线性回归
导入必须的包
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
导入数据
data=pd.read_csv(‘ex1data1.txt’,names=[‘population’,‘profit’])
查看信息
data.head()
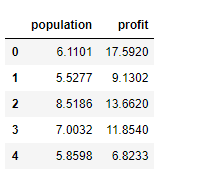
插入1
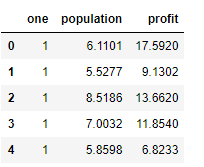
data.insert(0,‘one’,1)
data.head()
切割数据获取X,y值
cols=data.shape[1]
X=data.iloc[:,0:cols-1]
y=data.iloc[:,cols-1:cols]
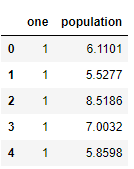
查看X
X.head()
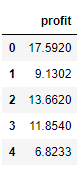
y.head()
转换为矩阵形式
X=np.matrix(X.values)
y=np.matrix(y.values)
theta=np.matrix(np.array([0,0]))
查看维度信息
X.shape
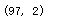
y.shape
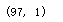
theta.shape
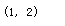
建立代价函数

def computeCost(X,y,theta):
inner=np.power(((Xtheta.T)-y),2)
return np.sum(inner)/(2len(X))
计算代价值,未调整参数
computeCost(X,y,theta)
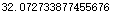
设置学习率 迭代次数
alpha=0.01
iters=1000

批量梯度下降
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters):
temp=np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape))
parameters=int(theta.ravel().shape[1])
cost=np.zeros(iters)
for i in range(iters):
error=(X*theta.T)-y
for j in range(parameters):
term=np.multiply(error,X[:,j])
temp[0,j]=theta[0,j]-((alpha/len(X))*np.sum(term))
theta=temp
cost[i]=computeCost(X,y,theta)
return theta,cost
计算批量梯度下降后代价函数值
g,cost=gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,iters)
computeCost(X,y,g)
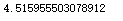
特征变量小于1W也可以使用正规方程计算参数值

def normalEpn(X,y):
theta=np.linalg.inv(X.T@X)@X.T@y
return theta
final_theta2=normalEpn(X,y)
计算代价函数值
computeCost(X,y,final_theta2.T)
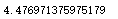





















 2253
2253











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








