一、几个关键宏定义
CONFIG_DEBUG_LL、 CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE
容我慢慢道来, 首先要使能早期打印, menuconfig必须选中CONFIG_DEBUG_LL, 我们再慢慢梳理其他所以宏及代码
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/kernel/Makefile */ obj-$(CONFIG_DEBUG_LL) += debug.o obj-$(CONFIG_EARLY_PRINTK) += early_printk.o

我们选中“Kernel low-level debugging functions (read help!)” 在linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug 中就是DEBUG_LL
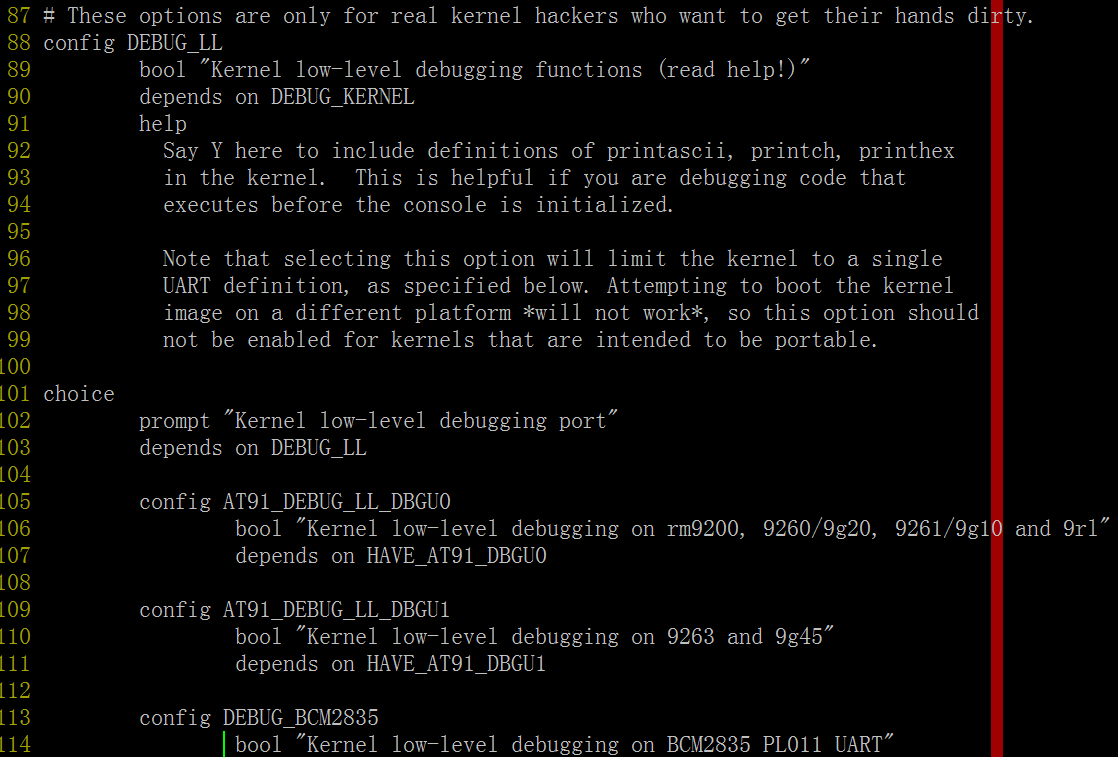
在这个选项中发现还有个依赖的子菜单“Kernel low-level debugging port”, 里面有一堆宏定义如AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU0、AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU1、DEBUG_BCM2835、DEBUG_ICEDCC,
实际上前面3个又依赖其他宏定义所以在menuconfig中只看到几个子选项如下:
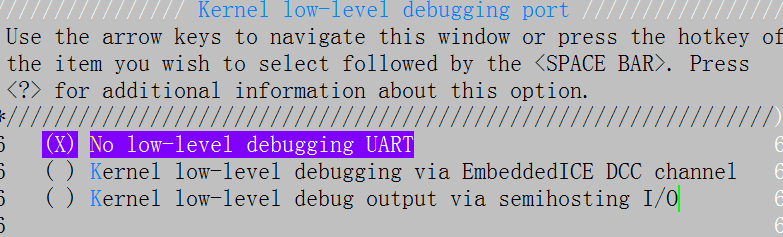
这几个子选项用来干嘛呢? 一是代码文件debug.S(obj-$(CONFIG_DEBUG_LL) += debug.o) 会根据子宏定义走不同的分支; 二是这个代码里会引用宏CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE,
这个宏在“linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug”中定义如下:
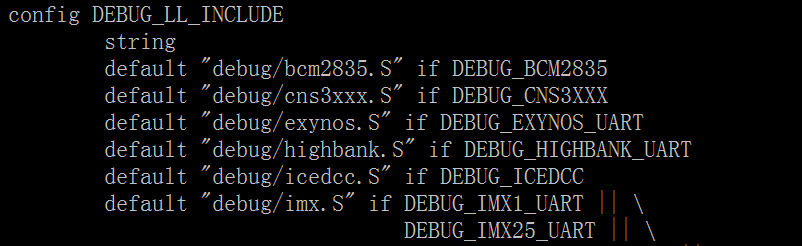
看到没? 子选项定义的DEBUG_BCM2835 在DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE中被依赖了, 也就是我们移植一个新平台, 需要在子选项定义新的宏, 然后在这添加依赖这个新宏对应的文件, 我们现在就这么做:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug */ choice prompt "Kernel low-level debugging port" depends on DEBUG_LL + config VEDIC_DEBUG_LL + bool "I just add a test macro" config AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU0 bool "Kernel low-level debugging on rm9200, 9260/9g20, 9261/9g10 and 9rl" depends on HAVE_AT91_DBGU0 config DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE string + default "debug/vedic.S" if VEDIC_DEBUG_LL default "debug/bcm2835.S" if DEBUG_BCM2835 default "debug/cns3xxx.S" if DEBUG_CNS3XXX
接下来我们在menuconfig选中VEDIC_DEBUG_LL宏和添加新文件vedic.S, 如下:

/* linux-3.10.65/.config */ +CONFIG_DEBUG_LL=y +CONFIG_VEDIC_DEBUG_LL=y +CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE="debug/vedic.S"
那这个vedic.S该怎么写呢? 我们看同目录下(linux-3.10.65/arch//arm/include/debug/)bcm2835.S文件写了什么:
/* * Debugging macro include header * * Copyright (C) 2010 Broadcom * Copyright (C) 1994-1999 Russell King * Moved from linux/arch/arm/kernel/debug.S by Ben Dooks * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as * published by the Free Software Foundation. * */ #define BCM2835_DEBUG_PHYS 0x20201000 #define BCM2835_DEBUG_VIRT 0xf0201000 .macro addruart, rp, rv, tmp ldr \rp, =BCM2835_DEBUG_PHYS ldr \rv, =BCM2835_DEBUG_VIRT .endm #include <asm/hardware/debug-pl01x.S>
