关于bash的-c选项
bash的-c选项, 表示把后续的参数当做命令行, 而不是脚本.
manual page中, 关于bash的synopsis是这样的:
[mg@fedora d2]$ man -f bash
bash (1) - GNU Bourne-Again SHell
然后执行 man 1 bash, 显示如下
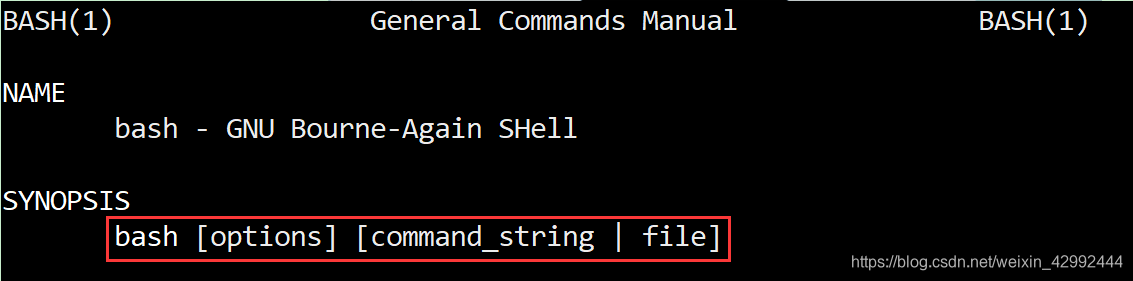
可以看到, 它的SYNOPSIS是
bash [options] [command_string | file]
bash的options有很多种, -c就是其中一种options.
当没有-c时, bash将后面的参数, 当做是file, 即脚本文件.
当有-c时, bash将后续的参数, 当做是命令.
先看几个例子就明白说的是啥意思了:
[mg@fedora foo]$ cat ex.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "hello world!"
[mg@fedora foo]$
[mg@fedora foo]$ file ex.sh
ex.sh: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash ex.sh
hello world!
## 从上可知, bash将它的参数ex.sh当做是一个脚本.
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash -c ex.sh
bash: ex.sh: command not found
## 从上可知, bash加了-c选项后, 将ex.sh当做是一个command
[mg@fedora foo]$
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash -c emacs hello.c
hello.c: emacs: command not found
## 这里的意图是, 用emacs来编辑hello.c文件, 显然根据bash的报错
## 可知, emacs是当做一个command.
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash emacs hello.c
bash: emacs: No such file or directory
## 这里, 从报错信息可知, emacs被当做一个脚本文件
[mg@fedora foo]$
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash ls -l
/usr/bin/ls: /usr/bin/ls: cannot execute binary file
## ls被当做脚本, 但实际它是一个二进制文件
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash "ls -l"
bash: ls -l: No such file or directory
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash -c "ls -l"
total 60
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 11080 Sep 19 2019 a2
-rwxrwxr-x. 1 mg mg 8312 Jan 27 08:52 a.out
-rwxrwxr-x. 1 mg mg 99 Oct 29 2019 awkexample
drwxrwxr-x. 4 mg mg 62 Jul 4 12:22 d2
-rwxrwxr-x. 1 mg mg 8264 Oct 29 2019 echoarg
-rw-rw-r--. 1 mg mg 145 Oct 29 2019 echoarg.c
-rw-rw-r--. 1 mg mg 34 Jul 12 11:25 ex.sh
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 40 Sep 20 2019 foo2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 367 Sep 19 2019 open_existed_symbol_link.c
-rw-rw-r--. 1 mg mg 241 Jan 27 08:52 return_before_increment.c
-rw-rw-r--. 1 mg mg 6 Sep 19 2019 xx1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 3 Sep 19 2019 xx1.sl -> xx1
[mg@fedora foo]$ bash -c "ls -J"
ls: invalid option -- 'J'
Try 'ls --help' for more information.
再来看看manual page中, 对bash -c选项的说明:
SYNOPSIS
bash [options] [command_string | file]
OPTIONS
-c If the -c option is present, then commands
are read from the first non-option argument command_string.
If there are arguments after the command_string, the first
argument is assigned to $0 and any remaining arguments
are assigned to the positional parameters. The assignment
to $0 sets the name of the shell, which is used in warning
and error messages.
它的意思是说,
如果有-c选项,则从第一个非选项参数command_string读取命令。如果command_string后面有参数,则第一个参数被分配为$0,其余的参数被分配为位置参数。$0的赋值设置了shell的名称,用于警告和错误消息。
举例来说, 假设是这样:
bash -c str1 str2 str3 … strN
那么 str1作为command, str2, str3, … strN作为command的参数. 其中str1作为$0, str2, … strN依次作为位置参数.
[mg@fedora foo]$ cat print_args.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++)
printf("argv[%d] = %s\n", i, argv[i]);
return 0;
}
[mg@fedora foo]$ gcc print_args.c -o print_args
[mg@fedora foo]$ ./print_args
argv[0] = ./print_args
[mg@fedora foo]$ ./print_args a b c d e
argv[0] = ./print_args
argv[1] = a
argv[2] = b
argv[3] = c
argv[4] = d
argv[5] = e
[mg@fedora foo]$ sh -c "print_args a b c d e"
sh: print_args: command not found
[mg@fedora foo]$ sh -c "./print_args a b c d e"
argv[0] = ./print_args
argv[1] = a
argv[2] = b
argv[3] = c
argv[4] = d
argv[5] = e
[mg@fedora foo]$
问题
方式一: bash -c command arg1 arg2 … argN
方式二: 将command arg1 arg2 … argN 写到一个脚本文件test.sh中, 然后执行 bash test.sh
这两种方式有什么差异?


























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








