如何将下图的NFA转化为DFA呢?
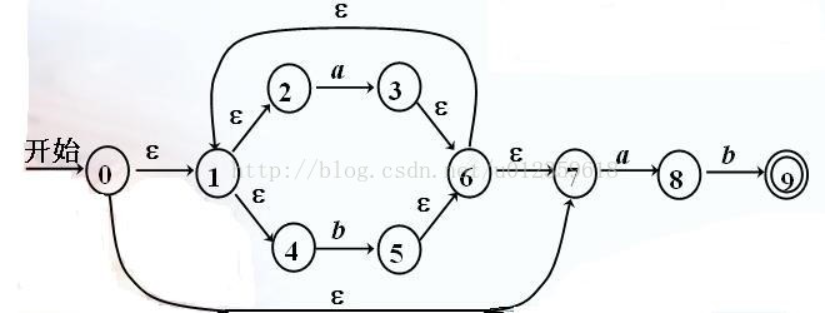
图1
解答如下:
- 求出
ε
_
c
l
o
s
u
r
e
(
s
)
ε\_closure(s)
ε_closure(s)
ε _ c l o s u r e ( s ) ε\_closure(s) ε_closure(s)表示由状态 s s s 经由条件 ε ε ε 可以到达的所有状态的集合
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } ε\_closure(0)=\{0,1,2,4,7\} ε_closure(0)={0,1,2,4,7}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 1 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 } ε\_closure(1)=\{1,2,4\} ε_closure(1)={1,2,4}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 2 ) = { 2 } ε\_closure(2)=\{2\} ε_closure(2)={2}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 3 ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 } ε\_closure(3)=\{1,2,3,4,6,7\} ε_closure(3)={1,2,3,4,6,7}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 4 ) = { 4 } ε\_closure(4)=\{4\} ε_closure(4)={4}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 5 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } ε\_closure(5)=\{1,2,4,5,6,7\} ε_closure(5)={1,2,4,5,6,7}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 6 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 6 , 7 } ε\_closure(6)=\{1,2,4,6,7\} ε_closure(6)={1,2,4,6,7}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 7 ) = { 7 } ε\_closure(7)=\{7\} ε_closure(7)={7}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 8 ) = { 8 } ε\_closure(8)=\{8\} ε_closure(8)={8}
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 9 ) = { 9 } ε\_closure(9)=\{9\} ε_closure(9)={9}
- 下面的A,B,C…表示一种状态。如A表示 { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } \{0,1,2,4,7\} {0,1,2,4,7},其实就是 ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) ε\_closure(0) ε_closure(0)
为了读懂下面的内容,在这里先解释几个东西。
- ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( A , a ) ) ε\_closure(move(A,a)) ε_closure(move(A,a)) 中的 m o v e ( A , a ) move(A,a) move(A,a)是什么意思呢?
它代表从状态A,经过a到达的状态。
A状态是 ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } ε\_closure(0) = \{0,1,2,4,7\} ε_closure(0)={0,1,2,4,7},在 { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } \{0,1,2,4,7\} {0,1,2,4,7}里面,对每一个元素都考虑其是否通过a到达了某个状态,观察图1,只有状态2和7经过了a,分别到达了3和8,所以 m o v e ( A , a ) move(A,a) move(A,a) = { 3 , 8 } \{3,8\} {3,8},从而有 ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( A , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } ε\_closure(move(A,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} ε_closure(move(A,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}, { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} {1,2,3,4,6,7,8}是未出现过的状态,所以可把它取名为B状态(其它名字也行).- ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}是怎么来的呢?
因为在步骤1我们已经知道, ε _ c l o s u r e ( 3 ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 } ε\_closure(3)=\{1,2,3,4,6,7\} ε_closure(3)={1,2,3,4,6,7}, ε _ c l o s u r e ( 8 ) = { 8 } ε\_closure(8)=\{8\} ε_closure(8)={8} ,然后取它们的并集就得到了 { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} {1,2,3,4,6,7,8}.