没错, 就是提供一个函数而已 -> addruart(rp, rv, tmp) , 其实就是返回参数 -- 串口物理地址和串口虚拟地址, 为什么要提供虚拟地址呢? 因为在kernel C语言的第一个入口start_kernel()时, 汇编期间已经开启了MMU, CPU取的都是
虚拟地址; 该函数只是返回地址而已, 如果是开启MMU,返回虚拟地址还不够, 还要事前构建好页表, 不然根据虚拟地址也找不到物理地址。 至于具体在哪里构建页表, 待会说, 根据我目前的硬件平台, 提供文件代码如下:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/vedic.S * phy_addr is fixed of hardware, but virt_addr? Why 0xF5368000 */ #define VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS 0x70400000 #define VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT 0xF5368000 .macro addruart, rp, rv, tmp ldr \rp, =VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS ldr \rv, =VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT .endm
二、源码分析
为方便待会分批解释功能我先贴出debug.S源码:


1 /* 2 * linux/arch/arm/kernel/debug.S 3 * 4 * Copyright (C) 1994-1999 Russell King 5 * 6 * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify 7 * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as 8 * published by the Free Software Foundation. 9 * 10 * 32-bit debugging code 11 */ 12 #include <linux/linkage.h> 13 #include <asm/assembler.h> 14 15 .text 16 17 /* 18 * Some debugging routines (useful if you've got MM problems and 19 * printk isn't working). For DEBUGGING ONLY!!! Do not leave 20 * references to these in a production kernel! 21 */ 22 23 #if !defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING) 24 #include CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE 25 #endif 26 27 #ifdef CONFIG_MMU 28 .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2 29 addruart \tmp1, \tmp2, \rx 30 mrc p15, 0, \rx, c1, c0 31 tst \rx, #1 32 moveq \rx, \tmp1 33 movne \rx, \tmp2 34 .endm 35 36 #else /* !CONFIG_MMU */ 37 .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2 38 addruart \rx, \tmp1 39 .endm 40 41 #endif /* CONFIG_MMU */ 42 43 /* 44 * Useful debugging routines 45 */ 46 ENTRY(printhex8) 47 mov r1, #8 48 b printhex 49 ENDPROC(printhex8) 50 51 ENTRY(printhex4) 52 mov r1, #4 53 b printhex 54 ENDPROC(printhex4) 55 56 ENTRY(printhex2) 57 mov r1, #2 58 printhex: adr r2, hexbuf 59 add r3, r2, r1 60 mov r1, #0 61 strb r1, [r3] 62 1: and r1, r0, #15 63 mov r0, r0, lsr #4 64 cmp r1, #10 65 addlt r1, r1, #'0' 66 addge r1, r1, #'a' - 10 67 strb r1, [r3, #-1]! 