
后端有时候rm,会出现一些问题。
这里作为一个子问题,讨论一下rm之后,发生的一些事。
打开rm源码:
[qianzichen@dev03v /src/app/coreutils/coreutils-8.21]$ vi src/rm.c从main函数开始:
intmain (int argc, char **argv){ ... while ((c = getopt_long (argc, argv, "dfirvIR", long_opts, NULL)) != -1) { switch (c) { case 'f': x.interactive = RMI_NEVER; break; ... } } ... enum RM_status status = rm (file, &x);}首先解析命令行参数,然后调用了rm:
enum RM_status status = rm (file, &x);作者把rm函数的实现从rm.c中抽了出来,放在remove.c中:
/* Remove FILEs, honoring options specified via X. Return RM_OK if successful. */enum RM_statusrm (char *const *file, struct rm_options const *x) { enum RM_status rm_status = RM_OK; if (*file) { FTS *fts = xfts_open (file, bit_flags, NULL); while (1) { ... } }...}file参数是一个只读指针数组,代表要删除的文件名列表,x参数的结构定义如下,存储从命令行中解析后的rm的选项。
struct rm_options{ /* If true, ignore nonexistent files. */ bool ignore_missing_files; /* If true, query the user about whether to remove each file. */ enum rm_interactive interactive;... /* If true, recursively remove directories. */ bool recursive; bool require_restore_cwd;};当file列表存在时,rm调用xfts_open:
FTS *xfts_open (char * const *argv, int options, int (*compar) (const FTSENT **, const FTSENT **)){ FTS *fts = fts_open (argv, options | FTS_CWDFD, compar); if (fts == NULL) {... return fts;}xfts_open返回fts_open的有效返回值。fts_open的实现如下:
FTS *fts_open (char * const *argv, register int options, int (*compar) (FTSENT const **, FTSENT const **)){ register FTS *sp; /* Options check. */ /* Allocate/initialize the stream */ /* Initialize fts_cwd_fd. */ sp->fts_cwd_fd = AT_FDCWD; if ( ISSET(FTS_CWDFD) && ! HAVE_OPENAT_SUPPORT) { int fd = open (".", O_SEARCH | (ISSET (FTS_NOATIME) ? O_NOATIME : 0)); /* * Start out with 1K of file name space, and enough, in any case, * to hold the user's file names. */ /* Allocate/initialize root's parent. */ if (*argv != NULL) { if ((parent = fts_alloc(sp, "", 0)) == NULL) goto mem2; parent->fts_level = FTS_ROOTPARENTLEVEL; } /* Allocate/initialize root(s). */ for (root = NULL, nitems = 0; *argv != NULL; ++argv, ++nitems) { /* * If comparison routine supplied, traverse in sorted * order; otherwise traverse in the order specified. */ if (compar) { p->fts_link = root; root = p; } else { p->fts_link = NULL; if (root == NULL) tmp = root = p; else { tmp->fts_link = p; tmp = p; } } } if (compar && nitems > 1) root = fts_sort(sp, root, nitems);... if (!ISSET(FTS_NOCHDIR) && !ISSET(FTS_CWDFD) && (sp->fts_rfd = diropen (sp, ".")) < 0) SET(FTS_NOCHDIR); i_ring_init (&sp->fts_fd_ring, -1); return (sp);mem3: fts_lfree(root);... return (NULL);}引用中已去除了一些Error handling,可以看出主要是获取文件系统的一些信息,保存在FTS结构中,FTS结构定义如下:
typedef struct { struct _ftsent *fts_cur; /* current node */ int (*fts_compar) (struct _ftsent const **, struct _ftsent const **); /* compare fn */... int fts_options; /* fts_open options, global flags */ struct hash_table *fts_leaf_optimization_works_ht; union {... struct cycle_check_state *state; } fts_cycle; I_ring fts_fd_ring;} FTS;再回到rm函数,它将在一个loop中通过fts_read读取文件系统信息,并缓存在ent中:
rm (char *const *file, struct rm_options const *x) { enum RM_status rm_status = RM_OK; if (*file) { FTS *fts = xfts_open (file, bit_flags, NULL); while (1) { ent = fts_read (fts); enum RM_status s = rm_fts (fts, ent, x); } }...}ent的结构比较大,这里不展开了。
