mosaic数据增强则利用了四张图片,对四张图片进行拼接,每一张图片都有其对应的框框,将四张图片拼接之后就获得一张新的图片,同时也获得这张图片对应的框框,然后我们将这样一张新的图片传入到神经网络当中去学习,相当于一下子传入四张图片进行学习了。论文中说这极大丰富了检测物体的背景!且在标准化BN计算的时候一下子会计算四张图片的数据!如下图所示:
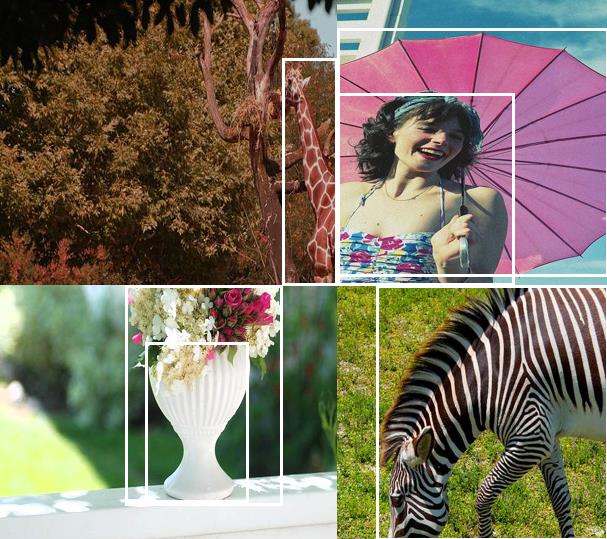

1、首先随机取四张图片
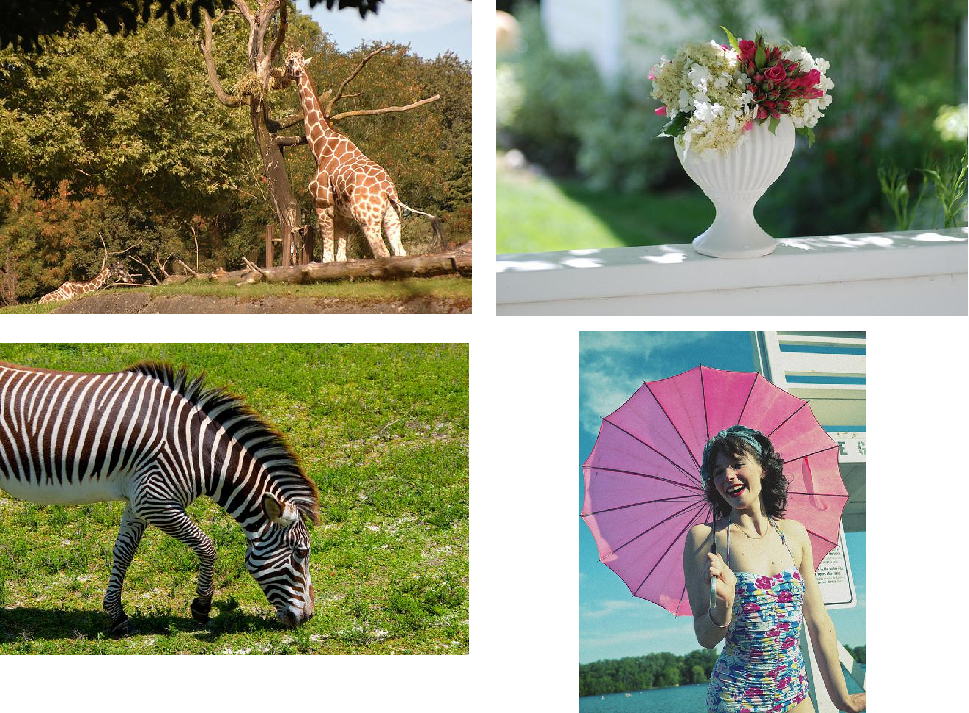

2、分别对四张图片进行数据增广操作,并分别粘贴至与最终输出图像大小相等掩模的对应位置。
操作包括:
1、翻转(对原始图片进行左右的翻转);
2、缩放(对原始图片进行大小的缩放);
3、色域变化(对原始图片的明亮度、饱和度、色调进行改变)等操作。
有两个比较关键的参数,最小偏移x, y。示例代码中设置为0.4,如:
# w = 800, h = 608
min_offset_x = 0.4
min_offset_y = 0.4
...
