一、条件随机场
首先,我们看一下条件随机场的定义:在给定一组输入序列的条件下,另一组输出序列的条件概率分布模型。设X=和Y=
是联合随机变量,若随机变量Y构成一个无向图G=(V,E)表示的马尔科夫模型,则其条件概率分布P(Y|X)称为条件随机场,即
其中,表示图G=(V,E)中与节点v有边连接的所有节点,
表示结点v以外的所有节点。在实际命名实体识别应用中,X是字符,Y是标签。
二、线性链条件随机场

如图,我们假设X与Y具有相同的结构,X=,Y=
,均为线性链表示的随机变量序列,若在给定的随机变量序列X的条件下,随机变量序列Y的条件概率分布P(Y|X)构成条件随机场,且满足马尔科夫性:
则称P(Y|X)为线性链的条件随机场。
与HMM相比,HMM是一个有向图,线性链CRF是一个无向图;HMM只考虑当前状态的上一个状态,线性链CRF依赖于当前状态的周围结点状态。
线性链CRF应用到命名实体识别就是在大量可选标注序列中,找出最靠谱的作为句子的标注。我们需要定义一个特征函数集合,用这个特征集合为标注序列打分,根据分数高低选择最靠谱的标注序列。
CRF有两种特征函数,分别是转移函数和状态函数
:
1)转移函数依赖于当前和前一个位置,表示从标注序列中位置i-1的标记
转移到位置i上的标记
的概率;
2)状态函数依赖当前位置,表示标记序列在位置i上为标记
的概率。通常特征函数取值1或0,表示符不符合该条规则约束,具体公式如下:
其中,Z(x)是规范化因子,和
是转移函数和状态函数对应的权值,目的是求
。求解类似于HMM,可用维特比算法。
三、CRF算法
这里以地名识别为例,使用CRF++工具来实现。
1)语料处理
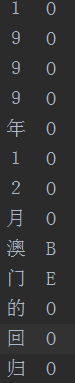
CRF++的训练数据要求一定的格式,一般是一行一个token,一句话由多行token组成,多个句子之间用空行分开。其中每行又分为多列,最后一列是要预测的标签(B,M,E,S,O),前面几列是特征,这里我们采用字符这一个特征。例如:
2)特征模板设计
特征模板的基本格式为%x[row,col],用于确定输入数据的一个token,row确定与当前的token的相对行数,col用于确定决定列数。CRF++有两种模板类型:
- 以字母U开头,是 Unigram template,CRF++会自动为其生成一个特征函数集合;
- 以字母B开头,是Bigram template,系统会自动生成当前输出与前一个输出token的集合,根据该组合特征构造函数。
模型使用可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u010626937/article/details/78414292
模型训练和测试完成后,可以使用以下代码输出准确率、召回率、F值等评估值。
import sys
import re
import codecs
from collections import defaultdict, namedtuple
ANY_SPACE = '<SPACE>'
class FormatError(Exception):
pass
Metrics = namedtuple('Metrics', 'tp fp fn prec rec fscore')
class EvalCounts(object):
def __init__(self):
self.correct_chunk = 0 # number of correctly identified chunks
self.correct_tags = 0 # number of correct chunk tags
self.found_correct = 0 # number of chunks in corpus
self.found_guessed = 0 # number of identified chunks
self.token_counter = 0 # token counter (ignores sentence breaks)
# counts by type
self.t_correct_chunk = defaultdict(int)
self.t_found_correct = defaultdict(int)
self.t_found_guessed = defaultdict(int)
def parse_args(argv):
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='evaluate tagging results using CoNLL criteria',
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
arg = parser.add_argument
arg('-b', '--boundary', metavar='STR', default='-X-',
help='sentence boundary')
arg('-d', '--delimiter', metavar='CHAR', default=ANY_SPACE,
help='character delimiting items in input')
arg('-o', '--otag', metavar='CHAR', default='O',
help='alternative outside tag')
arg('file', nargs='?', default=None)
return parser.parse_args(argv)
def parse_tag(t):
m = re.match(r'^([^-]*)-(.*)$', t)
return m.groups() if m else (t, '')
def evaluate(iterable, options=None):
if options is None:
options = parse_args([]) # use defaults
counts = EvalCounts()
num_features = None # number of features per line
in_correct = False # currently processed chunks is correct until now
last_correct = 'O' # previous chunk tag in corpus
last_correct_type = '' # type of previously identified chunk tag
last_guessed = 'O' # previously identified chunk tag
last_guessed_type = '' # type of previous chunk tag in corpus
for line in iterable:
line = line.rstrip('\r\n')
if options.delimiter == ANY_SPACE:
features = line.split()
else:
features = line.split(options.delimiter)
if num_features is None:
num_features = len(features)
elif num_features != len(features) and len(features) != 0:
raise FormatError('unexpected number of features: %d (%d)' %
(len(features), num_features))
if len(features) == 0 or features[0] == options.boundary:
features = [options.boundary, 'O', 'O']
if len(features) < 3:
raise FormatError('unexpected number of features in line %s' % line)
guessed, guessed_type = parse_tag(features.pop())
correct, correct_type = parse_tag(features.pop())
first_item = features.pop(0)
if first_item == options.boundary:
guessed = 'O'
end_correct = end_of_chunk(last_correct, correct,
last_correct_type, correct_type)
end_guessed = end_of_chunk(last_guessed, guessed,
last_guessed_type, guessed_type)
start_correct = start_of_chunk(last_correct, correct,
last_correct_type, correct_type)
start_guessed = start_of_chunk(last_guessed, guessed,
last_guessed_type, guessed_type)
if in_correct:
if (end_correct and end_guessed and
last_guessed_type == last_correct_type):
in_correct = False
counts.correct_chunk += 1
counts.t_correct_chunk[last_correct_type] += 1
elif (end_correct != end_guessed or guessed_type != correct_type):
in_correct = False
if start_correct and start_guessed and guessed_type == correct_type:
in_correct = True
if start_correct:
counts.found_correct += 1
counts.t_found_correct[correct_type] += 1
if start_guessed:
counts.found_guessed += 1
counts.t_found_guessed[guessed_type] += 1
if first_item != options.boundary:
if correct == guessed and guessed_type == correct_type:
counts.correct_tags += 1
counts.token_counter += 1
last_guessed = guessed
last_correct = correct
last_guessed_type = guessed_type
last_correct_type = correct_type
if in_correct:
counts.correct_chunk += 1
counts.t_correct_chunk[last_correct_type] += 1
return counts
def uniq(iterable):
seen = set()
return [i for i in iterable if not (i in seen or seen.add(i))]
