| Problem Description |
| The twenty-first century is a biology-technology developing century. We know that a gene is made of DNA. The nucleotide bases from which DNA is built are A(adenine), C(cytosine), G(guanine), and T(thymine). Finding the longest common subsequence between DNA/Protein sequences is one of the basic problems in modern computational molecular biology. But this problem is a little different. Given several DNA sequences, you are asked to make a shortest sequence from them so that each of the given sequence is the subsequence of it.
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one. 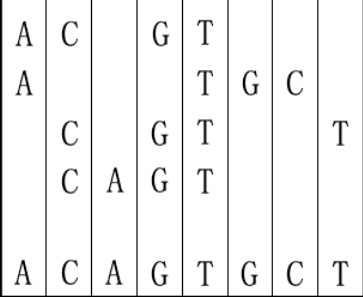
|
| Input |
| The first line is the test case number t. Then t test cases follow. In each case, the first line is an integer n ( 1<=n<=8 ) represents number of the DNA sequences. The following k lines contain the k sequences, one per line. Assuming that the length of any sequence is between 1 and 5. |
| Output |
| For each test case, print a line containing the length of the shortest sequence that can be made from these sequences. |
| Sample Input |
1
4
ACGT
ATGC
CGTT
CAGT |
| Sample Output 8 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/libin56842/article/details/46582685 思路:IDDFS是每次按照限制的深度进行搜索,如果在k深度没有找到解,则进行k+1深度的搜索; 这题的做法就是按照从max_size的深度开始增加深度,如果找到解直接return; AC代码如下: #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define esp 1e-4
using namespace std;
/*
迭代加深搜索,如果当前搜索深度+最少要搜索的深度>限制的深度,则return;
*/
int n;
char str[10][10];
int si[10];//代表每个字符串的长度
int deep;//限制深度
int ans;
char key[5] = "ACGT";
void dfs(int cnt, int len[])//cnt 代表当前的搜索深度,len[i]代表i字符串已经匹配到的位置
{
if (cnt > deep)
return;
int maxx = 0;//代表每个字符串剩余要匹配的字符个数
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
maxx = max(maxx, si[i] - len[i]);
}
if (maxx == 0)
{
ans = cnt;
return;
}
if (cnt + maxx > deep)//当前搜索深度+最少要搜索的深度>限制的深度
return;
int pos[10];
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (str[j][len[j]] == key[i])
{
flag = 1;//代表str[0-9]匹配到的位置中有key[i],就构成了一个结果
pos[j] = len[j] + 1;
}
else
pos[j] = len[j];
}
if (flag)
dfs(cnt + 1, pos);
if (ans != -1)
return;
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n;
int max_size = 0;//这些字符串中最长的长度
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> str[i];
si[i] = strlen(str[i]);
if (si[i] > max_size)
max_size = si[i];
}
int pos[10] = { 0 };//当前搜索到的位置,一开始都是从0开始
deep = max_size;
ans = -1;
while (1)
{
dfs(0, pos);
if (ans != -1)
break;
deep++;//增加搜索深度
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
|
A计划 |
| Problem Description |
| 可怜的公主在一次次被魔王掳走一次次被骑士们救回来之后,而今,不幸的她再一次面临生命的考验。魔王已经发出消息说将在T时刻吃掉公主,因为他听信谣言说吃公主的肉也能长生不老。年迈的国王正是心急如焚,告招天下勇士来拯救公主。不过公主早已习以为常,她深信智勇的骑士LJ肯定能将她救出。
现据密探所报,公主被关在一个两层的迷宫里,迷宫的入口是S(0,0,0),公主的位置用P表示,时空传输机用#表示,墙用*表示,平地用.表示。骑士们一进入时空传输机就会被转到另一层的相对位置,但如果被转到的位置是墙的话,那骑士们就会被撞死。骑士们在一层中只能前后左右移动,每移动一格花1时刻。层间的移动只能通过时空传输机,且不需要任何时间。 |
| Input |
| 输入的第一行C表示共有C个测试数据,每个测试数据的前一行有三个整数N,M,T。 N,M迷宫的大小N*M(1 <= N,M <=10)。T如上所意。接下去的前N*M表示迷宫的第一层的布置情况,后N*M表示迷宫第二层的布置情况。 |
| Output |
| 如果骑士们能够在T时刻能找到公主就输出“YES”,否则输出“NO”。 |
| Sample Input |
1
5 5 14
S*#*.