# 计算图像等比例缩放比例
scale_low = 1 - min(min_offset_x, min_offset_y) # 0.6
scale_high = scale_low + 0.2 # 0.8
scale = rand(scale_low, scale_high)
...
#
place_x = [0, 0, int(w * min_offset_x), int(w * min_offset_x)] # [0, 0, 320, 320]
place_y = [0, int(h * min_offset_y), int(w * min_offset_y), 0] # [0, 243, 320, 0]首先进行图像数据增强,图像缩放,之后通过它计算四个缩放、变换后图像图贴图的起始位置。分别为:[0,0], [0,243], [320,320], 320,0[]。超出范围的剪裁掉,对应的标注框进行范围的收缩,防止越界,如下图:
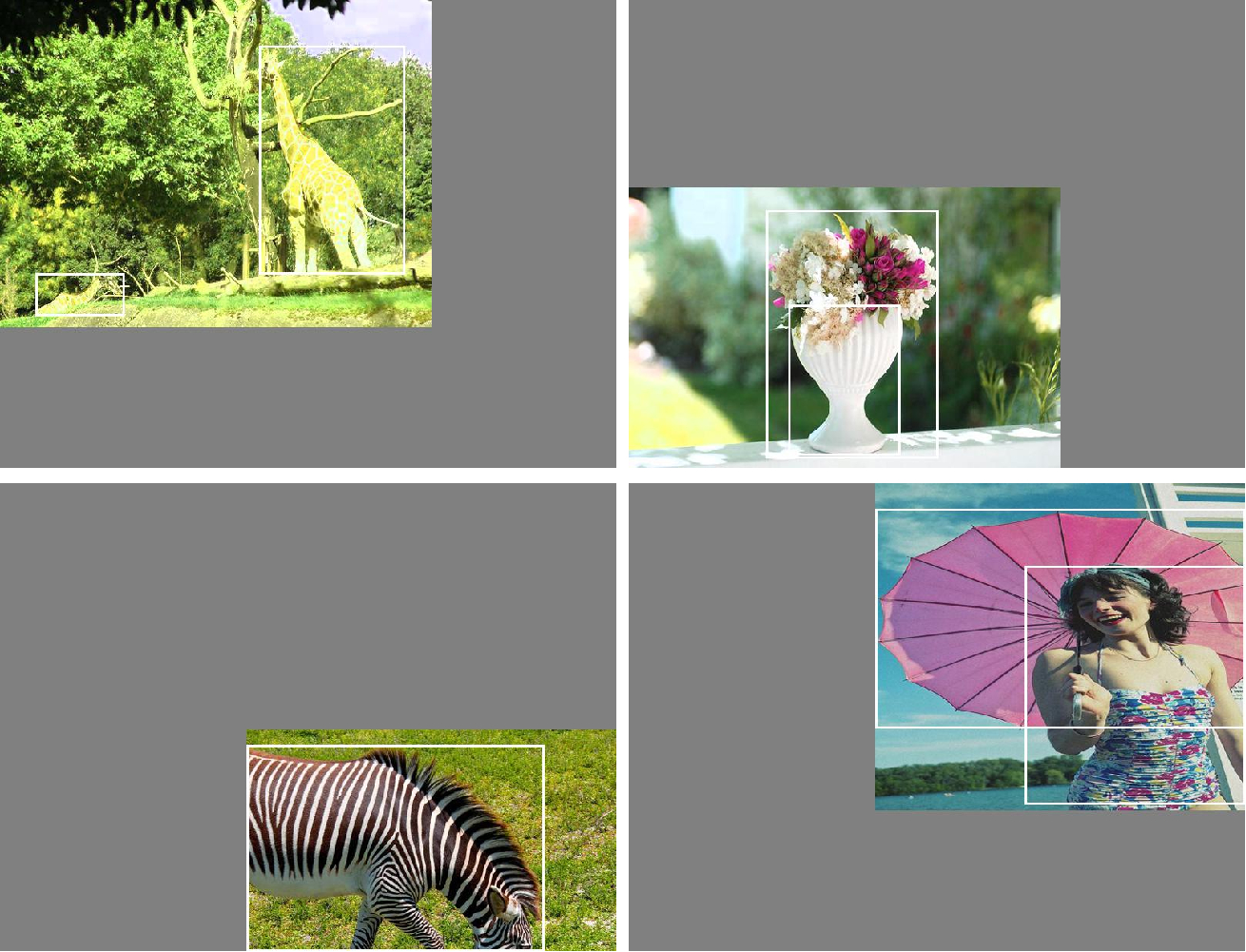

3、进行图片的组合和框的组合
完成四张图片的摆放之后,我们利用矩阵的方式将四张图片它固定的区域截取下来,然后将它们拼接起来,拼接成一 张新的图片,新的图片上含有框框等一系列的内容。

拼图时,依据min_offset_x、min_offset_y生成cutx, cuty的拼图中心坐标。也就是我们事先设置好的随机的分割线。
cutx = np.random.randint(int(w * min_offset_x), int(w * (1 - min_offset_x)))
cuty = np.random.randint(int(h * min_offset_y), int(h * (1 - min_offset_y)))对于最终拼图,按照拼图顺序后面覆盖前面图像,对应的区域被剪裁掉后,框坐标做对应处理。对于过小的目标,则丢弃掉。
测试代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf-8
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
from matplotlib.colors import rgb_to_hsv, hsv_to_rgb
def rand(a=0, b=1):
return np.random.rand() * (b - a) + a
def merge_bboxes(bboxes, cutx, cuty):
merge_bbox = []
for i in range(len(bboxes)):
for box in bboxes[i]:
tmp_box = []
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
if i == 0:
if y1 > cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if y2 - y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if x2 - x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 1:
if y2 < cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if y2 - y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if x2 - x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 2:
if y2 < cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if y2 - y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
