sklearn中的SVM以及使用多项式特征以及核函数
sklearn中的SVM的使用
SVM的理论部分
需要注意的是,使用SVM算法,和KNN算法一样,都是需要做数据标准化的处理才可以,因为不同尺度的数据在其中的话,会严重影响SVM的最终结果
(在notebook中)
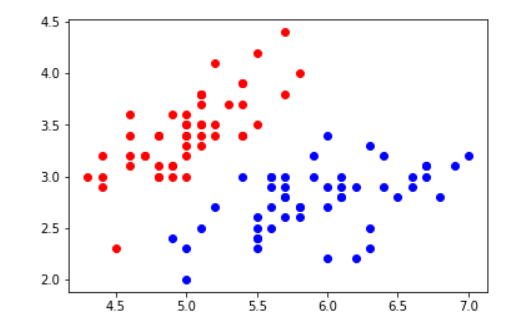
加载好需要的包,使用鸢尾花数据集,为了方便可视化,只取前两个特征,然后将其绘制出来
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X = X[y<2,:2]
y = y[y<2]
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1],color='red')
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1],color='blue')
图像如下
首先进行数据的标准化的操作,实例化并fit操作,然后对x进行transform操作,传入x_standard,这样就完成了标准化的操作
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X,y)
X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)
在标准化以后就可以调用SVM算法了,对于线性的SVM,可以直接使用LinearSVC类,然后实例化操作,在进行fit,设置C为10的九次方
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
svc = LinearSVC(C=1e9)
svc.fit(X_standard,y)
使用先前的绘制函数并绘制图像
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0,x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0],axis[1],int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1),
np.linspace(axis[2],axis[3],int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1)
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(),x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A', '#FFF59D&








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








