Nightmare
Problem Description
Ignatius had a nightmare last night. He found himself in a labyrinth with a time bomb on him. The labyrinth has an exit, Ignatius should get out of the labyrinth before the bomb explodes. The initial exploding time of the bomb is set to 6 minutes. To prevent the bomb from exploding by shake, Ignatius had to move slowly, that is to move from one area to the nearest area(that is, if Ignatius stands on (x,y) now, he could only on (x+1,y), (x-1,y), (x,y+1), or (x,y-1) in the next minute) takes him 1 minute. Some area in the labyrinth contains a Bomb-Reset-Equipment. They could reset the exploding time to 6 minutes.
Given the layout of the labyrinth and Ignatius' start position, please tell Ignatius whether he could get out of the labyrinth, if he could, output the minimum time that he has to use to find the exit of the labyrinth, else output -1.
Here are some rules:
1. We can assume the labyrinth is a 2 array.
2. Each minute, Ignatius could only get to one of the nearest area, and he should not walk out of the border, of course he could not walk on a wall, too.
3. If Ignatius get to the exit when the exploding time turns to 0, he can't get out of the labyrinth.
4. If Ignatius get to the area which contains Bomb-Rest-Equipment when the exploding time turns to 0, he can't use the equipment to reset the bomb.
5. A Bomb-Reset-Equipment can be used as many times as you wish, if it is needed, Ignatius can get to any areas in the labyrinth as many times as you wish.
6. The time to reset the exploding time can be ignore, in other words, if Ignatius get to an area which contain Bomb-Rest-Equipment, and the exploding time is larger than 0, the exploding time would be reset to 6.
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of the input is a single integer T which is the number of test cases. T test cases follow.
Each test case starts with two integers N and M(1<=N,Mm=8) which indicate the size of the labyrinth. Then N lines follow, each line contains M integers. The array indicates the layout of the labyrinth.
There are five integers which indicate the different type of area in the labyrinth:
0: The area is a wall, Ignatius should not walk on it.
1: The area contains nothing, Ignatius can walk on it.
2: Ignatius' start position, Ignatius starts his escape from this position.
3: The exit of the labyrinth, Ignatius' target position.
4: The area contains a Bomb-Reset-Equipment, Ignatius can delay the exploding time by walking to these areas.
Output
For each test case, if Ignatius can get out of the labyrinth, you should output the minimum time he needs, else you should just output -1.
Sample Input
3
3 3
2 1 1
1 1 0
1 1 3
4 8
2 1 1 0 1 1 1 0
1 0 4 1 1 0 4 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 4 1 1 1 3
5 8
1 2 1 1 1 1 1 4
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
1 4 1 0 1 1 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 3 0 1
1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
4
-1
13
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36616023/article/details/72765469
题解:还是广搜问题,
但是需要注意炸弹六秒会炸,并且走过的路径可以重复,氮气根本还是走最短的步数,所以用广搜。
我们可以这样想,用一个map[][]来记录某点的数字,如果该点不是0,炸弹要炸的时间大于0秒,没有越界,则就可以判断该点是不是到达终点,是不是炸弹的时间可以重置(需要注意的是,炸弹重置只能重置一次,下次经过该点,不能再被重置)
下面给出AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = { 0,1,1,0,-1,0,0,-1 };
int map[10][10], m, n;
struct node
{
int x, y;
int time, step;
}start;
void bfs()
{
queue <node> q;
struct node head, tail;
q.push(start);
int k;
while (!q.empty())
{
head = q.front();
q.pop();
for (k = 0; k<4; k++)
{
tail.x = head.x + dir[k][0];
tail.y = head.y + dir[k][1];
tail.time = head.time - 1;
tail.step = head.step + 1;
if (tail.x >= 0 && tail.y >= 0 && tail.x<n&&tail.y<m&&map[tail.x][tail.y] != 0 && tail.time>0)
{
if (map[tail.x][tail.y] == 3)
{
cout << tail.step << endl;
return;
}
else if (map[tail.x][tail.y] == 4)
{
tail.time = 6;
map[tail.x][tail.y] = 0;
}
q.push(tail);
}
}
}
cout << "-1\n";
return;
}
int main()
{
int i, j, T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 2)
{
start.x = i;
start.y = j;
start.step = 0;
start.time = 6;
}
}
bfs();
}
}What Are You Talking About
Problem Desccription
Ignatius is so lucky that he met a Martian yesterday. But he didn't know the language the Martians use. The Martian gives him a history book of Mars and a dictionary when it leaves. Now Ignatius want to translate the history book into English. Can you help him?