if x2 - x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 3:
if y1 > cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if y2 - y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
if x2 - x1 < 5:
continue
tmp_box.append(x1)
tmp_box.append(y1)
tmp_box.append(x2)
tmp_box.append(y2)
tmp_box.append(box[-1])
merge_bbox.append(tmp_box)
return merge_bbox
def get_random_data(b_data, input_shape, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5):
h, w = input_shape # (540, 680)
min_offset_x = 0.4
min_offset_y = 0.4
scale_low = 1 - min(min_offset_x, min_offset_y) # 0.6
scale_high = scale_low + 0.2 # 0.8
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
place_x = [0, 0, int(w * min_offset_x), int(w * min_offset_x)] # [0, 0, 243, 243]
place_y = [0, int(h * min_offset_y), int(w * min_offset_y), 0] # [0, 216, 243, 0]
print("place:", place_x, place_y)
for i in range(4):
idx = i
img, box, img_path = b_data[i]
# print(img_path, boxes)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = Image.fromarray(img, mode="RGB")
# 图片的大小
iw, ih = image.size
# 是否翻转图片
flip = rand() < .5
if flip and len(box) > 0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0, 2]] = iw - box[:, [2, 0]]
# 对输入进来的图片进行缩放
new_ar = w / h
scale = (scale_low + scale_high) / 2
# scale = rand(scale_low, scale_high)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale * h)
nw = int(nh * new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale * w)
nh = int(nw / new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw, nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 进行色域变换
hue = rand(-hue, hue)
sat = rand(1, sat) if rand() < .5 else 1 / rand(1, sat)
val = rand(1, val) if rand() < .5 else 1 / rand(1, val)
x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image) / 255.)
