- 本文是对 Matlab 中 polyfit 函数进行原理解析,并没介绍该如何具体使用 polyfit 函数,具体方法请自行查阅官方文档。
- 主要涉及数值分析的相关内容。
- 简单介绍了数据标准化(Z-score 标准化)、QR 分解、Matlab 中的求逆运算符。
- 相对详细介绍了线性方程组求解的稳定性问题,并引出条件数的定义。
- 最后根据 polyfit 的源码对它进行计算流程解析,并分析相关的警告该如何处理。
预备知识
标准化
对向量
其中
-
标准分数(standard score)也叫 Z分数(Z-score);
为
- Z分数表示原始数据与平均值的差,单位为标准差,也就时给定值距离均值多少个标准差。
QR 分解定理
设
注:正交矩阵
求逆运算
Y = inv(X) 计算方阵
X^(-1)等效于inv(X)。x = Ab的计算方式与x = inv(A)*b不同,建议用于求解线性方程组。
方程组求解的稳定性
设线性方程组
由
考虑相对误差:
即
条件数
- 称
为
的条件数;
- 表示
变化时解的相对误差灵敏度的度量;
- 当
较小时,解对
的扰动不敏感。
注:
polyfit 函数原理
polyfit 使用一维向量
m = length(x) 行的范德蒙(Vandermonde)矩阵
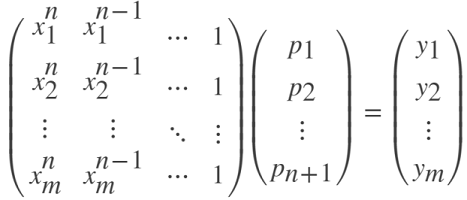
拟合多项式
polyfit 先对
具体过程如下:
p = R(Q'*y)。
异常处理逻辑
共以下4种情况
MATLAB:polyfit:XYSizeMismatchMATLAB:polyfit:PolyNotUniqueMATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPointsMATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPointsOrRescale
输入判断
polyfit函数只用于拟合(x,y)型二维数据,因此输入数据应是两两对应的,即向量长度相等(见源码43-45行)。
- 若提示
MATLAB:polyfit:XYSizeMismatch,请检查上述问题。
欠定方程
- 若提示
MATLAB:polyfit:PolyNotUnique表示线性方程组欠定(矩阵
的列数大于行数)
考虑
- 添加更多的不同的拟合点;
- 减少多项式的次数.
条件数过大
由于 Vandermonde 矩阵中的列是向量
[P,S,MU] = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) 才执行数据标准化(见源码50-53行)。
当
- 若提示
MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPoints,考虑添加更多的不同的拟合点 - 若提示
MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPointsOrRescale,考虑1、添加更多的不同的拟合点;2、减少多项式的次数
源码阅读
function [p,S,mu] = polyfit(x,y,n)
%POLYFIT Fit polynomial to data.
% P = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) finds the coefficients of a polynomial P(X) of
% degree N that fits the data Y best in a least-squares sense. P is a
% row vector of length N+1 containing the polynomial coefficients in
% descending powers, P(1)*X^N + P(2)*X^(N-1) +...+ P(N)*X + P(N+1).
%
% [P,S] = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) returns the polynomial coefficients P and a
% structure S for use with POLYVAL to obtain error estimates for
% predictions. S contains fields for the triangular factor (R) from a QR
% decomposition of the Vandermonde matrix of X, the degrees of freedom
% (df), and the norm of the residuals (normr). If the data Y are random,
% an estimate of the covariance matrix of P is (Rinv*Rinv')*normr^2/df,
% where Rinv is the inverse of R.
%
% [P,S,MU] = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) finds the coefficients of a polynomial in
% XHAT = (X-MU(1))/MU(2) where MU(1) = MEAN(X) and MU(2) = STD(X). This
% centering and scaling transformation improves the numerical properties
% of both the polynomial and the fitting algorithm.
%
% Warning messages result if N is >= length(X), if X has repeated, or
% nearly repeated, points, or if X might need centering and scaling.
%
% Example: simple linear regression with polyfit
%
% % Fit a polynomial p of degree 1 to the (x,y) data:
% x = 1:50;
% y = -0.3*x + 2*randn(1,50);
% p = polyfit(x,y,1);
%
% % Evaluate the fitted polynomial p and plot:
% f = polyval(p,x);
% plot(x,y,'o',x,f,'-')
% legend('data','linear fit')
%
% Class support for inputs X,Y:
% float: double, single
%
% See also POLY, POLYVAL, ROOTS, LSCOV.
% Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
if ~isequal(size(x),size(y))
error(message('MATLAB:polyfit:XYSizeMismatch'))
end
x = x(:);
y = y(:);
if nargout > 2
mu = [mean(x); std(x)];
x = (x - mu(1))/mu(2);
end
% Construct the Vandermonde matrix V = [x.^n ... x.^2 x ones(size(x))]
V(:,n+1) = ones(length(x),1,class(x));
for j = n:-1:1
V(:,j) = x.*V(:,j+1);
end
% Solve least squares problem p = Vy to get polynomial coefficients p.
[Q,R] = qr(V,0);
oldws = warning('off','all'); % Turn all warnings off before solving
try
p = R(Q'*y); % Same as p = Vy
catch ME
warning(oldws); % Restore initial warning state
throw(ME);
end
warning(oldws); % Restore initial warning state
% Issue warnings.
if size(R,2) > size(R,1)
warning(message('MATLAB:polyfit:PolyNotUnique'))
elseif warnIfLargeConditionNumber(R)
if nargout > 2
warning(message('MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPoints'));
else
warning(message('MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPointsOrRescale'));
end
end
if nargout > 1
r = y - V*p;
% S is a structure containing three elements: the triangular factor
% from a QR decomposition of the Vandermonde matrix, the degrees of
% freedom and the norm of the residuals.
S.R = R;
S.df = max(0,length(y) - (n+1));
S.normr = norm(r);
end
p = p.'; % Polynomial coefficients are row vectors by convention.
function flag = warnIfLargeConditionNumber(R)
if isa(R, 'single')
flag = (condest(R) > 1e+05);
else
flag = (condest(R) > 1e+10);
end参考资料
- Matlab inv
- Matlab @polyfit
- Stoer J, Bulirsch R. Introduction to Numerical Analysis[M]. Third Edition. New York, NY: Springer, 2002.
- 我的原始语雀文档




















 850
850











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