.#...
.....
****.
...#.
..*.P
#.*..
***..
...*.
*.#.. |
| Sample Output |
YES |
| 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/wyxeainn/article/details/52495648 解题思路:
如果遇到一‘#’,则遇到一个传送门,如果它对面也是传送门,那么这个勇士就会在两个门之间无数次地传送下去,不会停下。如果它对面是墙,那么这个勇士要是过去会撞死,如果发现对面已经是被访问过了,那么说明之前有点比这个点更早到达对面,因此一旦遇到传送门并发现对面是这三种情况,我们就直接将这个位置以及他得对面位置赋为‘*’,代表这些位置不能走,其他情况遇到传送门,就将勇士传送到另一层。如果第一个到达公主位置的那条路所经历的时间都比最大时间大的话,则公主就会挂掉,因为以后到达的只会比第一次的时间更长,因此一旦遇到当前位置是结束位置,我就判断当前所用的时间是否超过了限定的时间,如果没有超过,直接输出YES,结束搜索,如果超过了,也直接结束搜索,输出NO,代表不能成功救出公主,公主挂掉 #include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x, y, floor;
int step;
};
int t, n, m, lim;
int s[3], e[3];
int to[4][2] = { 1,0,0,1,-1,0,0,-1 };
char map[2][15][15];
int vis[2][15][15];
int check(int floor, int x, int y)
{
if (x<0 || y<0 || x >= n || y >= m)
return 1;
if (map[floor][x][y] == '*')
return 1;
return 0;
}
void bfs()
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
node a, next;
queue<node> Q;
int i, j, k;
a.floor = s[0];
a.x = s[1];
a.y = s[2];
a.step = 0;
vis[s[0]][s[1]][s[2]] = 1;
Q.push(a);
while (!Q.empty())
{
a = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (a.floor == e[0] && a.x == e[1] && a.y == e[2])
{
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
if (a.step >= lim)
break;
for (i = 0; i<4; i++)
{
next = a;
next.x += to[i][0];
next.y += to[i][1];
next.step++;
if (check(next.floor, next.x, next.y))
continue;
if (vis[next.floor][next.x][next.y])
continue;
vis[next.floor][next.x][next.y] = 1;
if (map[next.floor][next.x][next.y] == '#')
{
next.floor = !next.floor;
if (check(next.floor, next.x, next.y))
continue;
if (vis[next.floor][next.x][next.y])
continue;
if (map[next.floor][next.x][next.y] == '*' || map[next.floor][next.x][next.y] == '#')
continue;
vis[next.floor][next.x][next.y] = 1;
}
if (next.floor == e[0] && next.x == e[1] && next.y == e[2])
{
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
Q.push(next);
}
}
cout << "NO\n";
}
int main()
{
int i, j, k;
cin>>t;
while (t--)
{
cin >> n >> m >> lim;
for (k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> map[k][i];
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (map[k][i][j] == 'S')
{
s[0] = k, s[1] = i, s[2] = j;
}
else if (map[k][i][j] == 'P')
{
e[0] = k, e[1] = i, e[2] = j;
}
}
}
}
bfs();
}
}
|
Minimum Inversion Number |
| Problem Description |
| The inversion number of a given number sequence a1, a2, ..., an is the number of pairs (ai, aj) that satisfy i < j and ai > aj.
For a given sequence of numbers a1, a2, ..., an, if we move the first m >= 0 numbers to the end of the seqence, we will obtain another sequence. There are totally n such sequences as the following:
a1, a2, ..., an-1, an (where m = 0 - the initial seqence)
a2, a3, ..., an, a1 (where m = 1)
a3, a4, ..., an, a1, a2 (where m = 2)
...