这样应该解释明白了。继续往下看,然后不懂的话再倒回来看看。
ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } = A ε\_closure(0) = \{0,1,2,4,7\} = A ε_closure(0)={0,1,2,4,7}=A
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( A , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } = B ε\_closure(move(A,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} = B ε_closure(move(A,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}=B
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( A , b ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( 5 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } = C ε\_closure(move(A,b)) = ε\_closure(5) = \{1,2,4,5,6,7\} = C ε_closure(move(A,b))=ε_closure(5)={1,2,4,5,6,7}=C
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( B , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } = B ε\_closure(move(B,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} = B ε_closure(move(B,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}=B
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( B , b ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 5 , 9 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 9 } = D ε\_closure(move(B,b)) = ε\_closure(\{5,9\}) =\{1,2,4,5,6,7,9\} = D ε_closure(move(B,b))=ε_closure({5,9})={1,2,4,5,6,7,9}=D
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( C , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } = B ε\_closure(move(C,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} = B ε_closure(move(C,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}=B
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( C , b ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( 5 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } = C ε\_closure(move(C,b)) = ε\_closure(5) = \{1,2,4,5,6,7\} = C ε_closure(move(C,b))=ε_closure(5)={1,2,4,5,6,7}=C
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( D , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } = B ε\_closure(move(D,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} = B ε_closure(move(D,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}=B
ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( D , b ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( 5 ) = { 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } = C ε\_closure(move(D,b)) = ε\_closure(5) = \{1,2,4,5,6,7\} = C ε_closure(move(D,b))=ε_closure(5)={1,2,4,5,6,7}=C
- 画出DFA状态转换表
步骤2中有A,B,C,D四种情况,其中A是初始情况( ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 4 , 7 } ε\_closure(0)=\{0,1,2,4,7\} ε_closure(0)={0,1,2,4,7}. 多说几句,在NFA图1中,是从0出发的,所以初始情况是 ε _ c l o s u r e ( 0 ) ε\_closure(0) ε_closure(0),那假设如果是从X开始,则初始情况是 ε _ c l o s u r e ( X ) ε\_closure(X) ε_closure(X))
看步骤2, ε _ c l o s u r e ( m o v e ( A , a ) ) = ε _ c l o s u r e ( { 3 , 8 } ) = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 } = B ε\_closure(move(A,a)) = ε\_closure(\{3,8\}) = \{1,2,3,4,6,7,8\} = B ε_closure(move(A,a))=ε_closure({3,8})={1,2,3,4,6,7,8}=B,所以A行a列填B,其他同理。
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | C |
| B | B | D |
| C | B | C |
| D | B | C |
- 根据DFA状态转换表画出DFA状态转换图
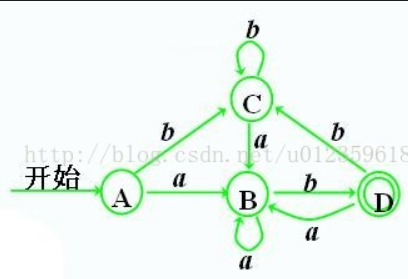
看步骤3的表格,A经过a到B,A经过b到C,B经过a到B,以此类推…
参考:
NFA到DFA的转化🔗








 本文详细介绍了如何将非确定有限状态自动机(NFA)转换为确定有限状态自动机(DFA),通过具体实例展示了ε-closure操作和状态转移过程。首先计算每个状态的ε-closure,接着根据NFA的状态转移,逐步构造DFA的转换表。最终形成DFA状态转换图,用于理解NFA到DFA的转换原理。
本文详细介绍了如何将非确定有限状态自动机(NFA)转换为确定有限状态自动机(DFA),通过具体实例展示了ε-closure操作和状态转移过程。首先计算每个状态的ε-closure,接着根据NFA的状态转移,逐步构造DFA的转换表。最终形成DFA状态转换图,用于理解NFA到DFA的转换原理。


















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










