声明: 此文章仅限于记录学习之用 , 受限于自身水平和理解能力 , 因此结论可能是不正确的. 如果您需要学习,建议参考其他文章
介绍
策略模式就是将同一行为的算法分开写, 用于消除if else. 比如 旅行的出游方式,选择骑自行车、坐汽车.
优点
符合单一职责, 缺点就是会类变得很多.
使用场景
策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,使他们可以相互替换。
类图
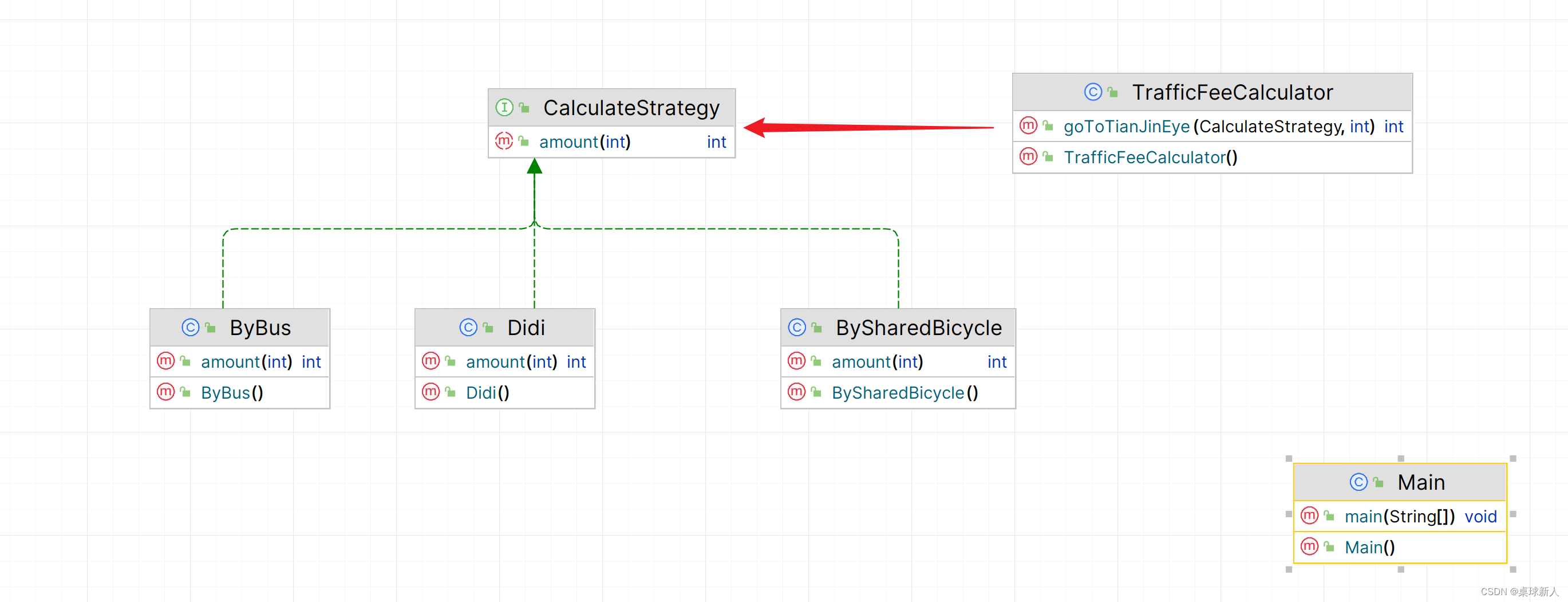
示例代码
- 定义出行接口.
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description: 出行方式
* @date 2023/11/11 19:29
*/
public interface CalculateStrategy {
int amount(int distance);
}
- 使用打的, 骑自行车, 坐公交车实现具体逻辑 /**
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description:
* @date 2023/11/11 19:32
*/
public class ByBus implements CalculateStrategy {
@Override
public int amount(int distance) {
return distance < 10 ? 4 : 6;
}
}
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description:
* @date 2023/11/11 19:32
*/
public class Didi implements CalculateStrategy{
@Override
public int amount(int distance) {
return distance<3?8:(8+(distance-3)*3);
}
}
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description:
* @date 2023/11/11 19:33
*/
public class BySharedBicycle implements CalculateStrategy {
@Override
public int amount(int distance) {
return 2;
}
}
- 定义使用算法 接口.
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description:
* @date 2023/11/11 19:34
*/
public class TrafficFeeCalculator {
public int goToTianJinEye(CalculateStrategy strategy,int distance){
return strategy.amount(distance);
}
}
- 测试
package com.demo;
/**
* @author Administrator
* @version 1.0
* @description:
* @date 2023/11/11 19:33
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TrafficFeeCalculator trafficFeeCalculator = new TrafficFeeCalculator();
int i = trafficFeeCalculator.goToTianJinEye(new Didi(), 20);
System.out.println("didi = " + i);
int bus = trafficFeeCalculator.goToTianJinEye(new ByBus(), 20);
System.out.println("ByBus = " + bus);
int bike = trafficFeeCalculator.goToTianJinEye(new BySharedBicycle(), 20);
System.out.println("bike = " + bike);
}
}
参考资料
https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/strategy-pattern.html
https://shusheng007.top/2020/02/16/strategy-pattern/
https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/strategy
<<header first 设计模式>>
学习后记 20240204
近期又看了<<Header first 设计模式>> 发现我以前的理解是片面的. 策略模式本身解决的问题是 行为算法可变的问题. 它是通过定义一个类,将不变的写入超类. 将可变的行为定义成接口并实现. 然后将接口注入到超类中, 由超类的子类做初始化. 如果使用中想要修改子类的行为算法, 直接去通过set来动态改变行为调用. 这可能才是此设计模式的真正意义. 同样,这个算法也教会了我 组合优于继承. 最后还是建议大家,尽量获取源头知识,我们要学习的是作者的解决问题的方式,而不是记UML类图.是理解而不是记忆,这是最重要的





















 4371
4371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