an, a1, a2, ..., an-1 (where m = n-1)
You are asked to write a program to find the minimum inversion number out of the above sequences. |
| nput |
| The input consists of a number of test cases. Each case consists of two lines: the first line contains a positive integer n (n <= 5000); the next line contains a permutation of the n integers from 0 to n-1. |
| Output |
| For each case, output the minimum inversion number on a single line. |
| Sample Input |
10
1 3 6 9 0 8 5 7 4 2 |
| Sample Output 16 |
| 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/sdutyangkun/article/details/54845981 思路: 总共有N个数,如何判断第i+1个数到最后一个数之间有多少个数小于第i个数呢?不妨假设有一个区间 [1,N],只需要判断区间[i+1,N]之间有多少个数小于第i个数。如果我们把总区间初始化为0,然后把第i个数之前出现过的数都在相应的区间把它的值定为1,那么问题就转换成了[i+1,N]值的总和。再仔细想一下,区间[1,i]的值+区间[i+1,N]的值=区间[1,N]的值(i已经标记为1),所以区间[i+1,N]值的总和等于N-[1,i]的值!因为总共有N个数,不是比它小就是比它(大或等于)。 现在问题已经转化成了区间问题,枚举每个数,然后查询这个数前面的区间值的总和,i-[1,i]既为逆序数。 AC代码如下: #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define lson l, m, rt<<1
#define rson m+1, r, rt<<1|1
#define size 5005
#define min(a, b) a > b ? b : a
int num[size << 2], x[size];
void pushup(int rt)
{
num[rt] = num[rt << 1] + num[rt << 1 | 1];
}
void build(int l, int r, int rt)
{
num[rt] = 0;
if (l == r) return;
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
}
int qurey(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (L <= l && r <= R)
return num[rt];
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
int ans = 0;
if (L <= m) ans += qurey(L, R, lson);
if (R > m) ans += qurey(L, R, rson);
return ans;
}
void updata(int p, int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
num[rt]++; return;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m) updata(p, lson);
else updata(p, rson);
pushup(rt);
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin>>n)
{
int sum = 0;
build(0, n - 1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> x[i];
sum += qurey(x[i], n - 1, 0, n - 1, 1);
updata(x[i], 0, n - 1, 1);
}
int tmp = sum;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sum += n - x[i] - x[i] - 1;
tmp = min(tmp, sum);
}
cout << tmp << endl;
}
}
|
Brownie Points II |
| Problem Description |
| Stan and Ollie play the game of Odd Brownie Points. Some brownie points are located in the plane, at integer coordinates. Stan plays first and places a vertical line in the plane. The line must go through a brownie point and may cross many (with the same x-coordinate). Then Ollie places a horizontal line that must cross a brownie point already crossed by the vertical line.
Those lines divide the plane into four quadrants. The quadrant containing points with arbitrarily large positive coordinates is the top-right quadrant.
The players score according to the number of brownie points in the quadrants. If a brownie point is crossed by a line, it doesn't count. Stan gets a point for each (uncrossed) brownie point in the top-right and bottom-left quadrants. Ollie gets a point for each (uncrossed) brownie point in the top-left and bottom-right quadrants.
Stan and Ollie each try to maximize his own score. When Stan plays, he considers the responses, and chooses a line which maximizes his smallest-possible score. |
| Input |
| Input contains a number of test cases. The data of each test case appear on a sequence of input lines. The first line of each test case contains a positive odd integer 1 < n < 200000 which is the number of brownie points. Each of the following n lines contains two integers, the horizontal (x) and vertical (y) coordinates of a brownie point. No two brownie points occupy the same place. The input ends with a line containing 0 (instead of the n of a test). |
| Output |
