
根据两种情况来看区别
一.首次计划执行的时间早于当前的时间
1.schedule方法
“fixed-delay”:如果第一次执行时间被延迟了,随后的执行时间按照上一次实际执行完成的时间点进行计算
演示:
public classDifferenceTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//规定时间格式
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//获取当前的具体时间
Calendar calendar =Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time is:" +sf.format(calendar.getTime()));//设置成6秒前的时间,若当前时间为2019-04-22 15:44:50//那么设置之后的时间变成2019-04-22 15:44:44
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6);
Timer timer= newTimer();//第一次执行时间为6秒前,之后每隔两秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule(newTimerTask() {
@Overridepublic voidrun() {//打印当前的计划执行时间
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is:" +sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(),2000);
}
}
执行效果:
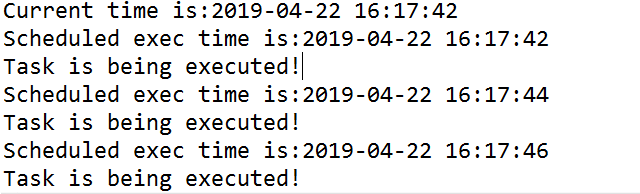
2.scheduleAtFixedRate方法
“fixed-rate”;如果第一次执行时间被延迟了,随后的执行时间按照上一次开始的时间点进行计算,
并且为了赶上进度会多次执行任务,因此TimerTask中的执行体需要考虑同步。
演示:
public classDifferenceTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//规定时间格式
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//获取当前的具体时间
Calendar calendar =Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time is:" +sf.format(calendar.getTime()));//设置成6秒前的时间,若当前时间为2019-04-22 15:44:50//那么设置之后的时间变成2019-04-22 15:44:44
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6);
Timer timer= newTimer();//第一次执行时间为6秒前,之后每隔两秒钟执行一次
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(newTimerTask() {
@Overridepublic voidrun() {//打印当前的计划执行时间
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is:" +sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(),2000);
}
}
执行效果如下:
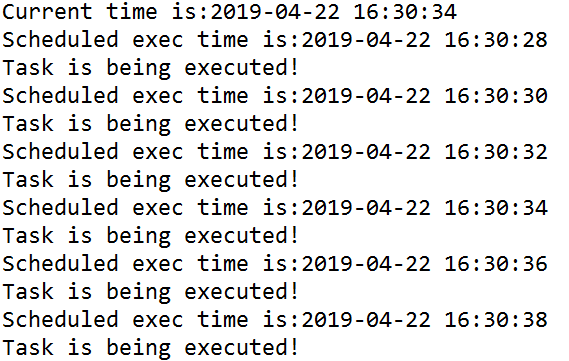
如图,因为设置了每隔2s执行一次,第一次执行时间比当前时间提早了6s,所以它会从原定最早的时间,先直接执行三次,来追上现在的进度。
二.任务执行时间超出执行周期间隔
1.schedule方法
下一次执行时间相对于上一次实际执行完成的时间点,因此执行时间会不断延后。
演示:
public classDifferenceTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//规定时间格式
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//获取当前的具体时间
Calendar calendar =Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time is:" +sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
Timer timer= newTimer();//第一次执行时间为6秒前,之后每隔两秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule(newTimerTask() {
@Overridepublic voidrun() {try{
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {//TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//打印当前的计划执行时间
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is:" +sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task executes!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(),2000);
}
}
执行结果:
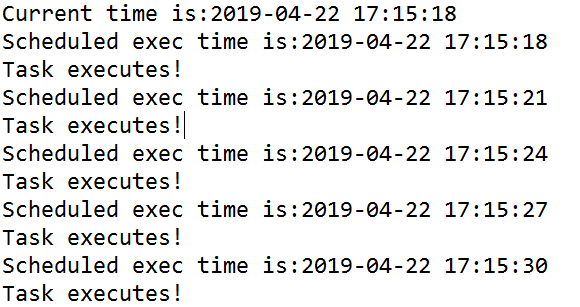
用sleep,模拟执行任务时间为三秒,大于任务间隔时间。
2.scheduleAtFixedRate方法
下一次执行时间相对于上一次开始的时间点,因此执行时间一般不会延后,因此存在并发性。
演示:
public classDifferenceTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//规定时间格式
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//获取当前的具体时间
Calendar calendar =Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time is:" +sf.format(calendar.getTime()));
Timer timer= newTimer();//第一次执行时间为6秒前,之后每隔两秒钟执行一次
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(newTimerTask() {
@Overridepublic voidrun() {try{
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {//TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//打印当前的计划执行时间
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is:" +sf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task executes!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(),2000);
}
}
执行结果如下:
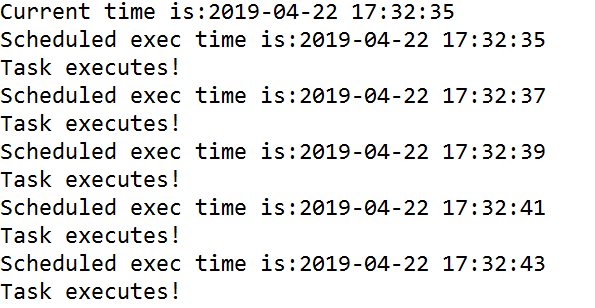
不会被任务执行所需要时间影响。




















 2139
2139











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








