1.栈的定义与用处
栈是只允许在一端进行插入或者删除操作的线性表。栈顶,线性表允许进行插入删除的那一端;栈底,固定的不允许插入的一端。如下图所示:
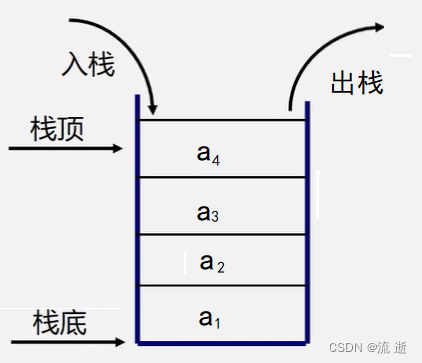
栈的操作是先进后出,因此常用在函数的传值或传值,就是一般在进行函数的操作时,如果传入的值超过函数栈时,就会报出栈溢出的错误。
栈与线性表的不同仅在于运算规则的不同:

2.栈的线性表实现
因为栈时从一端进入一端出来,因此用线性存储时,将插入的元素都置于表尾即可,因此插入取出删除都是在表尾进行。
这里栈的顺序表的实现定义,一个是数据的指针域一个为其栈顶,通过判断是否已经到达栈顶,从而去判断栈空或者栈满。而指针域指向的数据则是存储栈的内容。
另外一种栈的顺序表的实现定义,可以定义为栈底指针跟栈顶指针,通过判断栈顶与栈底相减从而判断栈空或者栈满。
栈顺序表的实现跟一般线性表顺序表实现是非常相似的,只有进栈出栈的规则不一样罢了。
栈的顺序定义可为:
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct Stack
{
Elemtype* data;
int top;
}SqStack;栈的顺序表实现有以下函数:
SqStack InitStack(SqStack* S); //初始化空栈
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S); //判断栈是否为空
Status Push(SqStack* S, int x); //进栈
Status Pop(SqStack* S, Elemtype* e); //出栈
Status GetTop(SqStack S, Elemtype* e); //返回栈顶元素
Status DestroyStack(SqStack* S); //销毁栈具体实现代码:
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef int Status;
typedef struct Stack
{
Elemtype* data;
int top;
}SqStack;
SqStack InitStack(SqStack* S); //初始化空栈
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S); //判断栈是否为空
Status Push(SqStack* S, int x); //进栈
Status Pop(SqStack* S, Elemtype* e); //出栈
Status GetTop(SqStack S, Elemtype* e); //返回栈顶元素
Status DestroyStack(SqStack* S); //销毁栈
Stack.c
#include "Stack.h"
SqStack InitStack(SqStack* S) //初始化空栈
{
S->data = (Elemtype*)malloc(sizeof(Elemtype) * MaxSize);
S->top = -1;
return *S;
}
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S) //判断栈是否为空
{
if (S.top == -1)
{
return OK;
}
else {
return FALSE;
}
}
Status Push(SqStack* S, int x) //进栈
{
if (S->top == MaxSize - 1) {
return FALSE;
}
S->data[++S->top] = x;
return OK;
}
Status Pop(SqStack* S, Elemtype* e) //出栈
{
if (S->top == -1) {
return FALSE;
}
*e = S->data[S->top];
S->top--;
return OK;
}
Status GetTop(SqStack S, Elemtype* e) //返回栈顶元素
{
if (S.top == -1)
{
return FALSE;
}
*e = S.data[S.top];
return OK;
}
Status ClearStack(SqStack* S)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MaxSize; i++)
{
if (S->top == -1)
{
break;
}
else {
S->top--;
}
}
return OK;
}
Status DestroyStack(SqStack* S) //销毁栈
{
ClearStack(S);
if (S->data)
{
free(S->data);
}
return OK;
}
test.c
#include "Stack.h"
int main()
{
SqStack S;
Elemtype e;
int x = 0;
InitStack(&S); //初始化空栈
int Flag = StackEmpty(S); //判断栈是否为空
for (x = 0; x < 10; x++)
{
Push(&S, x); //进栈
}
for (x = 0; x < 5; x++)
{
Pop(&S, &e); //出栈
printf("%d ", e);
}
printf("\n");
GetTop(S, &e); //返回栈顶元素
printf("%d \n", e);
DestroyStack(&S); //销毁栈
if (GetTop(S, &e)) {
printf("%d \n", e);
}
else {
printf("出错了!");
}
return 0;
}3.栈的链表实现
栈的链表的实现,跟一般线性表的链表实现也是非常的相似,只有插入的位置在链表的头,而有带头结点的链表和没有带头结点的链表也有一定的区别,这里实现采用的是有带头结点的链表。带头结点的链表则是通过判断下一个指针是否为NULL从而来判断指针空与否。
没有带头结点的链表的话其第一个元素就为栈顶,通过定义栈的长度从而去判断栈是否已经到底了。
以下实现是带头结点的链表;
栈链表定义:一个数据域跟一个指针域,指针域指向下一个结点的位置。
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct SNode
{
Elemtype data;
struct SNode* next;
}SNode,*LinkStack;各种函数的定义:
typedef int Status;
LinkStack InitLinkStack(LinkStack S); //初始化栈
Status StackEmpty(LinkStack S); //判断栈空
Status Posh(LinkStack S,Elemtype e); //进栈
Status Pop(LinkStack S, Elemtype* e); //出栈
Status PrintStack(LinkStack S); //打印栈
Status GetTop(SNode S, Elemtype* e); //获取栈顶
Status ClearStack(LinkStack S); //清空栈
Status DestryStack(LinkStack S); //销毁栈具体实现的文件