| For each input test, print a line of output in the format shown below. The first number is the largest score which Stan can assure for himself. The remaining numbers are the possible (high) scores of Ollie, in increasing order. |
| Sample Input |
11
3 2
3 3
3 4
3 6
2 -2
1 -3
0 0
-3 -3
-3 -2
-3 -4
3 -7
0 |
| Sample Output |
Stan: 7; Ollie: 2 3; |
| 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/libin56842/article/details/46582685 这道题怎么着都没懂,看别人的博客: 题意:平面上有若干点,stan通过一个点划了一条直线,ollie通过在这条垂直直线上的点作了一条水平线,平面被分成4个象限,定义stan获得的分数为1,3象限的点的数量,ollie获得的分数为2,4象限上的点的数量,线上的点不归任何人所有。两人都采用最优的策略使自己获得的点数最大。由于stan的选择具有主动权,为了对自己有利,求stan所能够获得的最小的可能的分数最大,输出该分数,并输出ollie可能的分数。 思路:首先分析可以得到:stan画的线上如果没有其他点,那么ollie的选择只有一个。如果有多个点,ollie会选择自己分数高的点,如果相同,选择stan分数低的点。 实现: 定义right[i],第i个点的正右方向,left[i],第i个点的负左方向,up[i]第i个点的正上方向,down[i]第i个点的负下方向。并且定义:TR,TL,BL,BR为第一象限上的点。 首先对y升序排序(y相同按x升序排序),获得对large(反向),left(正向),right(反向)的统计。由于题目中没有明确的坐标范围,因此需要对点进行离散化,并且排序操作已经已经使得一个点对的一维操作已经有序,那么我们只要离散此时的y值,得到原来的下标对应的按x排序后的下标。为了得到up,down的统计值,然后再对x升序排序(x相同升序y)。如此就有我们所需要的所有数据。设定一条垂直线,水平从第一个点向右移动,得到最小的没有被访问过的点的横坐标的原来的编号对应的通过y离散化后的编号,,用树状数组维护左下的点数,计算并统计更新答案。 #include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 200005;
int c[maxn];
int up[maxn];
int down[maxn];
int righ[maxn];
int lef[maxn];
int large[maxn];
int id[maxn];
int n;
int lowbit(int i) { return i&(-i); }
void add(int x, int v) {
while (x<maxn) {
c[x] += v;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int getsum(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x>0) {
res += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
struct node {
int x, y, id;
}p[maxn];
void init(void) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
c[i] = large[i] = up[i] = down[i] = lef[i] = righ[i] = 0;
}
}
int cmp1(node a, node b) {
if (a.x != b.x)return a.x<b.x;
return a.y<b.y;
}
int cmp2(node a, node b) {
if (a.y != b.y)return a.y<b.y;
return a.x<b.x;
}
int main() {
while (cin>>n&& n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
p[i].id = i;
}
init();
sort(p, p + n, cmp2);//先对y排序
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (p[i].y == p[i - 1].y) {
lef[p[i].id] = lef[p[i - 1].id] + 1;
}
if (p[n - i - 1].y == p[n - i].y) {
large[p[n - i - 1].id] = large[p[n - i].id];
righ[p[n - i - 1].id] = righ[p[n - i].id] + 1;
}
else {
large[p[n - i - 1].id] = i;
}
}
int k = 1;
id[p[0].id] = k;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {//对y离散化
if (p[i].y == p[i - 1].y) {
id[p[i].id] = k;
}
else {
id[p[i].id] = ++k;
}
}
sort(p, p + n, cmp1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (p[i].x == p[i - 1].x) {
down[p[i].id] = down[p[i - 1].id] + 1;
}
if (p[n - i - 1].x == p[n - i].x) {
up[p[n - i - 1].id] = up[p[n - i].id] + 1;
}
}
int px = p[0].x;//垂直线
set<int>st;
int s_min_max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int omin = maxn;
int omax = 0;
while (i < n&&p[i].x == px) {//竖直线上的所有的点
int yid = id[p[i].id];//离散化后的点
int BL = getsum(yid) - lef[p[i].id] - down[p[i].id];
int TL = i - BL - lef[p[i].id] - down[p[i].id];
int TR = large[p[i].id] - TL - up[p[i].id];
int BR = n - 1 - TL - TR - BL - up[p[i].id] - lef[p[i].id] - righ[p[i].id] - down[p[i].id];
add(yid, 1);
int ollie = TL + BR;
if (omax < ollie) {
omax = ollie;
omin = TR + BL;
}
else if (omax == ollie) {
omin = min(omin, TR + BL);
}
i++;
}
if (i < n)px = p[i--].x;
if (omin > s_min_max) {
s_min_max = omin;
st.clear();
st.insert(omax);
}
else if (omin == s_min_max) {
st.insert(omax);
}
}
cout << "Stan: " << s_min_max << "; Ollie:";
set<int>::iterator it;
for (it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); it++) {
cout <<" "<<*it;
}
cout << ";\n";
}
}
|























 174
174

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








