线性回归算法从0开始的实现
参考:
range函数作用
sum()函数作用
backward作用
torch.matmul()用法介绍
yield作用
with语法
grad作用
各模块分析
构造数据集
我们是构造已知W,b的具体数据
- num_examples为生成的样本数
- torch.matmul()用法介绍
- torch.normal生成均值为0,方差为1,大小为W的长度的n各样本的随机数
- y.reshape((-1, 1)的作用为转化y的形状
#构造人造数据集
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples): #@save
"""生成y=Xw+b+噪声"""
#生成一个均值为0,方差为1的随机数X,
# 大小为n个样本,列数为w的长度
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w)))
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b
#加入一个均值为0,方差为0.01,形状为y同样形状的噪音
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
#print("X.shape==",X.shape,"y.shape==",y.shape)
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
print('features:', features[0],'\nlabel:', labels[0])
我们可以输出查看X,y的形状
print("X.shape==",X.shape,"y.shape==",y.shape)
>>>X.shape== torch.Size([1000, 2]) y.shape== torch.Size([1000])
读取小批量数据
- 每次读入batch_size长度的数据
- features, labels分别为synthetic_data构造数据集中返回的X,y.reshape
- yield作用,相当于一个下一次返回地点是上一次结束地点的return
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
#生成每个样本的列表数据
indices = list(range(num_examples))
# 这些样本是随机读取的,没有特定的顺序
#使用random.shuffle将下标完全打乱,随机打乱后用随机顺序访问样本
random.shuffle(indices) print("num+examples:",num_examples,'\nbatch_size:',batch_size)
#产生从0到num_examples,每一次跳batch_size的大小
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
#min的在作用是防止最后一次取值不能取满,所有如果没有取满,就用num_examples
batch_indices = torch.tensor(
indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
#生成batch_size的小批量
batch_size = 10
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print('X==',X, '\ny==', y)
break
对for循环中的数据进行检查如下
num_examples: 1000
batch_size: 10
i== 0 batch_indices== tensor([499, 440, 731, 154, 335, 898, 874, 842, 238, 969])
i== 10 batch_indices== tensor([ 12, 794, 745, 243, 780, 357, 379, 405, 669, 551])
i== 20 batch_indices== tensor([218, 309, 565, 839, 858, 579, 718, 818, 429, 519])
i== 30 batch_indices== tensor([726, 988, 475, 531, 829, 3, 580, 658, 948, 861])
......
i== 980 batch_indices== tensor([127, 623, 95, 553, 156, 474, 947, 884, 518, 997])
i== 990 batch_indices== tensor([935, 200, 267, 472, 782, 351, 674, 48, 632, 511])
初始化模型参数
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2,1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
print('\n\nw==',w,'\nb==',b)
w== tensor([[-0.0048],[-0.0116]],requires_grad=True)
b== tensor([0.], requires_grad=True)
线性回归模型函数
线性回归模型原理

线性回归模型实现
def linreg(X, w, b):
"""线性回归模型。"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
其中可以看出torch.matmul(X, w)的形状
print(torch.matmul(X, w).shape)
torch.Size([1000, 1])
均方损失模型
均方损失模型原理

