spring加载属性(properties)文件
一、注解方式加载
jdbc.driver=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mariadb://localhost:3306/kt
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=12345
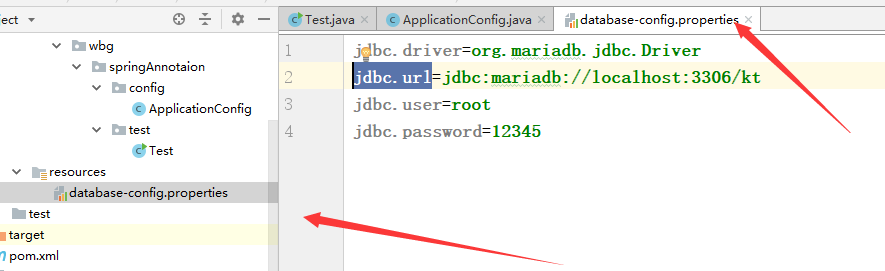
创建配置类:


package com.wbg.springAnnotaion.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; @Configuration //ignoreResourceNotFound 为false时候找不到会忽略 @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:database-config.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true) public class ApplicationConfig { }

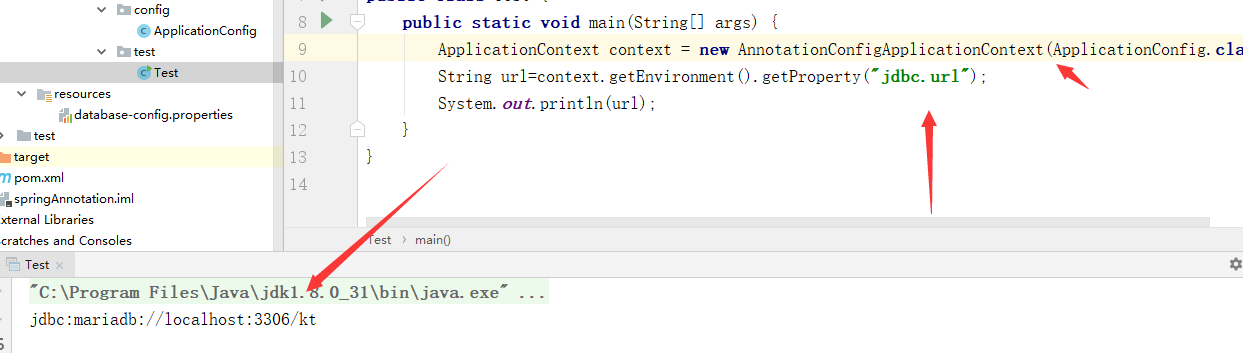
测试:


ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationConfig.class); String url=context.getEnvironment().getProperty("jdbc.url"); System.out.println(url);
 使用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer注解来占位符
使用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer注解来占位符
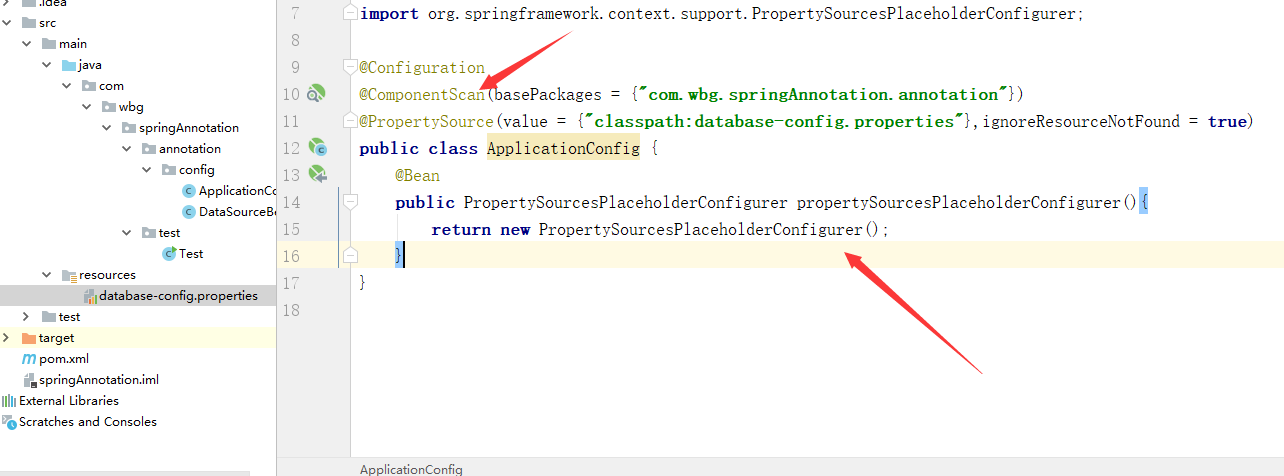
1、在原来类上加代码