68 teq r3, r2 69 bne 1b 70 mov r0, r2 71 b printascii 72 ENDPROC(printhex2) 73 74 hexbuf: .space 16 75 76 .ltorg 77 78 #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING 79 80 ENTRY(printascii) 81 addruart_current r3, r1, r2 82 b 2f 83 1: waituart r2, r3 84 senduart r1, r3 85 busyuart r2, r3 86 teq r1, #'\n' 87 moveq r1, #'\r' 88 beq 1b 89 2: teq r0, #0 90 ldrneb r1, [r0], #1 91 teqne r1, #0 92 bne 1b 93 mov pc, lr 94 ENDPROC(printascii) 95 96 ENTRY(printch) 97 addruart_current r3, r1, r2 98 mov r1, r0 99 mov r0, #0 100 b 1b 101 ENDPROC(printch) 102 103 #ifdef CONFIG_MMU 104 ENTRY(debug_ll_addr) 105 addruart r2, r3, ip 106 str r2, [r0] 107 str r3, [r1] 108 mov pc, lr 109 ENDPROC(debug_ll_addr) 110 #endif 111 112 #else 113 114 ENTRY(printascii) 115 mov r1, r0 116 mov r0, #0x04 @ SYS_WRITE0 117 ARM( svc #0x123456 ) 118 THUMB( svc #0xab ) 119 mov pc, lr 120 ENDPROC(printascii) 121 122 ENTRY(printch) 123 adr r1, hexbuf 124 strb r0, [r1] 125 mov r0, #0x03 @ SYS_WRITEC 126 ARM( svc #0x123456 ) 127 THUMB( svc #0xab ) 128 mov pc, lr 129 ENDPROC(printch) 130 131 ENTRY(debug_ll_addr) 132 mov r2, #0 133 str r2, [r0] 134 str r2, [r1] 135 mov pc, lr 136 ENDPROC(debug_ll_addr) 137 138 #endif
具体分析如下:
1. #if !defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING) #include CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE #endif ---> 因为没有定义CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING, 所以包含了CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE=linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/vedic.S, 也即提供addruart()功能 2. #ifdef CONFIG_MMU .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2 addruart \tmp1, \tmp2, \rx mrc p15, 0, \rx, c1, c0 tst \rx, #1 moveq \rx, \tmp1 movne \rx, \tmp2 .endm #else /* !CONFIG_MMU */ .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2 addruart \rx, \tmp1 .endm #endif /* CONFIG_MMU */ ---> 注意参数的位置!addruart()第一个参数是返回物理地址, 第二个是返回虚拟地址, 第三个不用 addruart_current(rx, tmp1, tmp2) rx是返回串口地址,至于是物理地址还是虚拟地址做了判断, 如果没有开MMU, 当然rx是物理地址,所以直接 将rx作为addruart()第一个参数, 如果使能MMU可以直接返回虚拟地址, 但开发者可能为保险起见, 判断p15协处理器硬件是否真的开启MMU, 如果开启就返回虚拟地址rx=tmp2, 不然返回物理地址rx=tmp1 3. ENTRY(printascii) addruart_current r3, r1, r2 b 2f /* 先跳转到2,把要打印的值放置r1 */ 1: waituart r2, r3 senduart r1, r3 busyuart r2, r3 teq r1, #'\n' moveq r1, #'\r' beq 1b 2: teq r0, #0 ldrneb r1, [r0], #1 /* r0存放的是要打印字符内存地址, 该指令是加载r0地址上的值,取一个byte到r1, 同时r0偏移1个byte */ teqne r1, #0 bne 1b mov pc, lr ENDPROC(printascii) ENTRY(printch) addruart_current r3, r1, r2 mov r1, r0 mov r0, #0 b 1b ENDPROC(printch) ---> 这段汇编提供两个函数功能, 打印字符串printascii(), 和打印字符printch(), 这里需要再提供waituart() senduart() busyuart() 所以我们要在vedic.S提供这三个函数 4. #ifdef CONFIG_MMU ENTRY(debug_ll_addr) addruart r2, r3, ip str r2, [r0] str r3, [r1] mov pc, lr ENDPROC(debug_ll_addr) #endif ---> 这个函数其实就是将串口物理地址赋值给参数0, 虚拟地址赋值给参数1, 其C定义的含义为: #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LL extern void debug_ll_addr(unsigned long *paddr, unsigned long *vaddr); extern void debug_ll_io_init(void); #else static inline void debug_ll_io_init(void) {} #endif 可以理解debug_ll_addr()等效于addruart(), 那谁用这个功能呢? 在linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/mmu.c: #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LL void __init debug_ll_io_init(void) { struct map_desc map; debug_ll_addr(&map.pfn, &map.virtual); if (!map.pfn || !map.virtual) return; map.pfn = __phys_to_pfn(map.pfn); map.virtual &= PAGE_MASK; map.length = PAGE_SIZE; map.type = MT_DEVICE; create_mapping(&map, false); } #endif 没错, debug_ll_io_init()就是构建串口虚拟地址和物理地址页表, 一般放在 machine_desc.map_io: static void __init zynq_map_io(void) { debug_ll_io_init(); zynq_scu_map_io(); } MACHINE_START(XILINX_EP107, "Xilinx Zynq Platform") .smp = smp_ops(zynq_smp_ops), .map_io = zynq_map_io, .init_irq = irqchip_init, .init_machine = zynq_init_machine, .init_time = zynq_timer_init, .dt_compat = zynq_dt_match, .restart = zynq_system_reset, MACHINE_END 这个在: start_kernel() -> setup_arch() -> paging_init() -> devicemaps_init() ->mdesc->map_io() 从这里可以看出, 要使用printascii(), printch()功能必须在setup_arch()执行之后,因为之前页表都没有建立访问虚拟地址压根找不到物理地址 很明显跑到start_kernel()时已经开启MMU了,我就想在start_kernel()时就立马打印log出来, 当操作虚拟地址时由于页表没建立串口的映射导致系统Oops 这是非常不好的用户体验!串口虽然是device, 应该归属devicemaps_init(), 但由于它的特殊性, 我们希望这块映射越早越好, 因此稍微新的内核版本 都把这块映射放置在汇编阶段: linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/kernel/head.s __create_page_tables: #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LL #if !defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_ICEDCC) && !defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING) /* * Map in IO space for serial debugging. * This allows debug messages to be output * via a serial console before paging_init. */ addruart r7, r3, r0 mov r3, r3, lsr #SECTION_SHIFT mov r3, r3, lsl #PMD_ORDER add r0, r4, r3 mov r3, r7, lsr #SECTION_SHIFT ldr r7, [r10, #PROCINFO_IO_MMUFLAGS] @ io_mmuflags orr r3, r7, r3, lsl #SECTION_SHIFT #ifdef CONFIG_ARM_LPAE mov r7, #1 << (54 - 32) @ XN #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_ENDIAN_BE8 str r7, [r0], #4 str r3, [r0], #4 #else str r3, [r0], #4 str r7, [r0], #4 #endif #else orr r3, r3, #PMD_SECT_XN str r3, [r0], #4 #endif #else /* CONFIG_DEBUG_ICEDCC || CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING */ /* we don't need any serial debugging mappings */ ldr r7, [r10, #PROCINFO_IO_MMUFLAGS] @ io_mmuflags #endif 其他平台串口需要特殊映射的..... #endif Now,汇编阶段映射好页表, 然后跳转到start_kernel()就可以立马使用printascii(), 同时mdesc->map_io也不需要调用debug_ll_io_init()