再通过rm_fts对某一个ent进行操作,这里我们rm的是一个regular file,所以控制结构会执行到FTS_F分支下,最终调用execise。
static enum RM_statusrm_fts (FTS *fts, FTSENT *ent, struct rm_options const *x){ switch (ent->fts_info) { case FTS_D: /* preorder directory */ if (s == RM_OK && is_empty_directory == T_YES) { /* When we know (from prompt when in interactive mode) that this is an empty directory, don't prompt twice. */ s = excise (fts, ent, x, true); fts_skip_tree (fts, ent); } ... } case FTS_F: /* regular file */ { bool is_dir = ent->fts_info == FTS_DP || ent->fts_info == FTS_DNR; enum RM_status s = prompt (fts, ent, is_dir, x, PA_REMOVE_DIR, NULL); if (s != RM_OK) return s; return excise (fts, ent, x, is_dir); } ... }}这里再次忽略一些容错和优化,execise最终调用了unlinkat
static enum RM_statusexcise (FTS *fts, FTSENT *ent, struct rm_options const *x, bool is_dir){ int flag = is_dir ? AT_REMOVEDIR : 0; if (unlinkat (fts->fts_cwd_fd, ent->fts_accpath, flag) == 0) { if (x->verbose) { printf ((is_dir ? _("removed directory: %s\n") ... } return RM_OK; } ...}如上我们看出,rm最终调用了unlinkat这一核心函数,比如,删除a.txt:
unlinkat(AT_FDCWD, "a.txt", 0)用户态rm调用了C库中的unlinkat,经查找,其声明是在中
#ifdef __USE_ATFILE/* Remove the link NAME relative to FD. */extern int unlinkat (int __fd, const char *__name, int __flag) __THROW __nonnull ((2));#endif/* Remove the directory PATH. */extern int rmdir (const char *__path) __THROW __nonnull ((1));用户态进程只要调用unlink函数就可以了,具体unlinkat函数的实现是由glibc
提供的,其定义在io/unlink.c中:
* Remove the link named NAME. */int__unlink (name) const char *name;{ if (name == NULL) { __set_errno (EINVAL); return -1; } __set_errno (ENOSYS); return -1; }stub_warning (unlink)weak_alias (__unlink, unlink)额好吧,这儿是个弱符号,真正的实现在./sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/unlinkat.c
.../* Remove the link named NAME. */intunlinkat (fd, file, flag) int fd; const char *file; int flag;{ int result;#ifdef __NR_unlinkat# ifndef __ASSUME_ATFCTS if (__have_atfcts >= 0)# endif { result = INLINE_SYSCALL (unlinkat, 3, fd, file, flag);# ifndef __ASSUME_ATFCTS if (result == -1 && errno == ENOSYS) __have_atfcts = -1; else# endif return result; } char *buf = NULL; }... INTERNAL_SYSCALL_DECL (err); if (flag & AT_REMOVEDIR) result = INTERNAL_SYSCALL (rmdir, err, 1, file); else result = INTERNAL_SYSCALL (unlink, err, 1, file);...}syscall的name为__NR_##name,通过宏中字符串粘合而得本例中的__NR_unlinkat。其定义在/usr/include/asm/unistd_64.h中。
#ifndef _ASM_X86_UNISTD_64_H#define _ASM_X86_UNISTD_64_H 1#define __NR_read 0#define __NR_write 1...#define __NR_newfstatat 262#define __NR_unlinkat 263...#define __NR_kexec_file_load 320#define __NR_userfaultfd 323#endif /* _ASM_X86_UNISTD_64_H */所以该宏被启用。
/* The *at syscalls were introduced just after 2.6.16-rc1. Due to the way the kernel versions are advertised we can only rely on 2.6.17 to have the code. On PPC they were introduced in 2.6.17-rc1, on SH in 2.6.19-rc1. */#if __LINUX_KERNEL_VERSION >= 0x020611 \ && (!defined __sh__ || __LINUX_KERNEL_VERSION >= 0x020613)# define __ASSUME_ATFCTS 1#endif显然可以看出,若kernel版本在2.6.17之后,__ASSUME_ATFCTS宏被启用。无需校验__have_atfcts >= 0,直接调用INLINE_SYSCALL (unlinkat, 3, fd, file, flag)。
这里直接看底层实现吧(./sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/x86_64/sysdep.h),是一段内联汇编:
# undef INLINE_SYSCALL_TYPES# define INLINE_SYSCALL_TYPES(name, nr, args...) \ ({ \ unsigned long int resultvar = INTERNAL_SYSCALL_TYPES (name, , nr, args); \ if (__builtin_expect (INTERNAL_SYSCALL_ERROR_P (resultvar, ), 0)) \ { \ __set_errno (INTERNAL_SYSCALL_ERRNO (resultvar, )); \ resultvar = (unsigned long int) -1; \ } \ (long int) resultvar; })# undef INTERNAL_SYSCALL_DECL# define INTERNAL_SYSCALL_DECL(err) do { } while (0)# define INTERNAL_SYSCALL_NCS(name, err, nr, args...) \ ({ \ unsigned long int resultvar; \ LOAD_ARGS_##nr (args) \ LOAD_REGS_##nr \ asm volatile ( \ "syscall\n\t" \ : "=a" (resultvar) \ : "0" (name) ASM_ARGS_##nr : "memory", "cc", "r11", "cx"); \ (long int) resultvar; })# undef INTERNAL_SYSCALL# define INTERNAL_SYSCALL(name, err, nr, args...) \ INTERNAL_SYSCALL_NCS (__NR_##name, err, nr, ##args)# define INTERNAL_SYSCALL_NCS_TYPES(name, err, nr, args...) \在syscall之前先将参数传入寄存器。返回值在eax寄存器中,通常0表示成功。
从C库代码上来看,就是这么实现了的,rm实用程序调用glibc,然后再到汇编syscall -> kernel
但是当前机器安装的不一定是upstream的C库。
我们还是来亲眼看一下最终机器码是如何实现的吧,我这里直接反汇编一下:
[qianzichen@dev03v /usr/lib64]$ objdump -D -S libc.so.6 > /tmp/libc.txt[qianzichen@dev03v /usr/lib64]$ cd /tmp[qianzichen@dev03v /tmp]$ grep -A12 'unlinkat' libc.txt 00000000000e9c00 : e9c00: 48 63 d2 movslq %edx,%rdx e9c03: 48 63 ff movslq %edi,%rdi e9c06: b8 07 01 00 00 mov $0x107,%eax e9c0b: 0f 05 syscall e9c0d: 48 3d 00 f0 ff ff cmp $0xfffffffffffff000,%rax e9c13: 77 02 ja e9c17 0x17> e9c15: f3 c3 repz retq e9c17: 48 8b 15 4a 12 2d 00 mov 0x2d124a(%rip),%rdx # 3bae68 <_dynamic> e9c1e: f7 d8 neg %eax e9c20: 64 89 02 mov %eax,%fs:(%rdx) e9c23: 48 83 c8 ff or $0xffffffffffffffff,%rax e9c27: c3 retq e9c28: 0f 1f 84 00 00 00 00 nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1) e9c2f: 00 00000000000e9c30 <rmdir>: e9c30: b8 54 00 00 00 mov $0x54,%eax e9c35: 0f 05 syscall [qianzichen@dev03v /tmp]$这里可以看到glibc-2.17最终使用了一些AT&T syntax Assembly language。
先用一个比较新的指令movslq,把第一个寄存器扩展到64位并复制到第二个寄存器中,不填充符号位。
下一步,将0x107这个值载入eax寄存器
随后,调用syscall指令。
打开Intel的相关芯片手册,搜索“syscall”,找到相关描述如下图。
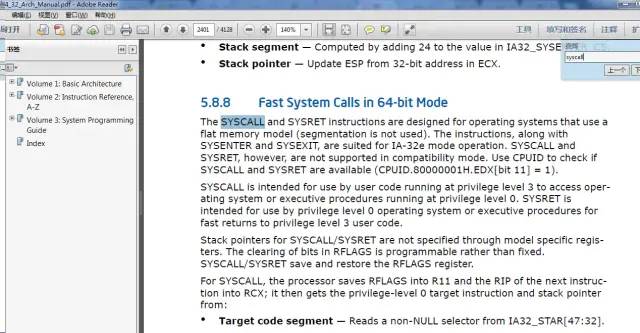
从这段描述中看出,syscall是Intel对64位处理器做的优化,被设计用来为操作系统提供一个平面内存模式,我的当前64位机器,syscall/sysret就和32位体系上的sysenter/sysexit的作用相似,可能和旧平台的int 80中断类似,主要是将CPU运行级别从level 3升级为level 0,操作一些应用层无法访问的资源。
从"Use CPUID to check if SYSCALL and SYSRET are available (CPUID.80000001H.EDX[bit 11] = 1)"这一句可以看出,在调用前需要置edx寄存器中的11位来使能64位平台的syscall/sysret,好的我们找出edx寄存器相关。

之前操作edx寄存器,就是“使能bit 11位和bit 29”这种准备工作。
我们确定了,unlinkat是一个system call,rm实用程序将删除文件的任务交给操作系统,至此程序陷入内核态。
好的,我们现在到kernel下,直接搜索unlinkat:
[qianzichen@dev03v /src/linux/linux]$ grep unlinkat ./ -rn./arch/parisc/include/uapi/asm/unistd.h:297:#define __NR_unlinkat (__NR_Linux + 281)./arch/parisc/kernel/syscall_table.S:379: ENTRY_SAME(unlinkat)./arch/m32r/include/uapi/asm/unistd.h:309:#define __NR_unlinkat 301./arch/m32r/kernel/syscall_table.S:303: .long sys_unlinkat./arch/sparc/include/uapi/asm/unistd.h:358:#define __NR_unlinkat 290./arch/sparc/kernel/systbls_32.S:78:/*290*/ .long sys_unlinkat, ./arch/ia64/include/uapi/asm/unistd.h:279:#define __NR_unlinkat 1287./arch/ia64/kernel/entry.S:1695: data8 sys_unlinkat./arch/ia64/kernel/fsys.S:815: data8 0 // unlinkat./arch/alpha/include/uapi/asm/unistd.h:420:#define __NR_unlinkat 456./arch/alpha/kernel/systbls.S:477: .quad sys_unlinkat..../arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_32.tbl:310:301 i386 unlinkat sys_unlinkat./arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl:272:263 common unlinkat sys_unlinkat...[qianzichen@dev03v /src/linux/linux]$直接看x86体系下的源码:
[qianzichen@dev03v /src/linux/linux]$ vi arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl这是一个列表文件,
## 64-bit system call numbers and entry vectors## The format is:# ## The abi is "common", "64" or "x32" for this file.#0 common read sys_read...261 common futimesat sys_futimesat262 common newfstatat sys_newfstatat263 common unlinkat sys_unlinkat264 common renameat sys_renameat265 common linkat sys_linkat...## x32-specific system call numbers start at 512 to avoid cache impact# for native 64-bit operation.#512 x32 rt_sigaction compat_sys_rt_sigaction...这里看出,unlinkat对应的number是263
还记得写入eax寄存器中的值吗,是0x107。
很显然,0x107 = 1 * 16 ^ 2 + 0 * 16 ^ 1 + 7 * 16 ^ 0 = 263
common代表32/64位平台通用
user space 和 kernel space 的 system call 映射建立。
其实kernel space对编号的映射不是这么简单,这里不再展开。
我们大概知道 user space 的 unlinkat 最终在 kernel space 的 entry point 是 sys_unlinkat 就好了。
还是直接查看汇编代码吧:
[qianzichen@dev03v /src/linux/linux]$ vi arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S...ENTRY(entry_SYSCALL_64) /* * Interrupts are off on entry. * We do not frame this tiny irq-off block with TRACE_IRQS_OFF/ON, * it is too small to ever cause noticeable irq latency. */ SWAPGS_UNSAFE_STACK movq %rsp, PER_CPU_VAR(rsp_scratch) movq PER_CPU_VAR(cpu_current_top_of_stack), %rsp TRACE_IRQS_OFF /* Construct struct pt_regs on stack */ pushq $__USER_DS... ja 1f /* return -ENOSYS (already in pt_regs->ax) */ movq %r10, %rcx /* * This call instruction is handled specially in stub_ptregs_64. * It might end up jumping to the slow path. If it jumps, RAX * and all argument registers are clobbered. */ call *sys_call_table(, %rax, 8)...END(entry_SYSCALL_64)rax中存的就是这次syscall的num,即__NR_unlinkat。
ENTRY(entry_SYSCALL_64)是64位的 syscall 汇编入口点,在准备一系列寄存器之后,call *sys_call_table(, %rax, 8)将跳转到系统调用表中的偏移地址,也就是sys_call_table数组中下标为syscall num对应的函数。
sys_call_table在另一个文件中定义,这里用到了一点编译器扩展和预编译技术的一种高效用法,这里也不再展开。
/* System call table for x86-64. */...#define __SYSCALL_64_QUAL_(sym) sym#define __SYSCALL_64_QUAL_ptregs(sym) ptregs_##sym#define __SYSCALL_64(nr, sym, qual) extern asmlinkage long __SYSCALL_64_QUAL_##qual(sym)(unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);#include #undef __SYSCALL_64#define __SYSCALL_64(nr, sym, qual) [nr] = __SYSCALL_64_QUAL_##qual(sym),extern long sys_ni_syscall(unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);asmlinkage const sys_call_ptr_t sys_call_table[__NR_syscall_max+1] = { /* * Smells like a compiler bug -- it doesn't work * when the & below is removed. */ [0 ... __NR_syscall_max] = &sys_ni_syscall,#include <asm/syscalls_64.h>};什么时候建立syscall number和sys_unlinkat的映射呢?这要看,这个头文件是一个过程文件,在编译时生成。原映射信息就是从上文提到的./arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl中获得。
编译出来的syscalls_64.h结果为:
__SYSCALL_COMMON(49, sys_bind, sys_bind)__SYSCALL_COMMON(50, sys_listen, sys_listen)...__SYSCALL_COMMON(263, sys_unlinkat, sys_unlinkat)__SYSCALL_COMMON就是__SYSCALL_64,如上文述sys_call_table的定义,第一个__SYSCALL_64的定义是为了将syscalls_64.h展开为函数声明,之后将__SYSCALL_64重新定义后,是为了将syscalls_64.h展开为数组成员的定义。
所以最终内核得到的,是一个只读的sys_call_table数组,下标为syscall number,指向的是内核的sys_call_ptr_t。syscall num从0开始,所以直接根据263就可以找到sys_unlinkat。