均方损失模型实现
def squared_loss(y_hat, y): #@save
"""均方损失"""
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape)) ** 2 / 2
其中y_hat为真实值
y.reshape(y_hat.shape)
因为y与y_hat的元素个数可能是一样,但是可能会一个是向量,一个是行向量或者列向量,所以将y和y_hat的维度统一,方便进行计算
定义优化算法
优化算法原理
通过对初始值的迭代,按学习率沿梯度方向逐步求最优值
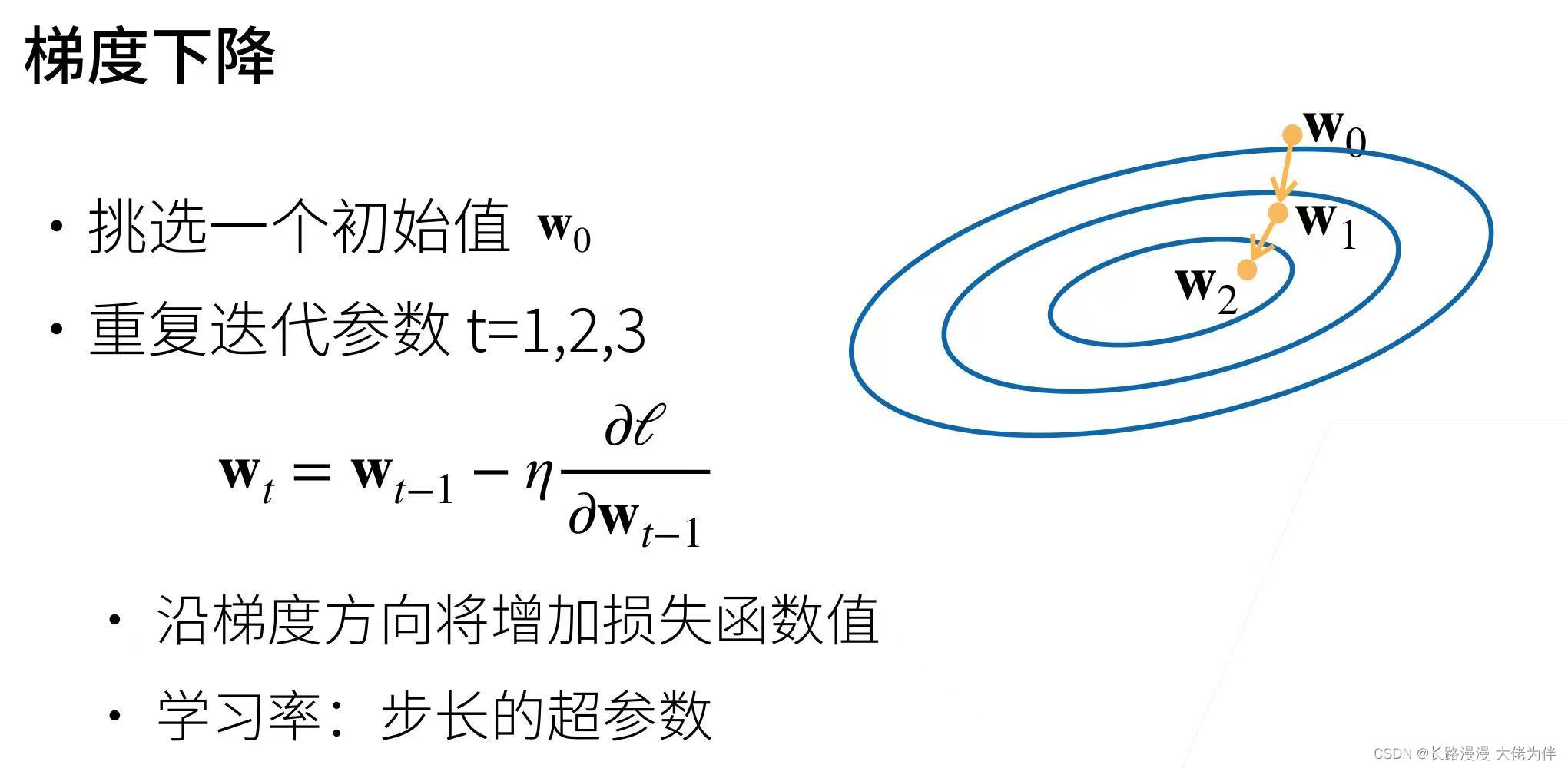
优化算法实现
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size): #@save
"""小批量随机梯度下降"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
grad作用,用来求导
param.grad.zero_()
pytorch中不会对梯度自动设为0,这里需要人为设置
最终实现
先来看看调用实现,
- 将学习率设为lr
- 梯度更新次数为3次
- linreg函数为定义线性回归模型的函数
- squared_loss函数为损失函数
- data_iter函数作用为读取小批量数据
- sgd函数作用为更新梯度
l.sum().backward()
- sum的作用,将向量转化为标量,因为backward是对标量进行处理,backward只能被应用在一个标量上,也就是一个一维tensor
- backward作用:对标量自动求导
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) # X和y的小批量损失
# 因为l形状是(batch_size,1),而不是一个标量。l中的所有元素被加到一起,
# 并以此计算关于[w,b]的梯度
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 使用参数的梯度更新参数
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')
print(f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b}')
运行结果:
epoch 1, loss 0.042265
epoch 2, loss 0.000164
epoch 3, loss 0.000053
w的估计误差: tensor([ 0.0006, -0.0007], grad_fn=<SubBackward0>)
b的估计误差: tensor([0.0002], grad_fn=<RsubBackward1>)






















 336
336











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