/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/vedic.S * phy_addr is uart base addr which fixed by hardware, but virt_addr? Why 0xF5368000 */ #define VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS 0x70400000 #define VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT 0xF5368000 .macro addruart, rp, rv, tmp ldr \rp, =VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS ldr \rv, =VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT .endm .macro senduart,rd,rx and \rd,\rd,#0xFF str \rd, [\rx, #0x00] /* tx_reg is offset 0x00 */ .endm .macro waituart,rd,rx 1: ldr \rd, [\rx, #0x0C] /* fifo_reg is offset 0x0C */ mov \rd,\rd,lsr #8 and \rd,\rd,#0x7F teq \rd, #0x00 bne 1b .endm .macro busyuart,rd,rx 2: ldr \rd, [\rx, #0x0C] mov \rd,\rd,lsr #8 and \rd,\rd,#0x7F teq \rd, #0x00 bne 2b .endm
三、测试验证
/* linux-3.10.65/include/generated/autoconf.h */ #define CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE "debug/vedic.S"
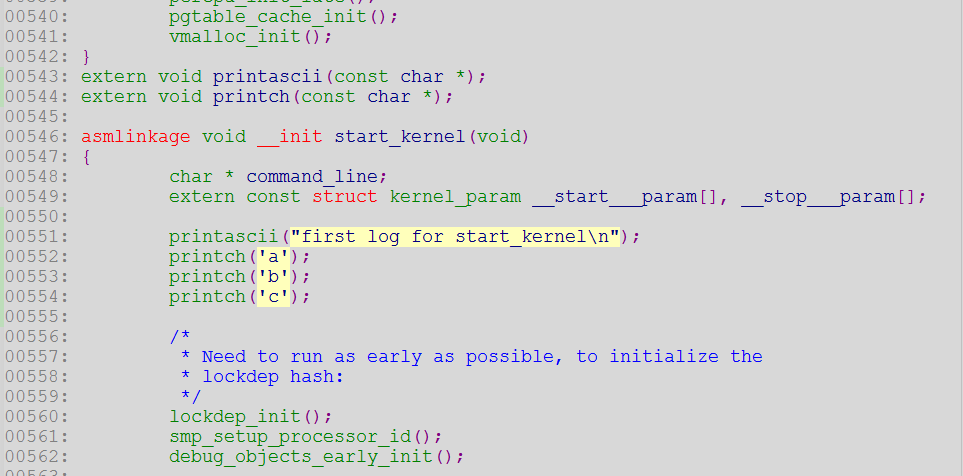
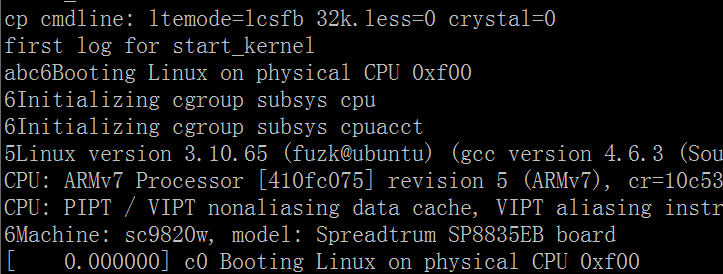
四、压缩镜像 zImage 使能打印
上面的调试都是解压后Image的log, 如果固件是压缩zImage呢? 如果想打印log? 我们先看一下log所在文件:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/boot/compressed/misc.c */ static void putstr(const char *ptr) { char c; while ((c = *ptr++) != '\0') { if (c == '\n') putc('\r'); putc(c); } flush(); } void decompress_kernel(unsigned long output_start, unsigned long free_mem_ptr_p, unsigned long free_mem_ptr_end_p, int arch_id) { int ret; output_data = (unsigned char *)output_start; free_mem_ptr = free_mem_ptr_p; free_mem_end_ptr = free_mem_ptr_end_p; __machine_arch_type = arch_id; arch_decomp_setup(); putstr("Uncompressing Linux..."); ret = do_decompress(input_data, input_data_end - input_data, output_data, error); if (ret) error("decompressor returned an error"); else putstr(" done, booting the kernel.\n"); }
