1.实验
在实验楼的Linux环境下,打开shell,输入以下代码:

运行结果如下,陷入死循环,对代码进行修改。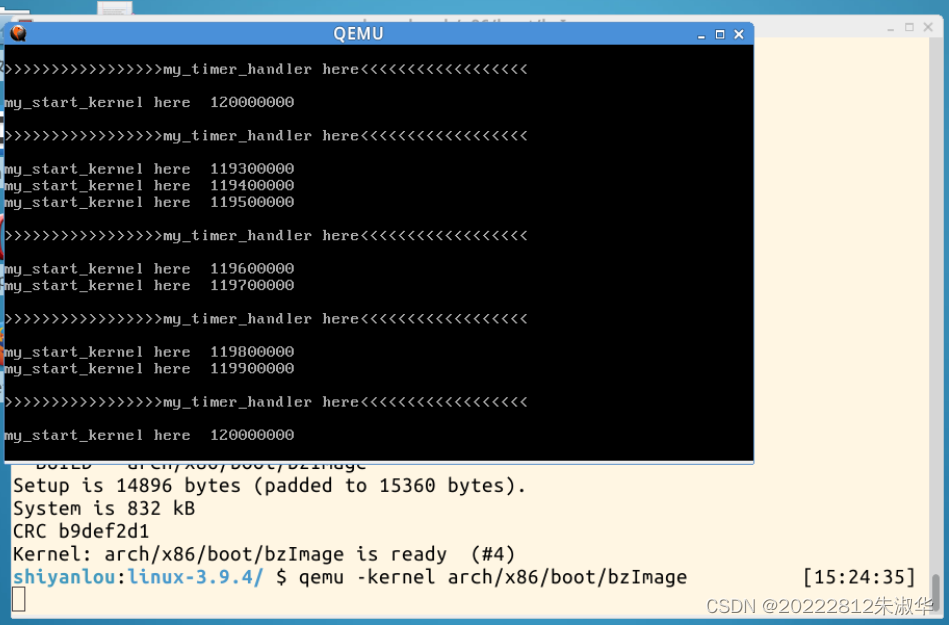
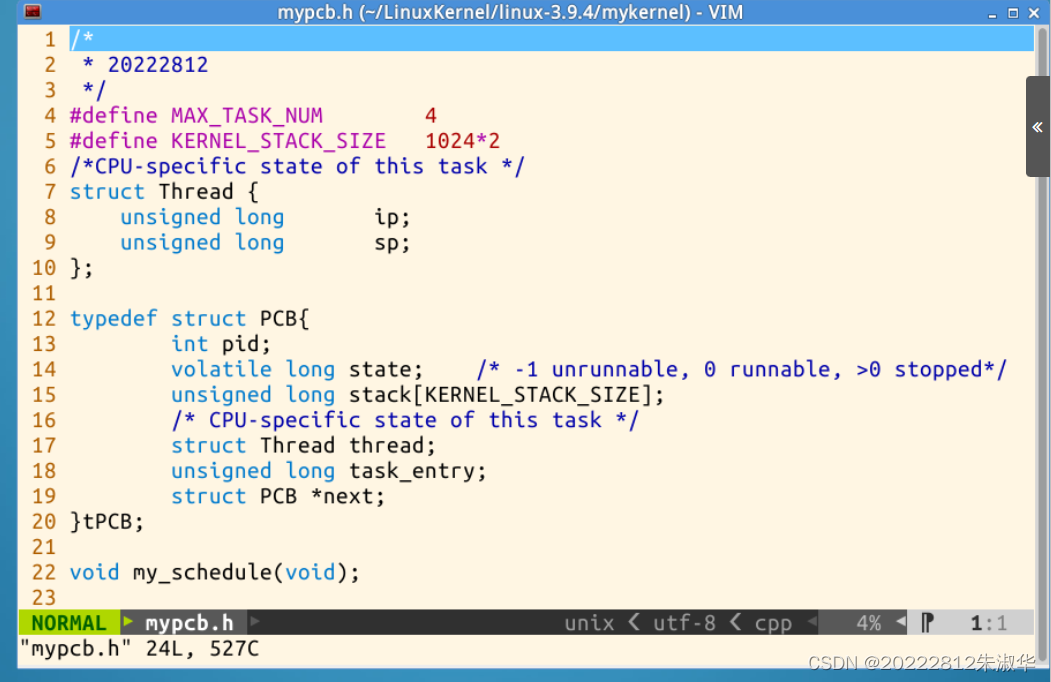
创建mypcb.h头文件,用来定义进程控制块PCB,也就是进程结构体的定义。
mymain.c
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
/*fork more process */
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)(&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]);
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movq %1,%%rsp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to rsp */
"pushq %1\n\t" /* push rbp */
"pushq %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to rip */
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
}
int i = 0;
void my_process(void)
{
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -\n",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +\n",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}myinterrupt.c
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
extern tPCB * my_current_task;
extern volatile int my_need_sched;
volatile int time_count = 0;
void my_timer_handler(void)
{
if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<\n");
my_need_sched = 1;
}
time_count ++ ;
return;
}
void my_schedule(void)
{
tPCB * next;
tPCB * prev;
if(my_current_task == NULL
|| my_current_task->next == NULL){
return;
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<\n");
/* schedule */
next = my_current_task->next;
prev = my_current_task;
if(next->state == 0)
{
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<\n",prev->pid,next->pid);
asm volatile(
"pushl %%ebp\n\t" /* save ebp of prev */
"movl %%esp,%0\n\t" /* save esp of prev */
"movl %2,%%esp\n\t" /* restore esp of next */
"movl $1f,%1\n\t" /* save rip of prev ,%1f指接下来的标号为1的位置*/
"pushl %3\n\t"
"ret\n\t" /* restore rip of next */
"1:\t" /* next process start here */
"popl %%ebp\n\t"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
return;
}
完成后重新编译。
总结
本章内容最重要的是进程的切换,进程在执行过程中,当时间片用完需要进行进程切换时,需要先保存当前的进程执行的上下文环境,下次进程被调度时,需要恢复进程的上下文环境。这样实现多道程序的并发执行。





















 913
913











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