现在内核已经确定了要调用的是sys_unlinkat,那么这个函数在哪里定义的呢?经过我的一番尝试,4.9中直接找sys_unlinkat是找不到实现的,因为这个字符串可能经过预编译粘合。
我最终找到的宏是这样定义的:
...#define SYSCALL_DEFINE1(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(1, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINE2(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(2, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINE3(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(3, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINE4(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(4, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINE5(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(5, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINE6(name, ...) SYSCALL_DEFINEx(6, _##name, __VA_ARGS__)#define SYSCALL_DEFINEx(x, sname, ...) \ SYSCALL_METADATA(sname, x, __VA_ARGS__) \ __SYSCALL_DEFINEx(x, sname, __VA_ARGS__)#define __PROTECT(...) asmlinkage_protect(__VA_ARGS__)#define __SYSCALL_DEFINEx(x, name, ...) \ asmlinkage long sys##name(__MAP(x,__SC_DECL,__VA_ARGS__)) \ __attribute__((alias(__stringify(SyS##name)))); \ static inline long SYSC##name(__MAP(x,__SC_DECL,__VA_ARGS__)); \ asmlinkage long SyS##name(__MAP(x,__SC_LONG,__VA_ARGS__)); \ asmlinkage long SyS##name(__MAP(x,__SC_LONG,__VA_ARGS__)) \ { \ long ret = SYSC##name(__MAP(x,__SC_CAST,__VA_ARGS__)); \ __MAP(x,__SC_TEST,__VA_ARGS__); \ __PROTECT(x, ret,__MAP(x,__SC_ARGS,__VA_ARGS__)); \ return ret; \ } \ static inline long SYSC##name(__MAP(x,__SC_DECL,__VA_ARGS__))asmlinkage long sys32_quotactl(unsigned int cmd, const char __user *special,...然后找到,sys_unlinkat的代码在fs/namei.c中:
4078 SYSCALL_DEFINE3(unlinkat, int, dfd, const char __user *, pathname, int, flag)4079 {4080 if ((flag & ~AT_REMOVEDIR) != 0)4081 return -EINVAL;4082 4083 if (flag & AT_REMOVEDIR)4084 return do_rmdir(dfd, pathname);4085 4086 return do_unlinkat(dfd, pathname);4087 }然后调用do_unlinkat:
3999 /*4000 * Make sure that the actual truncation of the file will occur outside its4001 * directory's i_mutex. Truncate can take a long time if there is a lot of4002 * writeout happening, and we don't want to prevent access to the directory4003 * while waiting on the I/O.4004 */4005 static long do_unlinkat(int dfd, const char __user *pathname)4006 {4007 int error;4008 struct filename *name;4009 struct dentry *dentry;4010 struct path path;4011 struct qstr last;4012 int type;4013 struct inode *inode = NULL;4014 struct inode *delegated_inode = NULL;4015 unsigned int lookup_flags = 0;4016 retry:4017 name = filename_parentat(dfd, getname(pathname), lookup_flags,4018 &path, &last, &type);4019 if (IS_ERR(name))4020 return PTR_ERR(name);4021 4022 error = -EISDIR;4023 if (type != LAST_NORM)4024 goto exit1;4025 4026 error = mnt_want_write(path.mnt);4027 if (error)4028 goto exit1;4029 retry_deleg:4030 inode_lock_nested(path.dentry->d_inode, I_MUTEX_PARENT);4031 dentry = __lookup_hash(&last, path.dentry, lookup_flags);4032 error = PTR_ERR(dentry);4033 if (!IS_ERR(dentry)) {4034 /* Why not before? Because we want correct error value */4035 if (last.name[last.len])4036 goto slashes;inode = dentry->d_inode;4038 if (d_is_negative(dentry))4039 goto slashes;4040 ihold(inode);4041 error = security_path_unlink(&path, dentry);4042 if (error)4043 goto exit2;4044 