def calculate_metrics(correct, guessed, total):
tp, fp, fn = correct, guessed-correct, total-correct
p = 0 if tp + fp == 0 else 1.*tp / (tp + fp)
r = 0 if tp + fn == 0 else 1.*tp / (tp + fn)
f = 0 if p + r == 0 else 2 * p * r / (p + r)
return Metrics(tp, fp, fn, p, r, f)
def metrics(counts):
c = counts
overall = calculate_metrics(
c.correct_chunk, c.found_guessed, c.found_correct
)
by_type = {}
for t in uniq(list(c.t_found_correct) + list(c.t_found_guessed)):
by_type[t] = calculate_metrics(
c.t_correct_chunk[t], c.t_found_guessed[t], c.t_found_correct[t]
)
return overall, by_type
def report(counts, out=None):
if out is None:
out = sys.stdout
overall, by_type = metrics(counts)
c = counts
out.write('processed %d tokens with %d phrases; ' %
(c.token_counter, c.found_correct))
out.write('found: %d phrases; correct: %d.\n' %
(c.found_guessed, c.correct_chunk))
if c.token_counter > 0:
out.write('accuracy: %6.2f%%; ' %
(100.*c.correct_tags/c.token_counter))
out.write('precision: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*overall.prec))
out.write('recall: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*overall.rec))
out.write('FB1: %6.2f\n' % (100.*overall.fscore))
for i, m in sorted(by_type.items()):
out.write('%17s: ' % i)
out.write('precision: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*m.prec))
out.write('recall: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*m.rec))
out.write('FB1: %6.2f %d\n' % (100.*m.fscore, c.t_found_guessed[i]))
def report_notprint(counts, out=None):
if out is None:
out = sys.stdout
overall, by_type = metrics(counts)
c = counts
final_report = []
line = []
line.append('processed %d tokens with %d phrases; ' %
(c.token_counter, c.found_correct))
line.append('found: %d phrases; correct: %d.\n' %
(c.found_guessed, c.correct_chunk))
final_report.append("".join(line))
if c.token_counter > 0:
line = []
line.append('accuracy: %6.2f%%; ' %
(100.*c.correct_tags/c.token_counter))
line.append('precision: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*overall.prec))
line.append('recall: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*overall.rec))
line.append('FB1: %6.2f\n' % (100.*overall.fscore))
final_report.append("".join(line))
for i, m in sorted(by_type.items()):
line = []
line.append('%-17s:' % i)
line.append('precision: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*m.prec))
line.append('recall: %6.2f%%; ' % (100.*m.rec))
line.append('FB1: %6.2f %d\n' % (100.*m.fscore, c.t_found_guessed[i]))
final_report.append("".join(line))
return final_report
def end_of_chunk(prev_tag, tag, prev_type, type_):
# check if a chunk ended between the previous and current word
# arguments: previous and current chunk tags, previous and current types
chunk_end = False
if prev_tag == 'E': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag == 'S': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag == 'B' and tag == 'B': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag == 'B' and tag == 'S': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag == 'B' and tag == 'O': chunk_end = True
if (prev_tag == 'I' or prev_tag == 'M') and tag == 'B': chunk_end = True
if (prev_tag == 'I' or prev_tag == 'M') and tag == 'S': chunk_end = True
if (prev_tag == 'I' or prev_tag == 'M') and tag == 'O': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag != 'O' and prev_tag != '.' and prev_type != type_:
chunk_end = True
# these chunks are assumed to have length 1
if prev_tag == ']': chunk_end = True
if prev_tag == '[': chunk_end = True
return chunk_end
def start_of_chunk(prev_tag, tag, prev_type, type_):
# check if a chunk started between the previous and current word
# arguments: previous and current chunk tags, previous and current types
chunk_start = False
if tag == 'B': chunk_start = True
if tag == 'S': chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'E' and tag == 'E': chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'E' and (tag == 'I' or tag == 'M'): chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'S' and tag == 'E': chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'S' and (tag == 'I' or tag == 'M'): chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'O' and tag == 'E': chunk_start = True
if prev_tag == 'O' and (tag == 'I' or tag == 'M'): chunk_start = True
if tag != 'O' and tag != '.' and prev_type != type_:
chunk_start = True
# these chunks are assumed to have length 1
if tag == '[': chunk_start = True
if tag == ']': chunk_start = True
return chunk_start
def return_report(input_file):
with codecs.open(input_file, "r", "utf8") as f:
counts = evaluate(f)
return report_notprint(counts)
def main(argv):
args = parse_args(argv[1:])
if args.file is None:
counts = evaluate(sys.stdin, args)
else:
with open(args.file) as f:
counts = evaluate(f, args)
report(counts)
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(sys.argv))




















 3193
3193











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








