Derived table实际上是一种特殊的subquery,它位于SQL语句中FROM子句里面,可以看做是一个单独的表。MySQL5.7之前的处理都是对Derived table进行Materialize,生成一个临时表保存Derived table的结果,然后利用临时表来协助完成其他父查询的操作,比如JOIN等操作。MySQL5.7中对Derived table做了一个新特性。该特性允许将符合条件的Derived table中的子表与父查询的表合并进行直接JOIN。下面我们看一下DBT-3中的一条被新特性优化过的执行计划:
SELECT t2.o_clerk, t1.price - t2.o_totalprice
FROM
(SELECT l_orderkey, SUM( l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) price
FROM lineitem GROUP by l_orderkey) t1
JOIN
(SELECT o_clerk, o_orderkey, o_totalprice
FROM orders
WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1995-01-01' AND '1995-12-31') t2
ON t1.l_orderkey = t2.o_orderkey WHERE t1.price > t2.o_totalprice;
MySQL5.6执行计划如下图所示(下图通过WorkBench的Visual Explain直观的对执行计划进行了展示):
对应的explain输出结果为:
ID SELECT_TYPE TABLE TYPEPOSSIBLE_KEYSKEY KEY_LENREF ROWS EXTRA
1PRIMARY ALL NULL NULLNULLNULL 4812318 NULL
1PRIMARY ref 4t2.o_orderkey599860 Using where; Using index
3DERIVED ordersALL i_o_orderdateNULLNULLNULL 15000000 Using where
2DERIVED lineitemindexPRIMARY, i_l_shipdate, …PRIMARY8NULL 59986052NULL
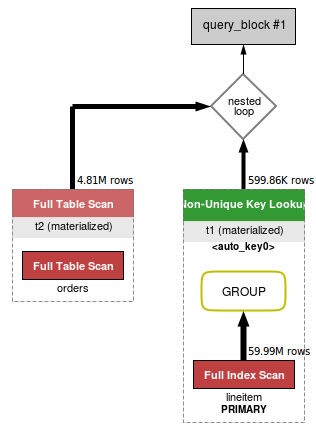
MySQL5.7 Merge derived table特性应用之后,执行计划变成了如下所示:

同样explain的输出结果为:
ID SELECT_TYPETABLE PARTITIONS TYPEPOSSIBLE_KEYS KEY KEY_LENREF ROWS FILTEREDEXTRA
1PRIMARY NULL ALL NULL NULLNULLNULL59986052100.00 NULL
1PRIMARY orders NULL eq_refPRIMARY, i_o_orderdatePRIMARY4 t1.l_orderkey110.69 Using where
2DERIVED lineitemNULL indexPRIMARY, i_l_shipdate, …PRIMARY8 NULL59986052100.00 NULL
可以看到orders已经从Derived table的子表里面merge到了父查询中,尽而简化了执行计划,同时也提高了执行效率。看一下MySQL5.6与MySQL5.7对于上面的DBT-3中的这条Query执行性能的对比图:

Merge Derived table有两种方式进行控制。第一种,通过开关optimizer_switch=’derived_merge=on|off’来进行控制。第二种,在CREATE VIEW的时候指定ALGORITHM=MERGE | TEMPTABLE, 默认是MERGE方式。如果指定是TEMPTABLE,将不会对VIEW进行Merge Derived table操作。只要Derived table里不包含如下条件就可以利用该特性进行优化:
UNION clause
GROUP BY
DISTINCT
Aggregation
LIMIT or OFFSET
Derived table里面包含用户变量的设置。
那么Merge Derived table在MySQL中是如何实现的呢?下面我们分析一下源码。
对于Derived table的merge过程是在MySQL的resolve阶段完成的,这意味着对于Merge操作是永久性的,经过resolve阶段之后就不会再对Derived table进行其他的变换。执行的简单流程如下:
SELECT_LEX::prepare
|
TABLE_LIST::resolve_derived // 这里首先递归对每个Derived table自身进行变换,经过变换后的Derived table开始考虑和最外层的父查询进行Merge
|
SELECT_LEX::merge_derived // 将Derived table与父查询进行Merge
下面我们重点研究一下merge_derived这个函数实现过程:
bool SELECT_LEX::merge_derived(THD *thd, TABLE_LIST *derived_table)
{
DBUG_ENTER("SELECT_LEX::merge_derived");
// 这里首先会判断是不是Derived table(这里view看做是带有名字的Derived table),同时也会看该Derived table是否已经被合并过了
if (!derived_table->is_view_or_derived() || derived_table->is_merged())