Input
The problem has only one test case, the test case consists of two parts, the dictionary part and the book part. The dictionary part starts with a single line contains a string "START", this string should be ignored, then some lines follow, each line contains two strings, the first one is a word in English, the second one is the corresponding word in Martian's language. A line with a single string "END" indicates the end of the directory part, and this string should be ignored. The book part starts with a single line contains a string "START", this string should be ignored, then an article written in Martian's language. You should translate the article into English with the dictionary. If you find the word in the dictionary you should translate it and write the new word into your translation, if you can't find the word in the dictionary you do not have to translate it, and just copy the old word to your translation. Space(' '), tab('\t'), enter('\n') and all the punctuation should not be translated. A line with a single string "END" indicates the end of the book part, and that's also the end of the input. All the words are in the lowercase, and each word will contain at most 10 characters, and each line will contain at most 3000 characters.
Output
In this problem, you have to output the translation of the history book.
Sample Input
START
from fiwo
hello difh
mars riwosf
earth fnnvk
like fiiwj
END
START
difh, i'm fiwo riwosf.
i fiiwj fnnvk!
END
Sample Output
hello, i'm from mars.
i like earth!
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
水题,直接给代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a, b;
map<string, string> mp;
cin >> a;
while (cin >> a&&a != "END")
{
cin >> b;
mp[b] = a;
}
cin >> a;
getchar();
char ch[3005];
while (1)
{
gets_s(ch);
int i, len;
if (strcmp(ch, "END") == 0)
break;
len = strlen(ch);
b = "";
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (ch[i]<'a' || ch[i]>'z')///当ch[i]不是字母的时候输出‘b’对应的单词;
{
if (mp[b] != "") ///如果‘b’有对应的单词时直接输出对应的单词
cout << mp[b];
else ///如果‘b’没有对应的值时直接输出‘b‘;
cout << b;
b = ""; ///初始化’b‘;
cout << ch[i];
}
else
b += ch[i];///当ch[i]是字母的时候用原来的字符串加上ch【i】;
}
cout << endl;
}
}11389 - The Bus Driver Problem
In a city there are n bus drivers. Also there are n morning bus routes and n afternoon bus routes with various lengths. Each driver is assigned one morning route and one evening route. For any driver, if his total route length for a day exceeds d, he has to be paid overtime for every hour after the first d hours at a flat r taka / hour. Your task is to assign one morning route and one evening route to each bus driver so that the total overtime amount that the authority has to pay is minimized.
Input
The first line of each test case has three integers n, d and r, as described above. In the second line, there are n space separated integers which are the lengths of the morning routes given in meters. Similarly the third line has n space separated integers denoting the evening route lengths. The lengths are positive integers less than or equal to 10000. The end of input is denoted by a case with three 0’s.
Output
For each test case, print the minimum possible overtime amount that the authority must pay. Constraints
• 1 ≤ n ≤ 100
• 1 ≤ d ≤ 10000
• 1 ≤ r ≤ 5
Sample Input
2 20 5
10 15
10 15
2 20 5
10 10
10 10
0 0 0
Sample Output
50
0
题意:n个司机,n个下午路线和n个夜间的行驶时间。每个司机恰好分配到一个下午路线和一个夜间路线。司机行驶如果超过规定的行驶总时间,每个单位时间要多付给司机r元,求最小要给所有司机的加班费。
思路;贪心,将两个时间段的行驶时间排序,然后依次取最大和最小相加减去规定时间。那么超过的时间将最小,加班费也会最小。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 105;
int x[MAXN], y[MAXN];
int n, d, r;
int main() {
while (cin>>n>>d>>r && n && d && r) {
if (!n && !d && !r)
break;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> x[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> y[i];
sort(x, x + n);
sort(y, y + n);
long long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int temp = x[i] + y[n - 1 - i];
if (temp - d > 0)
sum += temp - d;
}
cout << sum * r << endl;
}I Hate It
Problem Description
很多学校流行一种比较的习惯。老师们很喜欢询问,从某某到某某当中,分数最高的是多少。
这让很多学生很反感。
不管你喜不喜欢,现在需要你做的是,就是按照老师的要求,写一个程序,模拟老师的询问。当然,老师有时候需要更新某位同学的成绩。
Input
本题目包含多组测试,请处理到文件结束。
在每个测试的第一行,有两个正整数 N 和 M ( 0<N<=200000,0<M<5000 ),分别代表学生的数目和操作的数目。
学生ID编号分别从1编到N。
第二行包含N个整数,代表这N个学生的初始成绩,其中第i个数代表ID为i的学生的成绩。
接下来有M行。每一行有一个字符 C (只取'Q'或'U') ,和两个正整数A,B。
当C为'Q'的时候,表示这是一条询问操作,它询问ID从A到B(包括A,B)的学生当中,成绩最高的是多少。
当C为'U'的时候,表示这是一条更新操作,要求把ID为A的学生的成绩更改为B。
Output
对于每一次询问操作,在一行里面输出最高成绩。
Sample Input
5 6
1 2 3 4 5
Q 1 5
U 3 6
Q 3 4
Q 4 5
U 2 9
Q 1 5
Sample Output
5
6
5
9
题解:线段树入门题,照着模板写,但是总是TLE,看不懂.