看样子最终靠putc()实现, misc.c开头包含一个宏“CONFIG_UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE”, 定义在:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug */ /* Here I delete ARCH_MULTIPLATFORM since my menuconfig does not declare config DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS bool default y if ARCH_MULTIPLATFORM && DEBUG_LL && \ !DEBUG_OMAP2PLUS_UART && \ !DEBUG_TEGRA_UART config UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE string default "debug/uncompress.h" if ARCH_MULTIPLATFORM default "mach/uncompress.h" */ config DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS bool default y if DEBUG_LL && \ !DEBUG_OMAP2PLUS_UART && \ !DEBUG_TEGRA_UART config UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE string default "debug/uncompress.h" 所以: CONFIG_DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS=y CONFIG_UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE=linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/uncompress.h


#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS extern void putc(int c); #else static inline void putc(int c) {} #endif static inline void flush(void) {} static inline void arch_decomp_setup(void) {}
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/boot/compressed/Makefile */ ifeq ($(CONFIG_DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS),y) OBJS += debug.o 而linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/boot/compressed/debug.S:


#include <linux/linkage.h> #include <asm/assembler.h> #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING #include CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE ENTRY(putc) addruart r1, r2, r3 waituart r3, r1 senduart r0, r1 busyuart r3, r1 mov pc, lr ENDPROC(putc) #else ENTRY(putc) adr r1, 1f ldmia r1, {r2, r3} add r2, r2, r1 ldr r1, [r2, r3] strb r0, [r1] mov r0, #0x03 @ SYS_WRITEC ARM( svc #0x123456 ) THUMB( svc #0xab ) mov pc, lr .align 2 1: .word _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_ - . .word semi_writec_buf(GOT) ENDPROC(putc) .bss .global semi_writec_buf .type semi_writec_buf, %object semi_writec_buf: .space 4 .size semi_writec_buf, 4 #endif
核心思想就是选中DEBUG_UNCOMPRESS, 使其编译linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/boot/compressed/debug.S, 里面会提供putc()实现,
然后用户可以在misc.c删掉“#include CONFIG_UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE”, 添加申明代码“extern void putc(int c);”, 或者选中
UNCOMPRESS_INCLUDE=linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/uncompress.h 帮我们申明
我的开机log如下:

五、其他
说起早期打印不得不提CONFIG_EARLY_PRINTK, 这个可以理解为对printch()进一步的封装, 同时归属于console框架, 具备缓存数据等后期console的所有功能,与printascii() printch()最大不同在于eraly_printk()可以打印格式参数%d, %p等, 方便调试
具体请参考另一篇博文: Linux最小系统移植之早期打印CONFIG_EARLY_PRINTK





















 6091
6091











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








