model.train()和model.eval()用法和区别
1.1 model.train()
model.train()的作用是启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout。
如果模型中有BN层(Batch Normalization)和Dropout,需要在训练时添加model.train()。model.train()是保证BN层能够用到每一批数据的均值和方差。对于Dropout,model.train()是随机取一部分网络连接来训练更新参数。
1.2 model.eval()
model.eval()的作用是不启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout。
如果模型中有BN层(Batch Normalization)和Dropout,在测试时添加model.eval()。model.eval()是保证BN层能够用全部训练数据的均值和方差,即测试过程中要保证BN层的均值和方差不变。对于Dropout,model.eval()是利用到了所有网络连接,即不进行随机舍弃神经元。
训练完train样本后,生成的模型model要用来测试样本。在model(test)之前,需要加上model.eval(),否则的话,有输入数据,即使不训练,它也会改变权值。这是model中含有BN层和Dropout所带来的的性质。
在做one classification的时候,训练集和测试集的样本分布是不一样的,尤其需要注意这一点。
封装好的代码块如下
- Batch Normalization 和 Dropout 在代码中的使用
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64*10*10, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = self.bn1(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = self.bn2(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = F.relu(self.conv3(x))
x = self.bn3(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = x.view(-1, 64*10*10)
x = F.dropout(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
- 在Gpu上训练 模型初始化 定义损失函数和优化器
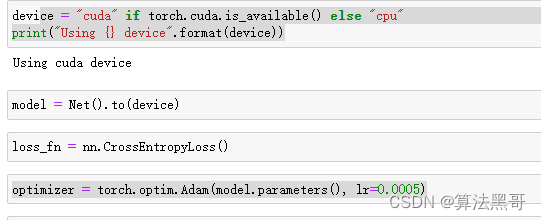
- 训练代码:(model.train()和model.eval()还没加进去 回头+里面)
def fit(epoch, model, trainloader, testloader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
for x, y in trainloader:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.to('cuda'), y.to('cuda')
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(trainloader)
epoch_acc = correct / total
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in testloader:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.to('cuda'), y.to('cuda')
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_test_loss = test_running_loss / len(testloader)
epoch_test_acc = test_correct / test_total
print('epoch: ', epoch,
'loss: ', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss: ', round(epoch_test_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(epoch_test_acc, 3)
)
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
- 记录结果方便画图
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc = fit(epoch,
model,
train_dl,
test_dl)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
完整的如下:
def fit(epoch, model, trainloader, testloader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
model.train()
for x, y in trainloader:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.to('cuda'), y.to('cuda')
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
# exp_lr_scheduler.step()
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(trainloader.dataset)
epoch_acc = correct / total
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in testloader:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.to('cuda'), y.to('cuda')
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_test_loss = test_running_loss / len(testloader.dataset)
epoch_test_acc = test_correct / test_total
print('epoch: ', epoch,
'loss: ', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss: ', round(epoch_test_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(epoch_test_acc, 3)
)
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
epochs = 50
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc = fit(epoch,
model,
train_dl,
test_dl)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
print("Done!")
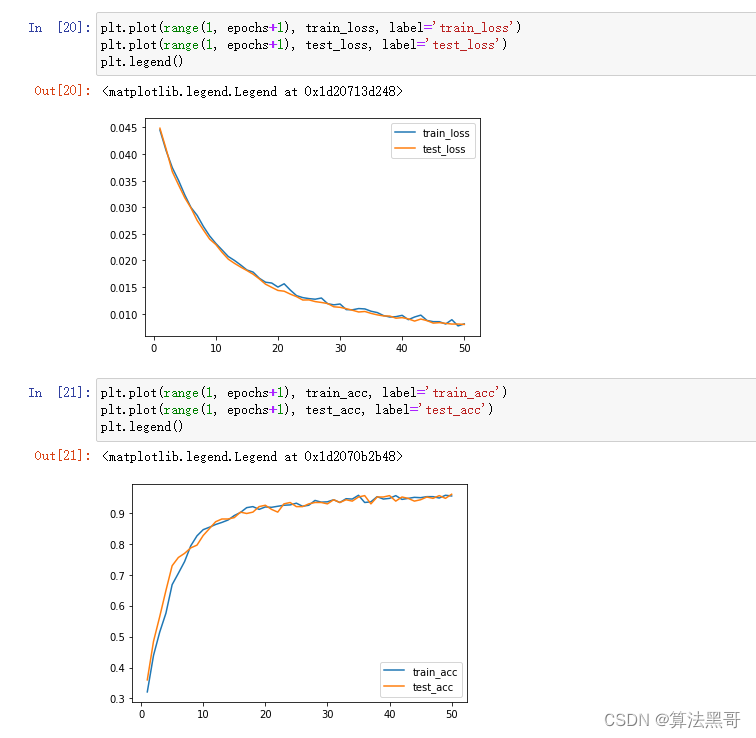






















 545
545











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








