroundColor) outPixels[index] = (float)INF; else outPixels[index] = 0; } } // transform along columns float[] f = new float[Math.max(width, height)]; for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { index = row * width + col; f[row] = outPixels[index]; } float[] disColumns = distance1DTransform(f, height); for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { index = row * width + col; outPixels[index] = disColumns[row]; } } // transform along rows for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) { index = row * width + col; f[col] = outPixels[index]; } float[] disColumns = distance1DTransform(f, width); for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) { index = row * width + col; outPixels[index] = disColumns[col]; } } // post sqrt calculation int[] result = new int[width*height]; for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { index = row * width + col; int pc = clamp(Math.sqrt(outPixels[index])); result[index] = (255 << 24) | (pc << 16) | (pc << 8) | pc; } } setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, result ); return dest; } public static int clamp(double c) { return c > 255 ? 255 : (c < 0 ? 0 : (int)c); } /** * 1D distance transform using squared distance * * @param data * @param n * @return */ private float[] distance1DTransform(float[] f, int n) { float[] d = new float[n]; int[] v = new int[n]; double[] z = new double[n+1]; int k = 0; v[0] = 0; z[0] = -INF; z[1] = +INF; for (int q = 1; q <= n-1; q++) { double s = ((f[q]+square(q))-(f[v[k]]+square(v[k])))/(2*q-2*v[k]); while (s <= z[k]) { k--; s = ((f[q]+square(q))-(f[v[k]]+square(v[k])))/(2*q-2*v[k]); } k++; v[k] = q; z[k] = s; z[k+1] = +INF; } k = 0; for (int q = 0; q <= n-1; q++) { while (z[k+1] < q) k++; d[q] = (float)square(q-v[k]) + f[v[k]]; } return d; } private double square(double v) { return v*v; } } 转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/gloomyfish/1400259





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








