如何使用Arduino ESP32将数据存储到MicroSD(软SPI和硬SPI)
- 主要针对使用这个库:github地址:https://github.com/nhatuan84/esp32-micro-sdcard
如果网页无法加载,将域名改为镜像地址的例如:https://hub.fastgit.org/nhatuan84/esp32-micro-sdcard
- 该库支持软SPI接口和硬SPI接口.如果使用硬SPI接口直接定义:
if (!SD.begin()) {
Serial.println("initialization failed!");
return;
}
- 如果是软SPI接口就:
if (!SD.begin(26, 14, 13, 27)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed!");
return;
}
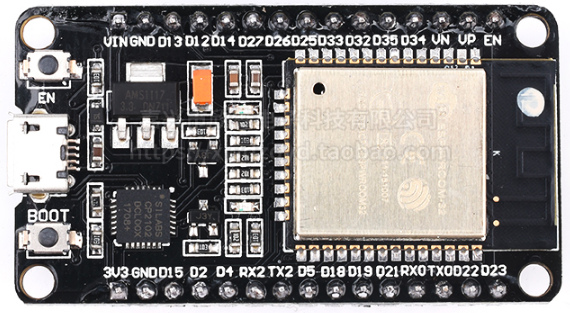
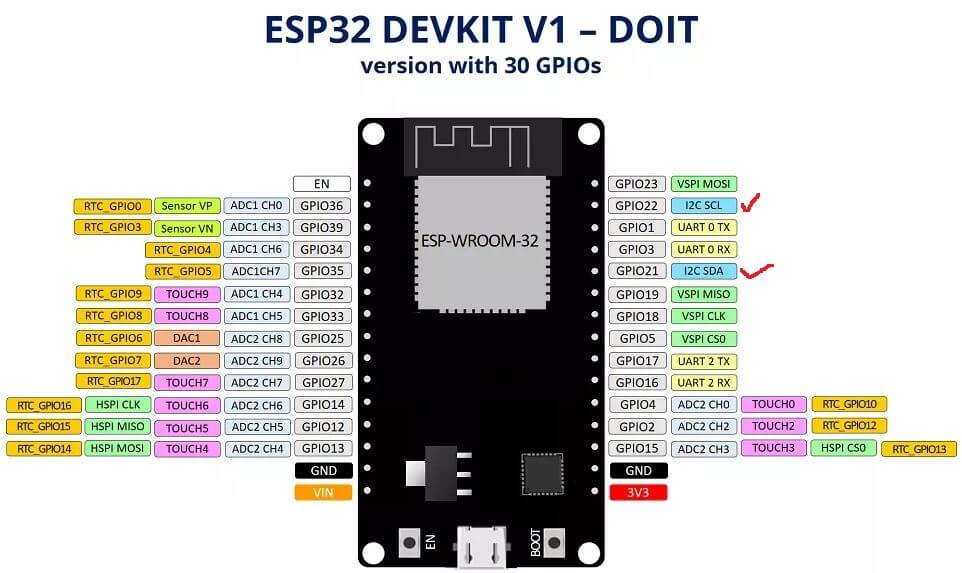

接线说明
- 软SPI接口接线方式:
Soft SPI
[ESP32 IO26 – CS MICRO SD]
[ESP32 IO14 – MOSI MICRO SD]
[ESP32 IO13 – MISO MICRO SD]
[ESP32 IO27 – SCK MICRO SD]
[ESP32 GND – GND MICRO SD]
[VIN – VCC MICRO SD]
- 硬SPI接口接线方式:
Hard SPI
* MICROSD CS - ESP32 IO5
MICROSD SCK - ESP32 IO18
MICROSD MOSI - ESP32 IO23
MICROSD MISO - ESP32 IO19
MICROSD Vcc - ESP32 VIN
MICROSD GND - ESP32 GND
实例代码
#include <mySD.h>
File root;
void printDirectory(File dir, int numTabs);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Initializing SD card...");
/* initialize SD library with Soft SPI pins, if using Hard SPI replace with this SD.begin()*/
// if (!SD.begin(26, 14, 13, 27)) {//采用软SPI接口
if (!SD.begin()) { 采用硬SPI接口
Serial.println("initialization failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("initialization done.");
/* Begin at the root "/" */
root = SD.open("/");
if (root) {
printDirectory(root, 0);
root.close();
} else {
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
/* open "test.txt" for writing */
root = SD.open("test.txt", FILE_WRITE);
/* if open succesfully -> root != NULL
then write string "Hello world!" to it
*/
if (root) {
root.println("Hello world!");
root.flush();
/* close the file */
root.close();
} else {
/* if the file open error, print an error */
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
delay(1000);
/* after writing then reopen the file and read it */
root = SD.open("test.txt");
if (root) {
/* read from the file until there's nothing else in it */
while (root.available()) {
/* read the file and print to Terminal */
Serial.write(root.read());
}
root.close();
} else {
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
Serial.println("done!");
}
void loop()
{
}
void printDirectory(File dir, int numTabs) {
while(true) {
File entry = dir.openNextFile();
if (! entry) {
break;
}
for (uint8_t i=0; i<numTabs; i++) {
Serial.print('\t'); // we'll have a nice indentation
}
// Print the name
Serial.print(entry.name());
/* Recurse for directories, otherwise print the file size */
if (entry.isDirectory()) {
Serial.println("/");
printDirectory(entry, numTabs+1);
} else {
/* files have sizes, directories do not */
Serial.print("\t\t");
Serial.println(entry.size());
}
entry.close();
}
}
相关接口函数
Class SD:
- -
SD.begin(uint8_t cs , int8_t mosi , int8_t miso , int8_t sck): 使用SPI引脚初始化库 SD.open(filename, FILE_WRITE): 打开文件进行写入SD.open(filename): 打开文件进行读取SD.open("/"): 打开sdcard at root“/”
Class File:
openNextFile(): 检查条目是否为目录- name(): get the name of file or directory
- isDirectory(): check if entry is directory
size(): 获取文件大小println(text): 将文本写入打开的文件available(): 检查可用的数据readingread(): 如果数据可用则读取数据close(): 关闭打开的文件























 5345
5345











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








