1.概述
《zabbix自动发现》server通过配置好的规则,自动添加host、group、template
《zabbix Active agent自动注册》与discovery相反,功能基本相同,active联系server,server自动添加host、group、template
以上目的都是发现host、添加host,本文的low-level discovery更底层点,用于发现item、trigger、graph等等。我们最常用如:filesystem(如/、/home、/proc、 C:、D:等),network(eth0,eth1等)
2. Discovery之文件系统
众多服务器,难免系统以及分区会有所不同。一般存在linux和windows两种系统,linux下分区有/、/data、/proc等等,windows有C:D:E:等,A服务器有/data分区,B服务器可能有/site分区。他有什么分区,我便监控什么分区,这就是low-level discovery的功能。
2.1 创建模板
创建模板A_Template_For_Discovery,…..过程省略….
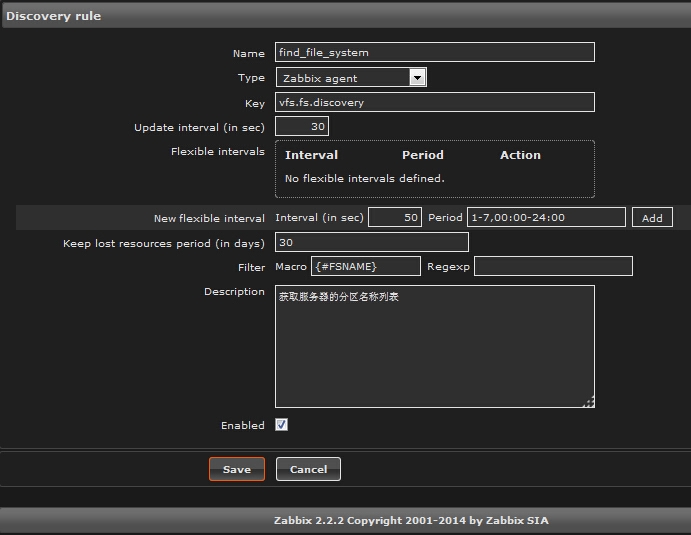
2.2 配置discovery规则
configuration>>templates>>找到模板“A_Template_For_Discovery”>>Discovery(0)>>Create discovery rule
属性说明:
Keep lost resources period(in days):数据保留天数,默认30天
Fileter:Macro为{#FSNAME},key “vfs.fs.discovery”返回json数据列表,里面内容为{#FSNAME}作为key,/、/data、C:等等作为value。 regext可以使用表达式,例如”^/data|/C:”,如果想通过{#FSTYPE}来过滤,那么Macro写{#FSTYPE},regexp写 ^(ext2|ext3|swap)$,或者引入zabbix中定义好的的正则表达式,@表达式名称。关于《zabbix正则表达式》请继续关注 ttlsa。
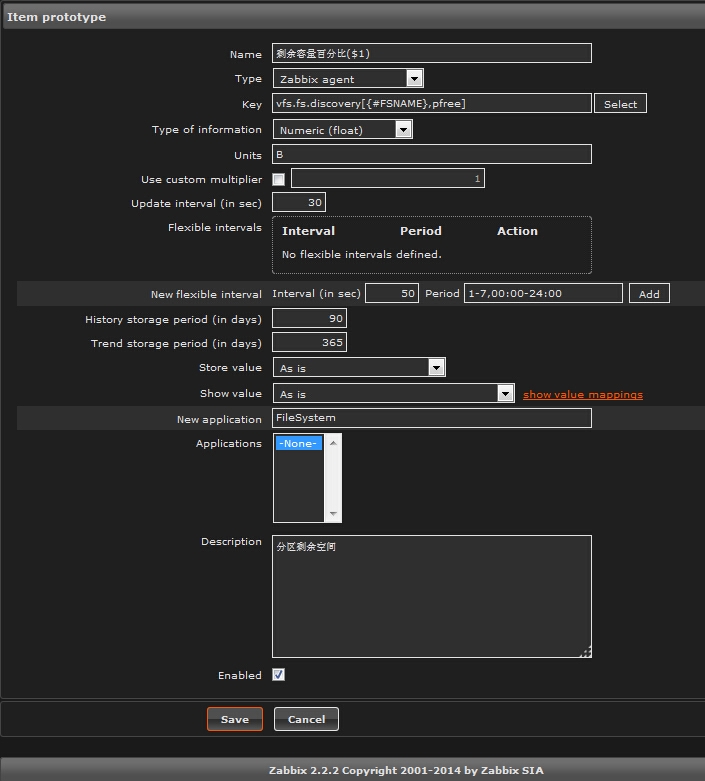
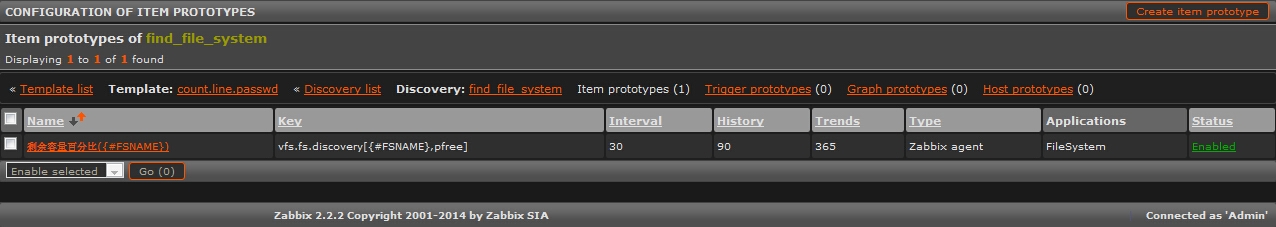
2.3 创建Item prototypes
其实就是一个创建一个item,configuration>>templates>>找到模板 “A_Template_For_Discovery”>>Discovery(1)>>find file system>>Item prototypes (0)>>create Item prototypes
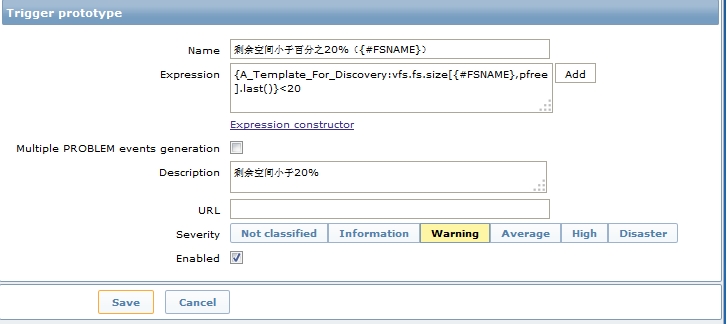
2.4 创建Trigger
当剩余量小于20%触发warnning
configuration>>templates>>找到模板 “A_Template_For_Discovery”>>Discovery(1)>>find file system>>Trigger prototypes (0)>>Create trigger prototypes
与普通的trigger区别在{#FSNAME}
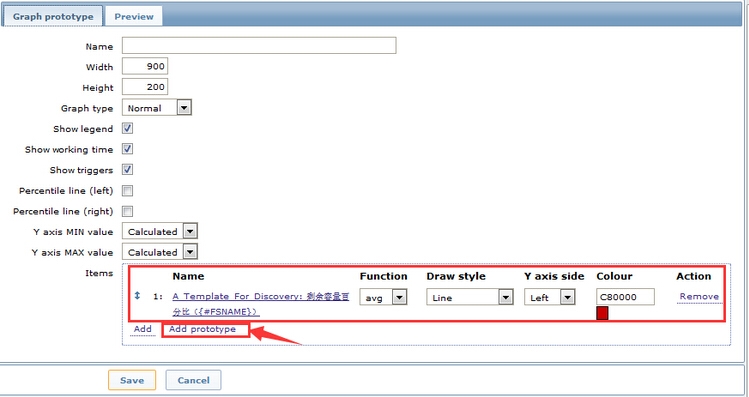
2.4 创建graph
绘制简单图表
configuration>>templates>>找到模板 “A_Template_For_Discovery”>>Discovery(1)>>find file system>>Graph prototypes (0)>>Create Graph prototypes
