题目
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
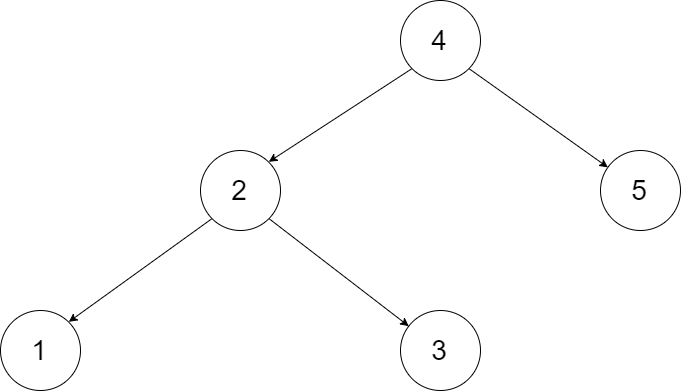
Let's take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:
We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
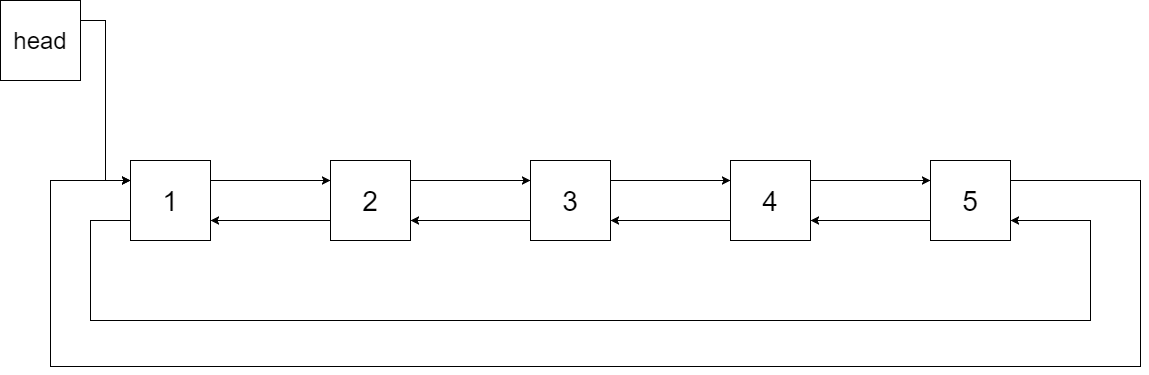
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The "head" symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
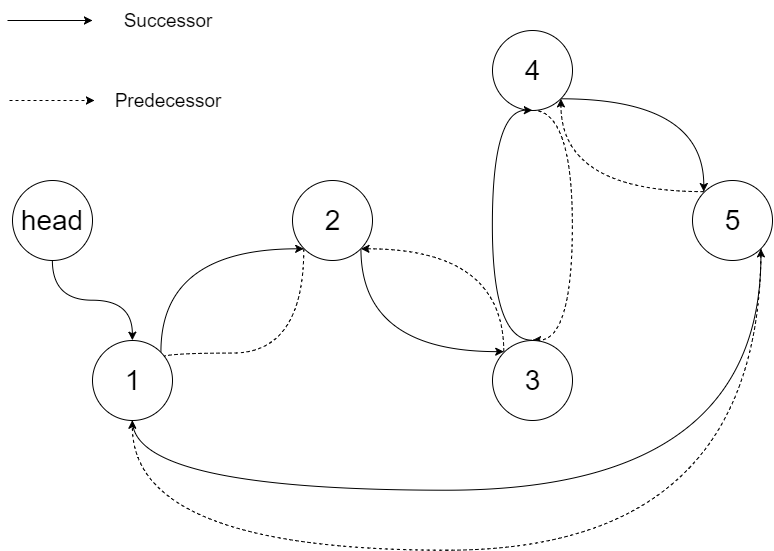
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
代码
法一 。分治法。递归。中序遍历。
跟二叉搜索树有关的题,肯定要利用其性质,即左<根<右,即左子结点值小于根结点值小于右子结点值。而且十有八九都得用中序遍历来解,因为中序遍历的顺序就是左根右啊,跟性质吻合。
我们观察原二叉搜索树中结点4连接着结点2和结点5,而在双向链表中,连接的是结点3和结点5,这就是为啥我们要用中序遍历了,因为只有中序遍历,结点3之后才会遍历到结点4,这时候我们可以将结点3和结点4串起来。
决定了用中序遍历之后,就要考虑是迭代还是递归的写法,博主建议写递归的,一般写起来都比较简洁,而且递归是解树类问题的神器啊,十有八九都是用递归,一定要熟练掌握。再写中序遍历之前,其实还有难点,因为我们需要把相邻的结点连接起来,所以我们需要知道上一个遍历到的结点是什么,所以用一个变量pre,来记录上一个遍历到的结点。
还需要一个变量head,来记录最左结点,这样的话,在递归函数中,先判空,之后对左子结点调用递归,这样会先一直递归到最左结点,此时如果head为空的话,说明当前就是最左结点,赋值给head和pre,对于之后的遍历到的结点,那么可以和pre相互连接上,然后pre赋值为当前结点node,再对右子结点调用递归即可。
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
Node *head = NULL, *pre = NULL;
inorder(root, pre, head);
pre->right = head;
head->left = pre;
return head;
}
void inorder(Node* node, Node*& pre, Node*& head) {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node->left, pre, head);
if (!head) {
head = node;
pre = node;
} else {
pre->right = node;
node->left = pre;
pre = node;
}
inorder(node->right, pre, head);
}
};法二 。分治法。递归。pre引用节点。中序遍历。 最后追溯到最左节点。(推荐)
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
if(!pRootOfTree) return nullptr;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
Core(pRootOfTree,pre);
while(pRootOfTree->left)
{
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree->left;
}
return pRootOfTree;
}
//中序遍历。递归。
void Core(TreeNode* root,TreeNode*& pre)
{
if(!root) return;//终止
//左
Core(root->left,pre);
if(pre)
{
pre->right=root;
root->left=pre;
}
//根
pre =root;
//右
Core(root->right,pre);
}
};
法3。分治法,顾名思义,就是把一项任务分成两半,用相同的逻辑去分别处理,之后再粘合起来。混合排序Merge Sort用的也是这种思路。那么我们可以对左右子结点调用递归函数,suppose我们得到了两个各自循环的有序双向链表,然后我们把根结点跟左右子结点断开,将其左右指针均指向自己,这样就形成了一个单个结点的有序双向链表,虽然只是个光杆司令,但人家仍然是有序双向链表。那么此时我们只要再写一个连接两个有序双向链表的子函数,就可以将这三个有序双向链表按顺序链接起来了。
而链接两个有序双向链表的子函数也简单,首先判空,若一个为空,则返回另一个。如果两个都不为空,则把第一个链表的尾结点的右指针链上第二个链表的首结点,同时第二个链表的首结点的左指针链上第一个链表的尾结点。同理,把第二个链表的尾结点的右指针链上第一个链表的首结点,同时第一个链表的首结点的左指针链上第二个链表的尾结点。
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
Node *leftHead = treeToDoublyList(root->left);
Node *rightHead = treeToDoublyList(root->right);
root->left = root;
root->right = root;
return connect(connect(leftHead, root), rightHead);
}
Node* connect(Node* node1, Node* node2) {
if (!node1) return node2;
if (!node2) return node1;
Node *tail1 = node1->left, *tail2 = node2->left;
tail1->right = node2;
node2->left = tail1;
tail2->right = node1;
node1->left = tail2;
return node1;
}
};






















 909
909

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