x[..., 0] += hue
x[..., 0][x[..., 0] > 1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0] < 0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x > 1] = 1
x[x < 0] = 0
image = hsv_to_rgb(x)
image = Image.fromarray((image * 255).astype(np.uint8))
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
dx = place_x[index]
dy = place_y[index]
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w, h), (128, 128, 128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image) / 255
index = index + 1
box_data = []
# 对box进行重新处理,处理越界问题。
if len(box) > 0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0, 2]] = box[:, [0, 2]] * nw / iw + dx
box[:, [1, 3]] = box[:, [1, 3]] * nh / ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2] < 0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2] > w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3] > h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w > 1, box_h > 1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box), 5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
img = Image.fromarray((image_data * 255).astype(np.uint8))
for j in range(len(box_data)):
thickness = 3
left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i], outline=(255, 255, 255))
# img.show()
img.save("box_%d.jpg" % (idx + 1))
# 将图片分割,放在一起
cutx = np.random.randint(int(w * min_offset_x), int(w * (1 - min_offset_x)))
cuty = np.random.randint(int(h * min_offset_y), int(h * (1 - min_offset_y)))
new_image = np.zeros([h, w, 3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
# 对框进行进一步的处理
new_boxes = merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)
return new_image, new_boxes
def get_4_data():
data_dir = r"E:\dataset\coco128"
file_paths = [os.path.join(data_dir, v) for v in os.listdir(data_dir)]
print(file_paths)
file_paths = [v for v in file_paths if v.endswith(".jpg") and os.path.exists(v[:-4] + ".txt")]
print("label img cnt:", len(file_paths), file_paths)
if len(file_paths) < 4:
print("数据不足!")
return
batch_data = []
for img_path in file_paths:
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
gt_boxes = []
lines = []
with open(img_path[:-4] + ".txt") as fp:
for item in fp.readlines():
lines.append(item.strip().split())
lines = [v for v in lines if v]
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
for item in lines:
item = [float(v) for v in item]
[cls, cx, cy, bw, bh] = item
x1 = max(0, int((cx - bw / 2) * img_w))
y1 = max(0, int((cy - bh / 2) * img_h))
x2 = min(int((cx + bw / 2) * img_w), img_w - 1)
y2 = min(int((cy + bh / 2) * img_h), img_h - 1)
gt_boxes.append([x1, y1, x2, y2, int(cls)])
batch_data.append([img, np.array(gt_boxes), img_path])
return batch_data
if __name__ == "__main__":
batch_data = get_4_data()
image_data, box_data = get_random_data(batch_data, [608, 800])
img = Image.fromarray((image_data * 255).astype(np.uint8))
for j in range(len(box_data)):
thickness = 3
left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i], outline=(255, 255, 255))
# img.show()
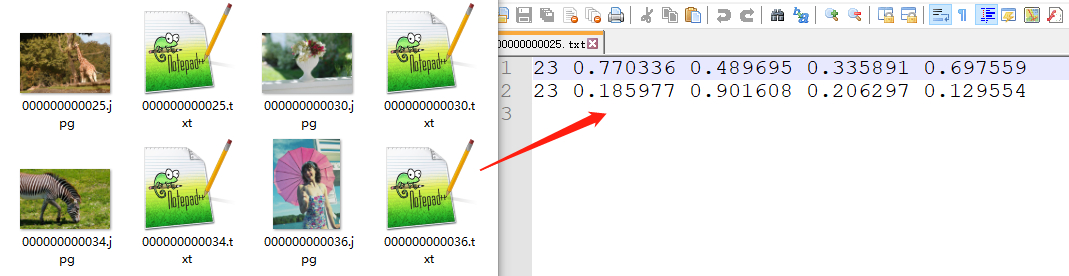
img.save("box_all.jpg")数据集格式:
coco128,标签为类别、量化至0~1后的中心点x,y、宽高。

























 905
905

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