DBUG_RETURN(false);
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *const derived_unit= derived_table->derived_unit();
// A derived table must be prepared before we can merge it
DBUG_ASSERT(derived_unit->is_prepared());
LEX *const lex= parent_lex;
// Check whether the outer query allows merged views
if ((master_unit() == lex->unit && // 只会在父查询进行merge Derived table操作。
// 这里会查看当前命令是否需要进行merge操作,比如CREATE VIEW,SHOW CREATE VIEW等。如果需要再继续
!lex->can_use_merged()) ||
lex->can_not_use_merged())
DBUG_RETURN(false);
// 查看当前的Derived table是否满足merge条件
if (!derived_unit->is_mergeable() ||
derived_table->algorithm == VIEW_ALGORITHM_TEMPTABLE ||
(!thd->optimizer_switch_flag(OPTIMIZER_SWITCH_DERIVED_MERGE) &&
derived_table->algorithm != VIEW_ALGORITHM_MERGE))
DBUG_RETURN(false);
SELECT_LEX *const derived_select= derived_unit->first_select();
/*
当前不会对包含 STRAIGHT_JOIN,且Derived table中包含semi-join的query进行merge操作。
这是因为MySQL为了保证正确性,必须先做semi-join之后才可以与其他表继续做JOIN。
例如:select straight_join * from tt , (select * from tt where a in (select a from t1)) as ttt;
*/
if ((active_options() & SELECT_STRAIGHT_JOIN) && derived_select->has_sj_nests)
DBUG_RETURN(false);
...
// 利用Nested_join结构来辅助处理OUTER-JOIN的情况。如果Derived table是OUTER-JOIN的内表,需要将Derived table中的每个表设置为JOIN的时候可以为空。具体请参考propagate_nullability。
if (!(derived_table->nested_join=
(NESTED_JOIN *) thd->mem_calloc(sizeof(NESTED_JOIN))))
DBUG_RETURN(true); /* purecov: inspected */
// 这里确保NESTED_JOIN结构是空的,在构造函数处理比较合适
derived_table->nested_join->join_list.empty();
// 该函数会将所有Derived table中的表merge到NESTED_JOIN结构体中
if (derived_table->merge_underlying_tables(derived_select))
DBUG_RETURN(true); /* purecov: inspected */
// 接下来需要将Derived table中的所有表连接到父查询的table_list列表中,进而将Derived table从父查询中剔除。
for (TABLE_LIST **tl= &leaf_tables; *tl; tl= &(*tl)->next_leaf)
{
if (*tl == derived_table)
{
for (TABLE_LIST *leaf= derived_select->leaf_tables; leaf;
leaf= leaf->next_leaf)
{
if (leaf->next_leaf == NULL)
{
leaf->next_leaf= (*tl)->next_leaf;
break;
}
}
*tl= derived_select->leaf_tables;
break;
}
}
// 下面会对父查询的所有相关数据结构进行重新计算,进而包含所有从Derived table merge之后的表的相关信息。
leaf_table_count+= (derived_select->leaf_table_count - 1);
derived_table_count+= derived_select->derived_table_count;
materialized_derived_table_count+=
derived_select->materialized_derived_table_count;
has_sj_nests|= derived_select->has_sj_nests;
partitioned_table_count+= derived_select->partitioned_table_count;
cond_count+= derived_select->cond_count;
between_count+= derived_select->between_count;
// Propagate schema table indication:
// @todo: Add to BASE options instead
if (derived_select->active_options() & OPTION_SCHEMA_TABLE)
add_base_options(OPTION_SCHEMA_TABLE);
// Propagate nullability for derived tables within outer joins:
if (derived_table->is_inner_table_of_outer_join())
propagate_nullability(&derived_table->nested_join->join_list, true);
select_n_having_items+= derived_select->select_n_having_items;
// 将Derived table的where条件合并到父查询
if (derived_table->merge_where(thd))
DBUG_RETURN(true); /* purecov: inspected */
// 将Derived table的结构从父查询中删除
derived_unit->exclude_level();
// 这里用来禁止对Derived table的继续访问
derived_table->set_derived_unit((SELECT_LEX_UNIT *)1);
// 建立对Derived table需要获取的列的引用。在后续函数中会对引用列进行相关处理,请参考函数setup_natural_join_row_types函数
if (derived_table->create_field_translation(thd))
DBUG_RETURN(true);
// 将Derived table中的列或者表的重命名合并到父查询
merge_contexts(derived_select);
repoint_contexts_of_join_nests(derived_select->top_join_list);
// 因为已经把Derived table中包含的表merge到了父查询,所以需要对TABLE_LIST中的表所在的位置进行重新定位。
remap_tables(thd);
// 将Derived table合并到父查询之后,需要重新修改原来Derived table中所有对Derived table中所有列的引用,
fix_tables_after_pullout(this, derived_select, derived_table, table_adjust);
// 如果Derived table中包含ORDER By语句,处理原则和正常SubQuery的处理方式类似:
// 1. 如果Derived table只包含一个表
// 2. 并且Derived table不包含聚集函数
// 满足上述两个条件之后,Derived table将会保留ORDER BY。其他情况subquery中的ORDER BY将会被忽略掉,这也是MySQL5.7区别于MySQL5.6的一点。
// 当Derived table保留了Order by,是否能合并到父查询,需要满足如下条件:
// 1. 父查询允许做Derived table中的ORDER BY。下面几种情况不允许做ORDER BY
// a) 如果父查询包含有自己的ORDER BY
// b) 如果父查询包含GROUP BY
// c) 如果父查询包含未被优化掉的DISTINCT
// 2. 父查询不能是UNION操作,因为UNION默认会做DISTINCT操作
// 3. 为了简化操作,只有当父查询只包含Derived table的时候(即FROM子句里面只有Derived table一个表)才可以保留ORDER BY。这里有相当大的改进空间可以尽量的来按照Derived table定义的ORDER BY操作来进行父查询的操作。比如有两个表以上,如果父查询没有ORDER BY的要求,也可以按照Derived table来对结果进行排序。
if (derived_select->is_ordered())
{
if ((lex->sql_command == SQLCOM_SELECT ||
lex->sql_command == SQLCOM_UPDATE ||
lex->sql_command == SQLCOM_DELETE) &&
!(master_unit()->is_union() ||
is_grouped() ||
is_distinct() ||
is_ordered() ||
get_table_list()->next_local != NULL))
order_list.push_back(&derived_select->order_list);
}
// 对于Derived table中包含的full-text functions需要添加到父查询的查询列表中。
if (derived_select->ftfunc_list->elements &&
add_ftfunc_list(derived_select->ftfunc_list))
DBUG_RETURN(true); /* purecov: inspected */
DBUG_RETURN(false);
}
综上所述,本篇文章简要的分析了MySQL Merge Derived table的作用以及实现方式。Merge Derived table的引入可以有效的提升Subquery query的执行效率,更重要的是为以后应对复杂查询提供了新的优化手段。





















 336
336











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








