1.课题概述
基于偏微分方程离散化计算的地下换热器建模与温度检测,模拟这个不锈钢圆桶中土壤的温度场和湿度场。
2.系统仿真结果
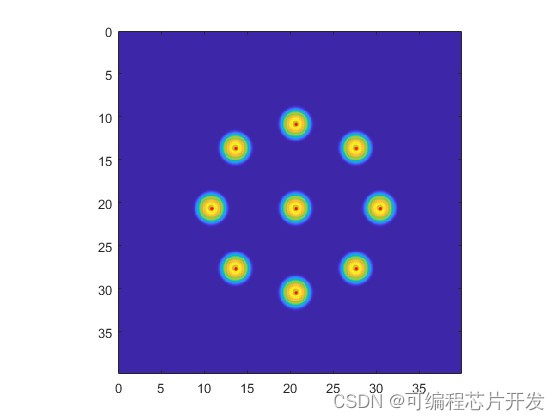
3.核心程序与模型
版本:MATLAB2022a
MM_updata = Model_Matrix;
Model_Matrix = Signal_Check;
ij2 = mod(ij-1,time2)+1;
Signal_Checks(Index0)= 0;
MM_updatas = Model_Matrixs;
Model_Matrixs = Signal_Checks;
%矩阵赋值,乘以一个增益因子25.
if ij2<=time4
if check1
Model_Matrix(index) = abs(waves1(:,ij2)');
else
waves1(:,ij2)=25*Model_Matrix(index)';
end
end
if mod(ij,time2)==(time4+1)
check1=~check1;
waves1 =-fliplr(waves1);
end
%矩阵赋值,乘以一个增益因子25.
if ij2<=time4
if check1
Model_Matrixs(index) = abs(waves1s(:,ij2)');
else
waves1s(:,ij2)=25*Model_Matrixs(index)';
end
end
if mod(ij,time2)==(time4+1)
check1=~check1;
waves1s =-fliplr(waves1s);
end
if mod(ij,25) == 0
set(figmatrix,'CData',Model_Matrix);%减去初始温度,使得显示效果明显
axis equal;
drawnow;
axis([0,dx*(LenX-1),0,dx*(LenY-1)]);
pause(1);
end
%定义不同深度下的温度
SX = LenX/2;
SY = LenY/2;
tmp1s = [tmp1s,mean(mean(Model_Matrix(SX-20:SX+20,SY-20:SY+20)))+initial_tmp];
%检测位置1
tmp2s = [tmp2s,mean(mean(Model_Matrix(SX-100:SX-60,SY-100:SY-60)))+initial_tmp];
%检测位置2
tmp3s = [tmp3s,mean(mean(Model_Matrix(SX+30:SX+80,SY+30:SY+80)))+initial_tmp];
%检测位置3
tmp4s = [tmp4s,mean(mean(Model_Matrix(SX-150:SX-40,SY+50:SY+150)))+initial_tmp];
%定义不同分层下的湿度
[XS,YS] = find(abs(Model_Matrixs)>0.1);
Model_Matrixs1 = Model_Matrixs;
for jj = 1:length(XS)
Model_Matrixs1(XS(jj),YS(jj))= 0;
end
tmp1ss = [tmp1ss,mean(mean(Model_Matrixs1))+initial_sd];
[XS,YS] = find(abs(Model_Matrixs)>0.2);
Model_Matrixs2 = Model_Matrixs;
for jj = 1:length(XS)
Model_Matrixs2(XS(jj),YS(jj))= 0;
end
tmp2ss = [tmp2ss,mean(mean(Model_Matrixs2))+initial_sd];
[XS,YS] = find(abs(Model_Matrixs)>0.3);
Model_Matrixs3 = Model_Matrixs;
for jj = 1:length(XS)
Model_Matrixs3(XS(jj),YS(jj))= 0;
end
tmp3ss = [tmp3ss,mean(mean(Model_Matrixs3))+initial_sd];
[XS,YS] = find(abs(Model_Matrixs)>0.4);
Model_Matrixs4 = Model_Matrixs;
for jj = 1:length(XS)
Model_Matrixs4(XS(jj),YS(jj))= 0;
end
tmp4ss = [tmp4ss,mean(mean(Model_Matrixs4))+initial_sd];
end
figure;
subplot(121);
plot(tmp1s,'r','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp2s,'b','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp3s,'m','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp4s,'g','linewidth',2);
hold on
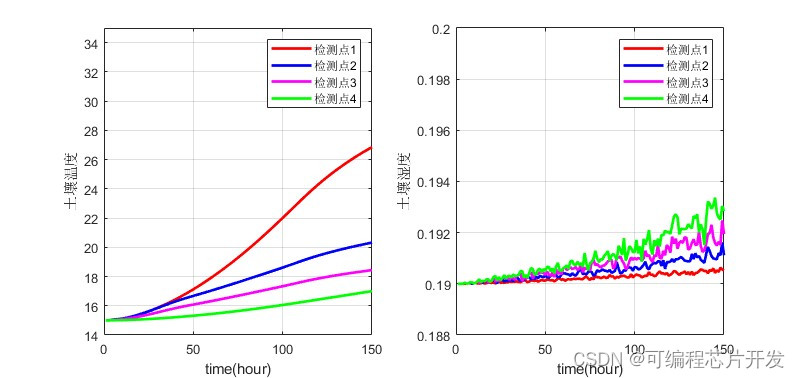
xlabel('time(hour)');
ylabel('土壤温度');
grid on
legend('检测点1','检测点2','检测点3','检测点4');
axis([0,150,14,35]);
subplot(122);
plot(tmp1ss,'r','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp2ss,'b','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp3ss,'m','linewidth',2);
hold on
plot(tmp4ss,'g','linewidth',2);
hold on
xlabel('time(hour)');
ylabel('土壤湿度');
grid on
legend('检测点1','检测点2','检测点3','检测点4');
axis([0,150,0.188,0.20]);
02_028m
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
4.系统原理简介
地下换热器是地源热泵系统中的关键组件,它通过与地下岩土的热交换来实现建筑空间的供暖和制冷。为了优化地下换热器的设计和运行,需要对其传热过程进行精确建模,并对温度分布进行实时监测。
4.1地下换热器的建模
基于上述离散化方程,可以建立地下换热器的数值模型。模型需要考虑地下换热器的几何形状、岩土的热物性参数(如热导率、比热容等)、地下水流速和温度等因素。

4.2温度检测技术
为了验证模型的准确性并优化地下换热器的运行策略,需要对实际运行中的地下换热器进行温度检测。常用的温度检测方法包括热电偶测温法、红外测温法和光纤测温法等。





















 1055
1055

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








