一、链表反转(逆序)
设置一个new_head代表反转后的头节点,利用头插法进行链表逆序
#include <stdio.h>
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x):val(x), next(NULL){}
};
class Solution{
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
ListNode* new_head = NULL; //指向新链表头节点的指针
while(head){
ListNode* next = head->next; //备份head->next
head->next = new_head; //更新head_next
new_head = head; //移动new_next
head = next; //遍历链表
}
return new_head;
}
};
void test(){
ListNode a(1);
ListNode b(2);
ListNode c(3);
ListNode d(4);
ListNode e(5);
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
Solution solve;
ListNode* head = &a;
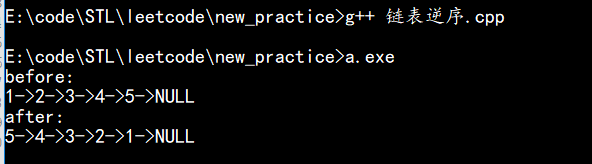
printf("before:\n");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
head = solve.reverseList(&a);
printf("after:\n");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main(void){
test();
return 0;
}
二、链表区间反转
modify_list_tail:指向当前的head,即逆置后的链表尾
pre_head:初始化开始逆置的节点前驱
#include <cstdio>
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int x):val(x), next(NULL){}
};
class Solution{
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n){
int change_len = n - m + 1; //计算需要逆置的节点个数
ListNode* pre_head = NULL; //初始化开始逆置的节点的前驱
ListNode* result = head; //最终转换后的链表头节点,非特殊情况下为head
while(head && --m){
pre_head = head; //记录head的前驱
head = head->next;
}
//将modify_list_tail指向当前的head,即逆置后的链表尾
ListNode* modify_list_tail = head;
ListNode* new_head = NULL;
while(head && change_len){ //逆置change_len个节点
ListNode* next = head->next;
head->next = new_head;
new_head = head;
head = next;
change_len--; //每完成一个节点逆序,change_len--
}
modify_list_tail->next = head; //连接逆序后的链表尾和逆序部分以后的一截列表
if(pre_head){
pre_head->next = new_head; //将逆序链表开始的节点的前驱与逆序后的头结点链接
}else{
result = new_head; //如果pre_head为空,说明m==1从第一个节点开始逆序 结果即为逆序后的头节点
}
return result;
}
};
void test(){
ListNode a(1);
ListNode b(2);
ListNode c(3);
ListNode d(4);
ListNode e(5);
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
Solution solve;
ListNode* head = &a;
printf("before\n");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
head = solve.reverseBetween(&a, 2, 4);
printf("after\n");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main(void){
test();
return 0;
}
三、链表求环
1、set的使用
法1:使用set求环起始节点(算法基础班使用的是hashSet,c++中对应unordered_set)
class Solution1{
public:
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* head){
set<ListNode*> node_set;
while(head){
//遍历链表,若在node_set中出现了
if(node_set.find(head) != node_set.end()){
return head; //返回环的第一个节点
}
node_set.insert(head); //将节点插入node_set
head = head->next;
}
return NULL; //没有遇到环,则返回NULL
}
};2、快慢指针法
快慢指针法:fast指针一次走两步,slow指针一次走一步