package com.wbg.springAnnotation.annotation.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wbg.springAnnotation.annotation"}) @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:database-config.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true) public class ApplicationConfig { @Bean public PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(){ return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(); } }
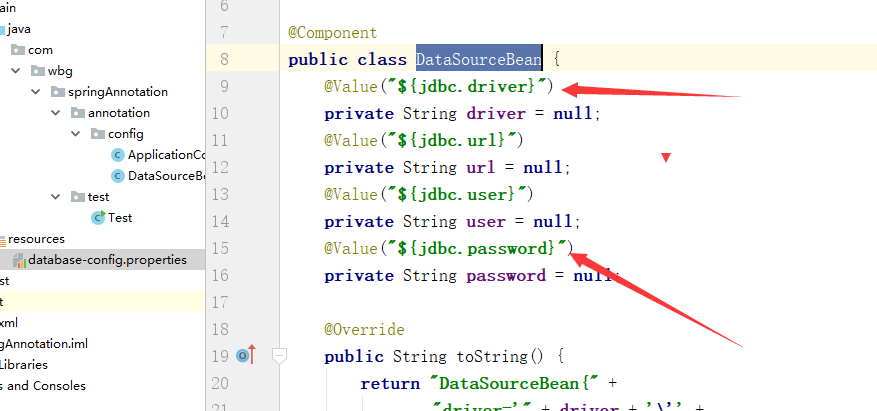
2、创建DataSourceBean类:
类上的@Value注解使用$占位符


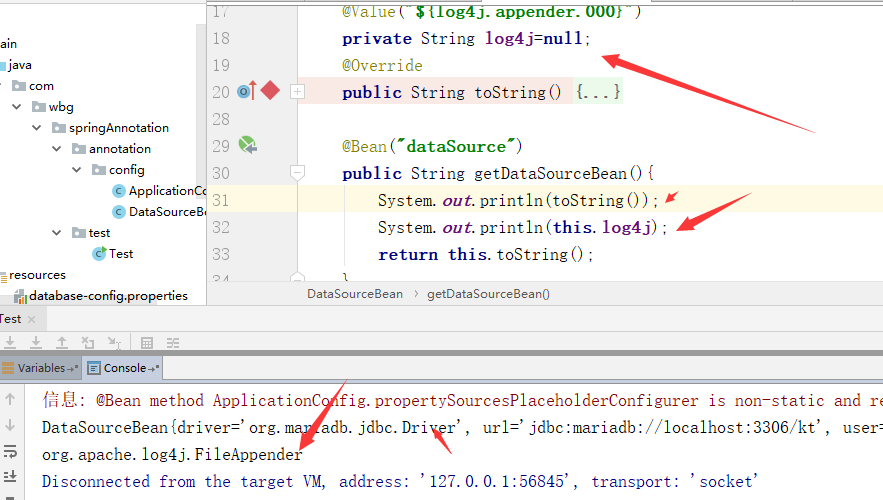
package com.wbg.springAnnotation.annotation.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class DataSourceBean { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver = null; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url = null; @Value("${jdbc.user}") private String user = null; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password = null; @Override public String toString() { return "DataSourceBean{" + "driver='" + driver + '\'' + ", url='" + url + '\'' + ", user='" + user + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + '}'; } @Bean("dataSource") public String getDataSourceBean(){ System.out.println(toString()); return this.toString(); } }
测试:

二、使用xml进行加载:
创建xml文件:
database-config.xml


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.wbg.springAnnotation.annotation"/> <!--ignore-resource-not-found:true允许不存在,否则异常--> <context:property-placeholder ignore-resource-not-found="true" location="classpath:database-config.properties"/> </beans>
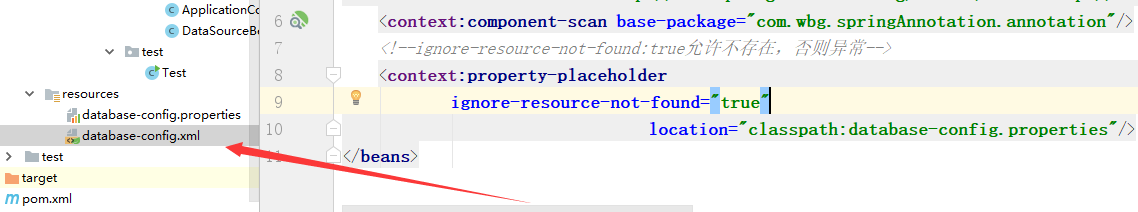
测试:
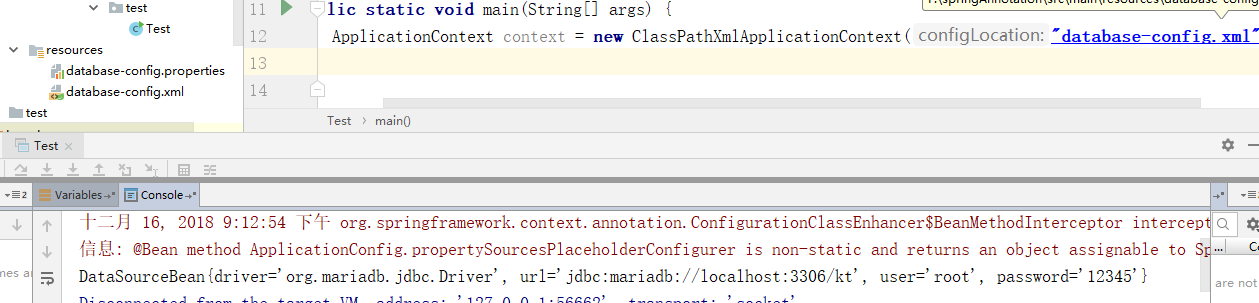
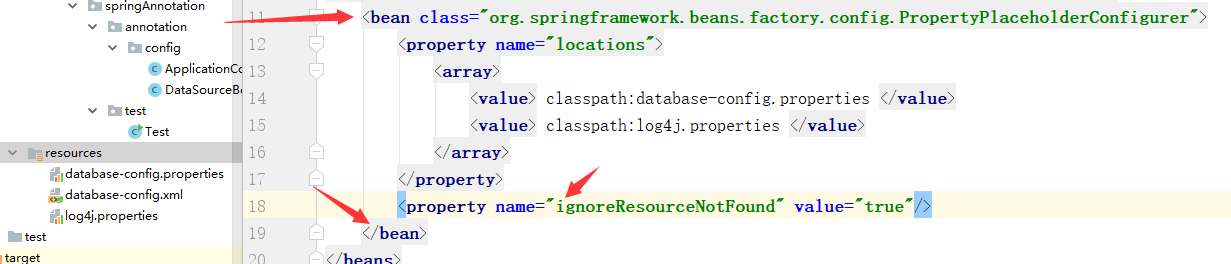
如果配置多个:


<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <array> <value> classpath:database-config.properties </value> <value> classpath:log4j.properties </value> </array> </property> <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true"/> </bean>
测试:

demo:https://github.com/weibanggang/springannotationproperties.git





















 235
235











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








