export command in Linux with Examples
The ‘export’ command is one of the essential built-in commands in the Bash shell, allowing users to manage environment variables effectively. It is defined in POSIX standards, which state that the shell will assign the export attribute to specified variables, causing them to be included in the environment of subsequently executed commands. Simply put, the export command makes environment variables available to child processes, enabling changes to be reflected immediately in the current shell session without needing to start a new session.
What is the ‘export’ Command?
In Bash, environment variables are set when you start a new shell session, and changes to these variables are not automatically picked up by the shell. The export command allows you to update and propagate the values of environment variables to the current session and any spawned child processes, ensuring that changes are immediately effective. This feature is crucial for tasks such as setting up paths, configuring environment-specific variables, or defining settings that multiple programs need to access.
Syntax:
export [-f] [-n] [name[=value] ...] or export -p
Options of ‘export’ command
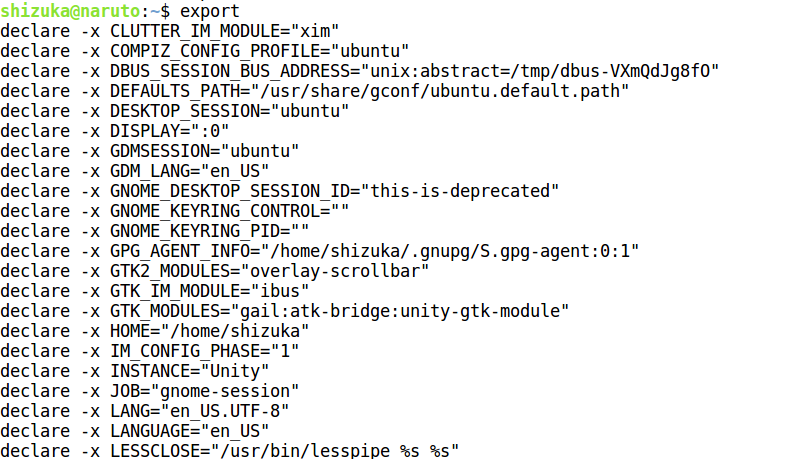
1. Without any argument:
To view all the exported variables.
Example:
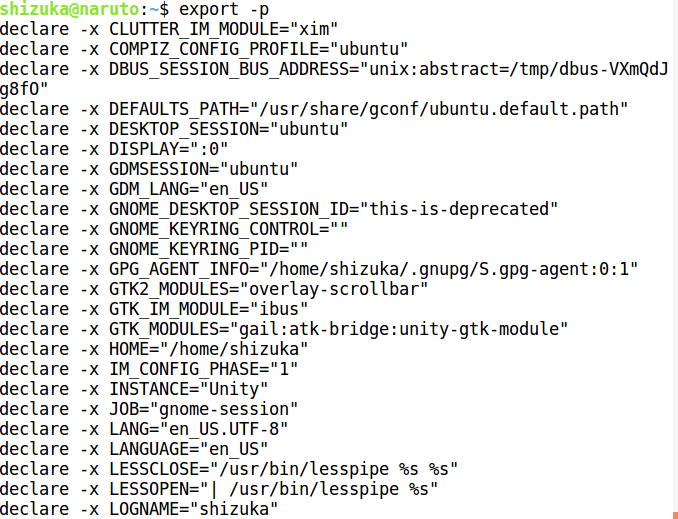
2. -p Option:
To view all exported variables on current shell.
Syntax:
$ export -p
Example:
3. -f Option:
It must be used if the names refer to functions. If -f is not used, the export will assume the names are variables.
Syntax:
$ export -f function_name
Example:
To export shell function:

Note: Bash command is used for showing that in the child shell, the shell function got exported.
4. name[=value]:
You can assign value before exporting using the following syntax.
Syntax:
$ export name[=value]
Example:
To set vim as a text editor
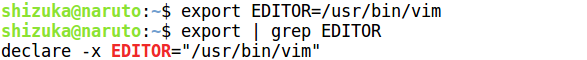
Note: No output will be seen on screen, to see exported variable grep from exported ones is used.
5. -n Option:
Named variables (or functions, with -f) will no longer be exported.
Syntax:
$ export -n variable_name
Example:

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








