-
概述
安全性在REST API开发中扮演着重要的角色。一个不安全的REST API可以直接访问到后台系统中的敏感数据。因此,企业组织需要关注API安全性。
Spring Security 提供了各种机制来保护我们的 REST API。其中之一是 API 密钥。API 密钥是客户端在调用 API 调用时提供的令牌。
在本教程中,我们将讨论如何在Spring Security中实现基于API密钥的身份验证。 -
REST API Security
Spring Security可以用来保护REST API的安全性。REST API是无状态的,因此不应该使用会话或cookie。相反,应该使用Basic authentication,API Keys,JWT或OAuth2-based tokens来确保其安全性。
-
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication是一种简单的认证方案。客户端发送HTTP请求,其中包含Authorization标头的值为Basic base64_url编码的用户名:密码。Basic authentication仅在HTTPS / SSL等其他安全机制下才被认为是安全的。 -
OAuth2
OAuth2是REST API安全的行业标准。它是一种开放的认证和授权标准,允许资源所有者通过访问令牌将授权委托给客户端,以获得对私有数据的访问权限。 -
API Keys
一些REST API使用API密钥进行身份验证。API密钥是一个标记,用于向API客户端标识API,而无需引用实际用户。标记可以作为查询字符串或在请求头中发送。
- 用API Keys保护REST API
- 添加Maven 依赖
- 让我们首先在我们的pom.xml中声明spring-boot-starter-security依赖关系:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 创建自定义过滤器(Filter)
实现思路是从请求头中获取API Key,然后使用我们的配置检查秘钥。在这种情况下,我们需要在Spring Security 配置类中添加一个自定义的Filter。
我们将从实现GenericFilterBean开始。GenericFilterBean是一个基于javax.servlet.Filter接口的简单Spring实现。
让我们创建AuthenticationFilter类:
public class AuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
Authentication authentication = AuthenticationService.getAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) request);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
} catch (Exception exp) {
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
httpResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
httpResponse.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
PrintWriter writer = httpResponse.getWriter();
writer.print(exp.getMessage());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
我们只需要实现doFilter()方法,在这个方法中我们从请求头中获取API Key,并将生成的Authentication对象设置到当前的SecurityContext实例中。
然后请求被传递给其余的过滤器处理,接着转发给DispatcherServlet最后到达我们的控制器。
在AuthenticationService类中,实现从Header中获取API Key并构造Authentication对象,代码如下:
public class AuthenticationService {
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME = "X-API-KEY";
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN = "Baeldung";
public static Authentication getAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String apiKey = request.getHeader(AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME);
if ((apiKey == null) || !apiKey.equals(AUTH_TOKEN)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Invalid API Key");
}
return new ApiKeyAuthentication(apiKey, AuthorityUtils.NO_AUTHORITIES);
}
}
在这里,我们检查请求头是否包含 API Key,如果为空 或者Key值不等于密钥,那么就抛出一个 BadCredentialsException。如果请求头包含 API Key,并且验证通过,则将密钥添加到安全上下文中,然后调用下一个安全过滤器。getAuthentication 方法非常简单,我们只是比较 API Key 头部和密钥是否相等。
为了构建 Authentication 对象,我们必须使用 Spring Security 为了标准身份验证而构建对象时使用的相同方法。所以,需要扩展 AbstractAuthenticationToken 类并手动触发身份验证。
- 扩展AbstractAuthenticationToken
为了成功地实现我们应用的身份验证功能,我们需要将传入的API Key转换为AbstractAuthenticationToken类型的身份验证对象。AbstractAuthenticationToken类实现了Authentication接口,表示一个认证请求的主体和认证信息。
让我们创建ApiKeyAuthentication类:
public class ApiKeyAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private final String apiKey;
public ApiKeyAuthentication(String apiKey,
Collection<?extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.apiKey = apiKey;
setAuthenticated(true);
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return apiKey;
}
}
ApiKeyAuthentication 类是类型为 AbstractAuthenticationToken 的对象,其中包含从 HTTP 请求中获取的 apiKey 信息。在构造方法中使用 setAuthenticated(true) 方法。因此,Authentication对象包含 apiKey 和authenticated字段:
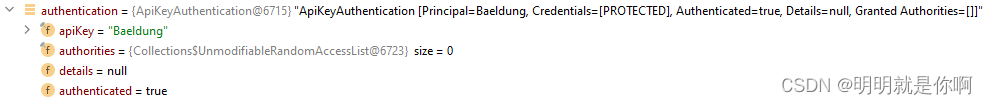
- Security Config
通过创建建一个SecurityFilterChain bean,可以通过编程方式把我们上面编写的自定义过滤器(Filter)进行注册。
我们需要在 HttpSecurity 实例上使用 addFilterBefore() 方法在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 类之前添加 AuthenticationFilter。
创建SecurityConfig 类:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/**")
.authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new AuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
}
此外注意代码中我们吧绘画策略(session policy)设置为无状态(STATELESS),因为我们使用的是REST。
- ResourceController
- 最后,我们创建ResourceController,实现一个Get请求 /home
@RestController
public class ResourceController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public String homeEndpoint() {
return "Baeldung !";
}
}
- 禁用 Auto-Configuration
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class, UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ApiKeySecretAuthApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiKeySecretAuthApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 测试
我们先不提供API Key进行测试
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home'
返回 401 未经授权错误。
请求头中加上API Key后,再次请求
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home' \
--header 'X-API-KEY: Baeldung'
请求返回状态200





















 633
633











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








