C++提供的STL,这个标准库里面包含了容器类,string就是容器类的其中一员,那么string容器有什么特点吗?让小编带你一起来了解一下吧。
目录
string
如果你要使用string容器,那么需要添加头文件
#include<string>1. string的定义和初始化
string ser_str1; // 定义一个空串
string ser_str2(10,'s'); // 定义一个字符串,由10个s组成
string ser_str3(ser_str2); // 使用serven_1来定义字符串
string ser_str4("三贝勒文子"); // 参数为常量的构造函数来定义字符串运行结果:
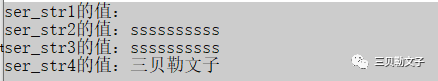
2. string的赋值操作
-
operator=:C++中string容器重写了operator=,包括了下面三种赋值的方式:
// string& operator=(const char* str); // char*类型字符赋值给当前的字符串
// string& operator=(char c); // 字符赋值给当前字符串
// string& operator=(const string& s); // 字符串s赋值给当前字符串
char* s = "你好";
ser_str1 = s;
cout<<"char*类型字符赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
char c = 'S';
ser_str1 = c;
cout<<"把字符赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1 = "三贝勒文子";
cout<<"把字符串s赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl<<endl;
运行结果:

-
assign():该函数是赋值函数:
// string assign(const char* s); // char*类型字符赋值给当前字符串
// string assign(int n, char c); // 把n个字符c赋值给当前字符串
// string assign(const string& s); // 把字符串s赋值给当前字符串
// string assign(const string& s, int nstart, int n); // 将字符串s下标为nstart开始的地方后n个字符赋值给当前字符串
// string assign(const string& s, int n;) // 将字符串s下标为0开始的地方后n个字符赋值给当前字符串
char* s = "你好";
ser_str1.assign(s);
cout<<"char*类型字符赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;out<<ser_str1<<endl;
char c = 'S';
ser_str1.assign(1,c);
cout<<"把1个c1字符赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.assign("三贝勒文子");
cout<<"把字符串s赋值给当前的字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.assign("Hello World!",3,5);
cout<<"将字符串s下标为3位置开始往后的5个字符赋值给新字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.assign("Hello World!", 5);
cout<<"将字符串s下标为0位置开始往后的5个字符赋值给新字符串:"<<ser_str1<<endl<<endl;
运行结果:

3. string获取字符的操作
-
string获取字符有两种方式,分别是at和operator[],代码如下:
// 通过at取字符
cout<<"字符串的第三个位置的字符:"<<ser_str1.at(2)<<endl;
// 通过operator[]取字符
cout<<"字符串的第二个位置的字符:"<<ser_str1[1]<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

4. string的拼接操作
拼接操作有两种方式,分别是operator+=和append,两种的操作方式如下:
operator+=:
// string& operator+=(const string& s);
// string& operator+=(const char* s);
// string& operator+=(const char c);
ser_str1 += "三贝勒文子, ";
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
char* s2 = "你真帅";
ser_str1 += s2;
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1 += '!';
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;append():
// string& append(const string& s);
// string& append(const char* s);
// string& append(int n, char c); // 在当前字符串结尾添加n个字符c
// string& append(const string& s, int pos, int n);
// string& append(const char* s, int n);
ser_str1.append("你好高吖!");
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
char* s3 = "眼睛真好看!";
ser_str1.append(s3);
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.append(1,'-');
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.append("I LOVE YOU",0,6);
cout<<ser_str1<<endl;
char* s4 = " YOU";
ser_str1.append(s4,4);
cout<<ser_str1<<endl<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

5. string的查找操作
查找字符或者字符串的方式有正向查找和反向查找,两者示例为:
-
find():正向查找
ser_str1 = "My name is Serven, I come from china, I like writting and Reading. this is My home";
// int find(const string& s, int pos = 0)const; 查找s第一次出现的位置,从pos开始找
// int find(const char* s, int pos = 0)const; 查找s第一次出现的位置,从pos开始找
// int find(const char* s, int pos, int n); 从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次出现的位置
// int find(const char c, int pos = 0)const; 查找字符c第一次出现的位置
cout<<"ser_str1"<<ser_str1<<endl;
cout<<"从0位置开始找第一个My的位置:"<<ser_str1.find("My",0)<<endl;
cout<<"从7位置开始找第一个My的位置:"<<ser_str1.find("My",17)<<endl;
cout<<"寻找Serven字符串中的Ser的第一次出现的位置:"<<ser_str1.find("Ser",0)<<endl;运行结果:

-
rfind():反向查找
// int rfind(const string& s, int pos=npos)const; 查找s最后出现的位置,从pos开始找
// int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos)condt; 查找s最后一次出现的位置,从pos开始查找
// int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n)const; 从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次的位置
// int rfind(const char c, int pos)const; 查找字符c最后一次出现的位置
cout<<"倒数第一个My的位置:"<<ser_str1.rfind("My")<<endl; // 第二个参数默认是字符串的结尾总字符数
cout<<"寻找writting字符串中的wri的倒数第一次出现的位置:"<<ser_str1.rfind("wri")<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

6. string的替换操作
-
replace():
/* string的替换操作 */
ser_str1 = "Hello world!";
// string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& s); 替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串s
ser_str1.replace(6, 6 ,"Serven");
cout<<ser_str1<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

7. string的比较操作
-
compare():compare函数在>时返回 1,<时返回 -1,==时返回 0。比较区分大小写,比较时参考字典顺序,排越前面的越小。大写的A比小写的a小。
//int compare(const string &s) const;//与字符串s比较
//int compare(const char *s) const;//与字符串s比较
ser_str1 = "Hello World";
ser_str2 = "Hello Serven";
cout<<"Hello World和Hello Serven作比较:"<<ser_str1.compare(ser_str2)<<endl;
cout<<"Hello World和Hello World作比较:"<<ser_str1.compare(ser_str1)<<endl;
cout<<"Hello Serven和Hello World作比较:"<<ser_str2.compare(ser_str1)<<endl;运行结果:
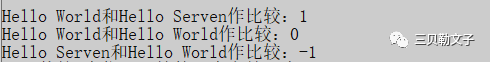
8. string的子串获取操作
-
substr():
ser_str1 = "Hello World";
// string subStr(int pos = 0, int n = npos)const; // 返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
cout<<"返回从第3个位置开始的三个字符子串:"<<ser_str1.substr(2,3)<<endl;运行结果:

9. string的插入和删除操作
-
insert():
-
erase():
/* string 插入和删除操作 */
//string& insert(int pos, const char* s); //插入字符串
//string& insert(int pos, const string& str); //插入字符串
//string& insert(int pos, int n, char c);//在指定位置插入n个字符c
//string& erase(int pos, int n = npos);//删除从Pos开始的n个字符
ser_str1 = "Hello orld";
ser_str1.insert(6,1,'W');
cout<<"在第六个位置插入字符W:"<<ser_str1<<endl;
ser_str1.erase(0,1);
cout<<"在第0个位置删除1个字符:"<<ser_str1<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

10. string 的reserve预留空间操作
-
reserve(n):给字符串预留空间
/* 为字符串预留空间 */
string serven_str_4;
cout<<"serven_str_4没有预留空间前的容量:"<<serven_str_4.capacity()<<endl;
serven_str_4.reserve(10);
cout<<"serven_str_4预留空间后的容量:"<<serven_str_4.capacity()<<endl;运行结果:

11. string的swap函数和容量、长度获取
-
s1.swap(s2):将字符串s1和s2互换;
-
size():获取字符串的长度;
-
capacity():获取字符串的容量;
/* string的长度和容量获取以及swap */
string serven_str_1 = "Hello World";
string serven_str_2 = "Serven";
cout<<"原本的serven_str_1:"<<serven_str_1<<endl;
cout<<"原本的serven_str_2:"<<serven_str_2<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_1的长度为:"<<serven_str_1.size()<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_1的容量为:"<<serven_str_1.capacity()<<endl;
serven_str_1.swap(serven_str_2); // 交换serven_str_1和serven_str_2
cout<<"交换后的serven_str_1:"<<serven_str_1<<endl;
cout<<"交换后的serven_str_2:"<<serven_str_2<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_1的长度为:"<<serven_str_1.size()<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_1的容量为:"<<serven_str_1.capacity()<<endl;
string serven_str_3 = serven_str_1;
cout<<"serven_str_3的长度为:"<<serven_str_3.size()<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_3的容量为:"<<serven_str_3.capacity()<<endl;
cout<<"serven_str_1的最大的长度为:"<<serven_str_2.max_size()<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

12. string判断是否为空串
-
empty():判断字符串是否为空串,是的话返回1
cout<<"serven_str_3是否为空串:"<<serven_str_3.empty()<<endl<<endl;运行结果:

13. string和char*的互换操作
/* string 和 char* 的转换*/
// string转char*
string serven = "helloworld";
const char* serven_1 = serven.c_str(); // 一i的那个要定义为常量指针,因为要保证指针不能指向别的位置了
cout<<serven_1<<endl;
//char*转string
char* serven_2 = "serven";
string serven_3(serven_2);
cout<<serven_3<<endl<<endl;运行结果:


























 1749
1749

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