LinkStack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status;
typedef int Elemtype;
typedef struct SNode
{
Elemtype data;
struct SNode* next;
}SNode,*LinkStack;
LinkStack InitLinkStack(LinkStack S); //初始化栈
Status StackEmpty(LinkStack S); //判断栈空
Status Posh(LinkStack S,Elemtype e); //进栈
Status Pop(LinkStack S, Elemtype* e); //出栈
Status PrintStack(LinkStack S); //打印栈
Status GetTop(SNode S, Elemtype* e); //获取栈顶
Status ClearStack(LinkStack S); //清空栈
Status DestryStack(LinkStack S); //销毁栈
LinkStack.c
#include "LinkStack.h"
LinkStack InitLinkStack(LinkStack S) //初始化栈
{
S = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode)*2);
if (S->next)
{
S->next = NULL;
}
return S;
}
Status StackEmpty(LinkStack S) //判断栈空
{
if (S->next == NULL)
return OK;
else
return FALSE;
}
Status Posh(LinkStack S,Elemtype e) //进栈
{
LinkStack new;
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
S->next = NULL;
new = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));
new->data = e;
new->next = S->next;
S->next = new;
}
else
{
new = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));
new->data = e;
new->next = S->next;
S->next = new;
}
return OK;
}
Status Pop(LinkStack S, Elemtype* e) //出栈
{
LinkStack p = S->next;
if (!StackEmpty(S)) {
*e = p->data;
S->next = p->next;
free(p);
return OK;
}
else
return FALSE;
}
Status PrintStack(LinkStack S) //打印栈
{
while (S->next != NULL )
{
S = S->next;
printf("%d ", S->data);
}
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
Status GetTop(SNode S, Elemtype* e) //获取栈顶
{
SNode* p = S.next;
if (S.next != NULL) {
*e = p->data;
return OK;
}
else
return FALSE;
}
Status ClearStack(LinkStack S) //清空栈
{
LinkStack p, q;
p = S->next;
while (p)
{
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
S->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
Status DestryStack(LinkStack S) //销毁栈
{
LinkStack p;
while(S)
{
p = S;
S = S->next;
free(S);
}
return OK;
}test.c
#include "LinkStack.h"
int main()
{
SNode S;
Elemtype e;
S = *InitLinkStack(&S); //初始化栈
if (StackEmpty(&S)) //判断栈空
{
printf("栈是空的!\n");
}
//Posh(&S, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Posh(&S, i); //进栈
}
PrintStack(&S);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//出栈
if (Pop(&S, &e))
{
printf("%d ", e);
}
else {
printf("栈下溢了!!\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
PrintStack(&S);
//获取栈顶
if (GetTop(S, &e)) {
printf("此时栈顶为:%d\n", e);
}
else {
printf("栈下溢了!!!\n");
}
PrintStack(&S);
ClearStack(&S); //清空栈
DestryStack(&S); //销毁栈
return 0;
}总结:栈的理解和实现都是基于线性表的,因此,其理解起来也是相对比较简单。
链表实现过程中,采用头插法的方式进行插入,但是跟在创建链表不同的是,其不是一次性全部插入的,因此需要进行判断是否是第一个插入的结点,如果是则将插入后的下一个结点置为NULL,其他插入的话就直接插在第一个结点之前。还有初始化栈链表的时候,需要将链表返回在main函数中重新赋值,这样子链表的初始化就能够比较稳妥的成功。我遇到过初始化后,在进行进栈时,链表初始化就没用了,因此重新赋值一下会比较稳妥。
S = *InitLinkStack(&S); //初始化栈
//进栈操作
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
S->next = NULL;
new = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));
new->data = e;
new->next = S->next;
S->next = new;
}
else
{
new = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));
new->data = e;
new->next = S->next;
S->next = new;
}





















 3390
3390











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