3. 自定义LLD规则
系统已经内建了文件系统的{#FSNAME},网络的{#IFNAME},因为业务的特殊性,我们如何定义我们自己需要的名称呢?
编写脚本,脚本输出json数据,包含key和value
脚本加入zabbix_agentd.conf UserParameter
重启zabbix_agentd
使用定义好的名称配置low-level discovery
3.1 脚本范例
#!/usr/bin/perl
$first = 1;
print "{\n";
print "\t\"data\":[\n\n";
for (`cat /proc/mounts`)
{
($fsname, $fstype) = m/\S+ (\S+) (\S+)/;
$fsname =~ s!/!\\/!g;
print "\t,\n" if not $first;
$first = 0;
print "\t{\n";
print "\t\t\"{#FSNAME}\":\"$fsname\",\n";
print "\t\t\"{#FSTYPE}\":\"$fstype\"\n";
print "\t}\n";
}
print "\n\t]\n";
print "}\n";
3.2 结果范例
执行后得到如下数据,是json格式
{ "data":[
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/",
"{#FSTYPE}":"rootfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/proc",
"{#FSTYPE}":"proc"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/sys",
"{#FSTYPE}":"sysfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/dev",
"{#FSTYPE}":"devtmpfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/dev\/pts",
"{#FSTYPE}":"devpts"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/dev\/shm",
"{#FSTYPE}":"tmpfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/",
"{#FSTYPE}":"ext4"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/proc\/bus\/usb",
"{#FSTYPE}":"usbfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/proc\/xen",
"{#FSTYPE}":"xenfs"
}
,
{
"{#FSNAME}":"\/proc\/sys\/fs\/binfmt_misc",
"{#FSTYPE}":"binfmt_misc"
}
]
}
本文转自:http://www.ttlsa.com/zabbix/zabbix-low-level-discover/
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/kaibinyuan/1630364





















 2285
2285











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