error = vfs_unlink(path.dentry->d_inode, dentry, &delegated_inode);4045 exit2:4046 dput(dentry);4047 }4048 inode_unlock(path.dentry->d_inode);4049 if (inode)4050 iput(inode); /* truncate the inode here */4051 inode = NULL;4052 if (delegated_inode) {4053 error = break_deleg_wait(&delegated_inode);4054 if (!error)4055 goto retry_deleg;4056 }4057 mnt_drop_write(path.mnt);4058 exit1:4059 path_put(&path);4060 putname(name);4061 if (retry_estale(error, lookup_flags)) {4062 lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_REVAL;4063 inode = NULL;4064 goto retry;4065 }4066 return error;4067 4068 slashes:4069 if (d_is_negative(dentry))4070 error = -ENOENT;4071 else if (d_is_dir(dentry))4072 error = -EISDIR;4073 else4074 error = -ENOTDIR;4075 goto exit2;4076 }好了,读者随着我到这一步,已经看到了软件工程中比较具有美感的一个地方:4044行,调用了vfs_unlink。从user space到system call再至此,sys_unlinkat将unlinkat的任务,dispatch给操作系统的虚拟文件系统。
我们看一下vfs_unlink的实现:
3941 /**3942 * vfs_unlink - unlink a filesystem object3943 * @dir: parent directory3944 * @dentry: victim3945 * @delegated_inode: returns victim inode, if the inode is delegated.3946 *3947 * The caller must hold dir->i_mutex.3948 *3949 * If vfs_unlink discovers a delegation, it will return -EWOULDBLOCK and3950 * return a reference to the inode in delegated_inode. The caller3951 * should then break the delegation on that inode and retry. Because3952 * breaking a delegation may take a long time, the caller should drop3953 * dir->i_mutex before doing so.3954 *3955 * Alternatively, a caller may pass NULL for delegated_inode. This may3956 * be appropriate for callers that expect the underlying filesystem not3957 * to be NFS exported.3958 */3959 int vfs_unlink(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, struct inode **delegated_inode)3960 {3961 struct inode *target = dentry->d_inode;3962 int error = may_delete(dir, dentry, 0);3963 3964 if (error)3965 return error;3966 3967 if (!dir->i_op->unlink)3968 return -EPERM;3969 3970 inode_lock(target);3971 if (is_local_mountpoint(dentry))3972 error = -EBUSY;3973 else {3974 error = security_inode_unlink(dir, dentry);3975 if (!error) {3976 error = try_break_deleg(target, delegated_inode);3977 if (error)3978 goto out;3979 error = dir->i_op->unlink(dir, dentry);3980 if (!error) {3981 dont_mount(dentry);3982 detach_mounts(dentry);3983 }}3985 }3986 out:3987 inode_unlock(target);3988 3989 /* We don't d_delete() NFS sillyrenamed files--they still exist. */3990 if (!error && !(dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_NFSFS_RENAMED)) {3991 fsnotify_link_count(target);3992 d_delete(dentry);3993 }3994 3995 return error;3996 }3997 EXPORT_SYMBOL(vfs_unlink);我们看到,3979行,调用inode实例中i_op成员的unlink函数指针,这个指针才指向了真正的HAL层实现。
现在看inode结构的定义:
/* * Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for * the RCU path lookup and 'stat' data) fields at the beginning * of the 'struct inode' */struct inode { umode_t i_mode;... const struct inode_operations *i_op; struct super_block *i_sb; /* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */ unsigned long i_ino;...#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */ struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *i_fsnotify_marks;#endif#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION) struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info;#endif void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */};可以看到上文的inode实例中的i_op成员是一个inode_operations结构指针。