以下是TLE代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxx = 200005;
int s[maxx], mx[maxx * 4];
void pushup(int rt)
{
mx[rt] = max(mx[rt * 2], mx[rt * 2 + 1]); //求最大值
}
void build(int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
mx[rt] = s[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(l, mid, rt * 2);
build(mid + 1, r, rt * 2 + 1);
pushup(rt);
}
int query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (L <= l && R >= r) return mx[rt];
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
int ret = 0;
if (L <= mid) ret = max(ret, query(L, R, l, mid, rt * 2));
if (R>mid) ret = max(ret, query(L, R, mid + 1, r, rt * 2 + 1));
return ret;
}
void update(int L, int s, int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
mx[rt] = s;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (L <= mid) update(L, s, l, mid, rt * 2);
else update(L, s, mid + 1, r, rt * 2 + 1);
pushup(rt);
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
while (cin>>n>>m&&n&&m)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> s[i];
build(1, n, 1);
int a, b;
char ch;
while (m--)
{
cin >> ch >> a >> b;
if (ch == 'Q') cout << query(a, b, 1, n, 1) << endl;
else update(a, b, 1, n, 1);
}
}
return 0;
}Jungle Roads
Description
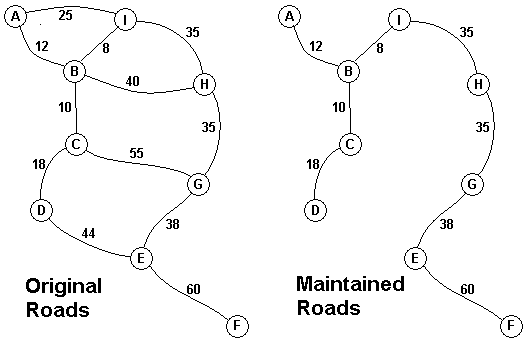
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
Input
The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
Output
The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
Sample Input
9 A 2 B 12 I 25 B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8 C 2 D 18 G 55 D 1 E 44 E 2 F 60 G 38 F 0 G 1 H 35 H 1 I 35 3 A 2 B 10 C 40 B 1 C 20
0
Sample Output
216
30
题解;最小生成树+并查集;但很难理解,只能看模板(Find函数)
下面给出AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 27;
struct Edge
{
int v, u;
int cost;
}e[N*(N - 1) / 2];
int set[N];
int Find(int x)
{
if (x == set[x]) return x;
return Find(set[x]);
}
bool operator < (const Edge& a, const Edge& b)
{
return a.cost < b.cost;
}
int main()
{
int n, k, w, minCost;
char c1, c2;
while (cin >> n && n)
{
minCost = 0;
int j = 0; //j为边数
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) set[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> c1 >> k;
for (; k--; j++)
{
cin >> c2 >> w;
e[j].v = c1 - 'A';
e[j].u = c2 - 'A';
e[j].cost = w;
}
}
sort(e, e + j);
//for(int i = 0; i < j; ++i)
//cout << e[i].v << " " << e[i].u << " " << e[i].cost << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < j; ++i)
{
int set1 = Find(e[i].v);
int set2 = Find(e[i].u);
if (set1 != set2)
{
minCost += e[i].cost;
if (set1 < set2)
set[set2] = set1;
else if (set1 > set2)
set[set1] = set2;
}
}
cout << minCost << endl;
}
}






















 549
549

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