class Solution2{
public:
ListNode* detectCycle2(ListNode* head){
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* meet = NULL; //相遇的节点
while(fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if(!fast){
return NULL; //如果fast遇到链表尾,则返回NULL
}
fast = fast->next; //fast再走一步
if(fast == slow){
meet = fast; //fast和slow相遇,记录相遇的位置
break;
}
}
if(meet == NULL){
return NULL; //如果没有相遇则证明无环
}
while(head && meet){
if(head == meet){ //当head和meet相遇,说明遇到环的起始位置
return head;
}
head = head->next;
meet = meet->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};3、两种方法测试
void my_test(){
ListNode a(1);
ListNode b(2);
ListNode c(3);
ListNode d(4);
ListNode e(5);
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
e.next = &c;
ListNode* head = &a;
ListNode* result = NULL;
printf("Solution1 after:\n");
Solution1 solve1;
result = solve1.detectCycle(&a);
if(result){
printf("环节点的值为:%d\n", result->val);
}else{
printf("该链表无环\n");
}
printf("--------------------------------\n");
printf("Solution2 after:\n");
Solution2 solve2;
result = solve2.detectCycle2(&a);
if(result){
printf("环节点的值为:%d", result->val);
}else{
printf("该链表无环\n");
}
}四、链表partition
链表区间划分:任意给一个数字,将链表划分为三个区间(小于、等于、大于),使得链表左边的数都小于这个数,右边的数都大于这个区间
#include <cstdio>
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int x):val(x), next(NULL){}
};
//定义三个区间
class Solution{
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x){
ListNode less_head(0); //三个区间链表
ListNode equal_head(0);
ListNode more_head(0);
ListNode* less_ptr = &less_head;
ListNode* equal_ptr= &equal_head;
ListNode* more_ptr = &more_head;
while(head){
if(head->val < x){
less_ptr->next = head;
less_ptr = head;
}else if(head->val == x){
equal_ptr->next = head;
equal_ptr = head;
}else{
more_ptr->next = head;
more_ptr = head;
}
head = head->next; //遍历链表
}
less_ptr->next = equal_head.next;
equal_ptr->next = more_head.next;
more_ptr->next = NULL;
return less_head.next;
}
};
int main(void){
ListNode a(1);
ListNode b(3);
ListNode c(5);
ListNode d(2);
ListNode e(6);
ListNode f(10);
ListNode g(5);
ListNode h(15);
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
e.next = &f;
f.next = &g;
g.next = &h;
h.next = NULL;
Solution solve;
ListNode* head = solve.partition(&a, 5);
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
return 0;
}
五、复杂链表的深度拷贝
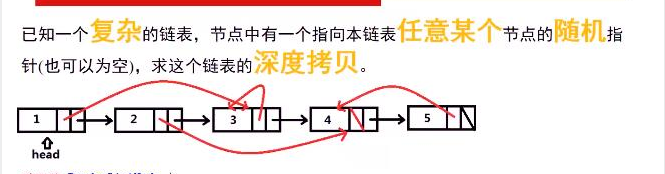
解决思路:

//STL Map的使用
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
struct RandomListNode{
int label;
RandomListNode *next, *random;
RandomListNode(int x): label(x),
next(NULL), random(NULL){}
};
class Solution{
public:
RandomListNode* copyRandomList(RandomListNode* head){
std::map<RandomListNode*, int> node_map; //地址到节点位置的map
std::vector<RandomListNode*> node_vec; //使用vector根据存储节点位置访问地址
RandomListNode* ptr = head;
int i = 0;
while(ptr){
node_vec.push_back(new RandomListNode(ptr->label));
node_map[ptr] = i; //记录原始链表地址至节点位置的node_map
ptr = ptr->next; //遍历原始序列
i++; //记录节点位置
}
node_vec.push_back(0);
ptr = head;
i = 0; //再次遍历原始链表,链接新链表的next指针、random指针
while(ptr){
node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1]; //链接新链表next指针
if(ptr->random){ //当random指针不为空时
int id = node_map[ptr->random]; //根据node_map确认
node_vec[i]->random = node_vec[id]; //原链表random指针,指向的位置即为id
}
ptr = ptr->next;
i++;
}
return node_vec[0];
}
};
int main(void){
RandomListNode a(1);
RandomListNode b(2);
RandomListNode c(3);
RandomListNode d(4);
RandomListNode e(5);
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = &d;
d.next = &e;
a.random = &c;
b.random = &d;
c.random = &c;
e.random = &d;
Solution solve;
RandomListNode* head = solve.copyRandomList(&a);
while(head){
printf("label = %d ", head->label);
if(head->random){
printf("rand = %d\n", head->random->label);
}else{
printf("rand = NULL\n");
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}























 625
625











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