现在看inode_operations的定义:
struct inode_operations { struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);... int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool); int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *); int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *); int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);...} ____cacheline_aligned;vfs下层的各种文件系统,需要按照inode_operations中的规范,完成unlink的实现,向kernel vfs注册。
这里不展开bootloader自举之后的硬件初始化,也忽略kernel接管机器资源之后的一些register机制,直接看当前机器是怎么向vfs最终注册。
看了一下,我机器上挂载的是ext4文件系统,直接看ext4的unlink的最终注册过程:
...3845 /*3846 * directories can handle most operations...3847 */3848 const struct inode_operations ext4_dir_inode_operations = {...3851 .link = ext4_link,3852 .unlink = ext4_unlink,3853 .symlink = ext4_symlink,...3865 }ext4_dir_inode_operations实例中,完成了函数指针的赋值。
直接看ext4_unlink的实现:
static int ext4_unlink(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry){ int retval; struct inode *inode; struct buffer_head *bh; struct ext4_dir_entry_2 *de; handle_t *handle = NULL; if (unlikely(ext4_forced_shutdown(EXT4_SB(dir->i_sb)))) return -EIO; trace_ext4_unlink_enter(dir, dentry); /* Initialize quotas before so that eventual writes go * in separate transaction */ retval = dquot_initialize(dir); if (retval) return retval; retval = dquot_initialize(d_inode(dentry)); if (retval) return retval; retval = -ENOENT; bh = ext4_find_entry(dir, &dentry->d_name, &de, NULL); if (IS_ERR(bh)) return PTR_ERR(bh); if (!bh) goto end_unlink; inode = d_inode(dentry); retval = -EFSCORRUPTED; if (le32_to_cpu(de->inode) != inode->i_ino) goto end_unlink; handle = ext4_journal_start(dir, EXT4_HT_DIR, EXT4_DATA_TRANS_BLOCKS(dir->i_sb)); if (IS_ERR(handle)) { retval = PTR_ERR(handle); handle = NULL; goto end_unlink; } if (IS_DIRSYNC(dir)) ext4_handle_sync(handle); if (inode->i_nlink == 0) { ext4_warning_inode(inode, "Deleting file '%.*s' with no links",dentry->d_name.len, dentry->d_name.name); set_nlink(inode, 1); } retval = ext4_delete_entry(handle, dir, de, bh); if (retval) goto end_unlink; dir->i_ctime = dir->i_mtime = current_time(dir); ext4_update_dx_flag(dir); ext4_mark_inode_dirty(handle, dir); drop_nlink(inode); if (!inode->i_nlink) ext4_orphan_add(handle, inode); inode->i_ctime = current_time(inode); ext4_mark_inode_dirty(handle, inode);end_unlink: brelse(bh); if (handle) ext4_journal_stop(handle); trace_ext4_unlink_exit(dentry, retval); return retval;}看d_inode的实现:
static inline struct inode *d_inode(const struct dentry *dentry){ return dentry->d_inode;}d_inode(dentry)将inode信息从dentry结构中取出来,dentry结构定义如下:
struct dentry { /* RCU lookup touched fields */... struct qstr d_name; struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is... union { struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */ struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */ struct rcu_head d_rcu; } d_u;};dentry这一层,不是简单的从硬盘中移除。为了高性能,当前ext4对目录做了一些缓存处理。应该是先设置标志位,然后根据sync机制回写存储。
vfs之下的机制就先不详述了,蛤蛤。
***
Linkerist
2018年1月19日于北京酒仙桥





















 597
597











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








