利用词袋模型和SVM进行图片分类 实验报告
1. 任务定义
-
任务: 编写一个图像分类系统,能够对输入图像进行类别预测。具体的说,利用数据库的 2250张 训练样本进行训练;对测试集中的2235张样本进行预测。
-
数据库说明: scene_categories 数据集包含15个类别(文件夹名就是类别名),每个类中 编号前 150号的样本作为训练样本,15个类一共2250张训练样本;剩下的样本构成测试集 合。 数据集详情可参阅: https://qixianbiao.github.io/Scene.html 数据集下载地址: https://figshare.com/articles/15-Scene_Image_Dataset/7007177
2. 实验环境
- Windows 10
- Python 3.7.8
- OpenCV 4.1.2
- sklearn 0.22.1
3. 算法说明
3.1 初始化
img_path:数据集路径
categories:数据集中种类
train_img_paths:训练集中图片路径
train_labels:训练集标签
test_img_paths:测试集中图片路径
test_labels:测试集标签
def __init__(self, img_path):
self.img_path = img_path
self.load_data()
def load_data(self):
categories = os.listdir(self.img_path)
train_labels = []
test_labels = []
train_img_paths = []
test_img_paths = []
for path, dirs, files in os.walk(self.img_path):
for i, file in enumerate(files):
if (i < 150):
train_img_paths.append(os.path.join(path, file))
else:
test_img_paths.append(os.path.join(path, file))
if (len(files) > 0):
train_labels.extend([path.split('/')[-1]] * 150)
test_labels.extend([path.split('/')[-1]] * (len(files) - 150))
self.categories = categories
self.train_img_paths = train_img_paths
self.test_img_paths = test_img_paths
self.train_labels = train_labels
self.test_labels = test_labels
3.2 提取SIFT特征
- SIFT特征具有放缩、旋转、光照不变性,同时兼有对几何畸变,图像几何变形的一定程度的鲁棒性。调用opencv库中提供的接口进行SIFT特征提取。
- SIFT特征提取算法主要有如下几步:
- 构建高斯金子塔图像,寻找极值点
- 极值点亚像素级别定位
- 图像梯度与角度直方图建立
- 特征描述子建立
feature:SIFT特征点
descriptor:描述子
def GetSiftFeature(self):
self.sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
# SIFT特征提取
descriptors = []
print('---------------Get SIFT feature---------------')
for img_path in tqdm(self.train_img_paths):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
feature = self.sift.detect(img)
feature, descriptor = self.sift.compute(img, feature)
descriptors.append(descriptor)
return descriptors
3.3 生成词汇字典
- 使用K-Means算法对描述子数据进行聚类分析,聚类中心也就是我们所需要的词汇字典
voc:词汇字典
def k_means(self, descriptors, k):
kmeans_trainer = cv2.BOWKMeansTrainer(k)
print('---------------K-means ing--------------------')
for descriptor in descriptors:
kmeans_trainer.add(descriptor)
voc = kmeans_trainer.cluster()
return voc
3.4 提取BOW特征描述
- 利用生成的词汇字典创建BOW特征提取器,对训练集中的每个图片进行特征提取组成训练数据。
self.sift:SIFT特征提取器
self.bow:BOW特征提取器
traindata:训练数据
def GetBOWFeature(self, voc):
print('---------------Get BOW feature----------------')
# 初始化flann匹配器
flann_params = dict(algorithm=1, tree=5)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(flann_params, {})
# 初始化BOW特征提取器
self.bow = cv2.BOWImgDescriptorExtractor(self.sift, flann)
# 设置词汇字典
self.bow.setVocabulary(voc)
traindata = []
# BOW特征提取组成训练数据
for img_path in tqdm(self.train_img_paths):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
traindata.extend(self.bow.compute(img, self.sift.detect(img)))
return traindata
3.5 使用SVM进行训练
- 调用sklearn.svm中的LinearSVC进行训练
traindata:训练数据
self.train_labels:训练数据标签
def SVMtrain(self, traindata):
print('---------------SVM training-------------------')
# 初始化SVM
self.SVM = LinearSVC()
# 模型训练
SVMmodel = self.SVM.fit(traindata, self.train_labels)
# 保存模型
joblib.dump(SVMmodel, './SVMmodel.model')
3.6 模型评估
- 遍历测试集,对测试集图片提取BOW特征进行预测,并生成分类报告和混淆矩阵。
def predict(self, img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
# 获取图片BOW特征
data = self.bow.compute(img, self.sift.detect(img))
# 进行预测
result = self.SVM.predict(data)
return result
def evaluate(self):
print('---------------Evaluating---------------------')
# 获得测试集预测结果
pred_labels = [self.predict(img_path) for img_path in tqdm(self.test_img_paths)]
print(len(pred_labels))
# 生成混淆矩阵
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(
self.test_labels,
pred_labels,
labels=self.categories
)
# 生成分类报告
report = classification_report(self.test_labels, pred_labels)
# 打印分类报告
print(report)
# 混淆矩阵可视化
self.print_cnf_mat(cnf_matrix)
- 混淆矩阵可视化
def print_cnf_mat(self, cnf_matrix):
# 对混淆矩阵进行归一化
cnf_matrix_norm = cnf_matrix.astype('float') / \
cnf_matrix.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
cnf_matrix_norm = np.around(cnf_matrix_norm, decimals=2)
# 显示混淆矩阵
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
sns.heatmap(cnf_matrix_norm, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.ylim(0, 15)
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
tick_marks = np.arange(len(self.categories))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, self.categories, rotation=90)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, self.categories, rotation=45)
plt.show()
4. 结果分析
4.1 LinearSVC分类报告以及混淆矩阵
分类报告
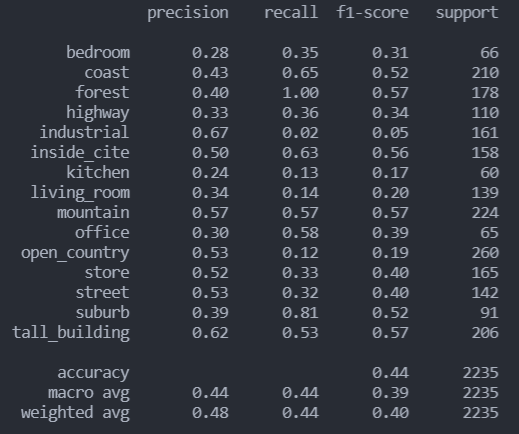
混淆矩阵

- 可以看到,直接使用线性SVM分类在industrial、kitchen、living_room和open_country类上表现并不理想,尤其是在industrial类上,recall仅有0.02,于是决定调整参数看看分类效果。
4.2 调整参数后分类效果
- 参考样例,使用rbf核函数,并设置惩罚因子为1000,选用一对一法构建多分类器
- 分类效果确实得到显著提升
rbf分类报告
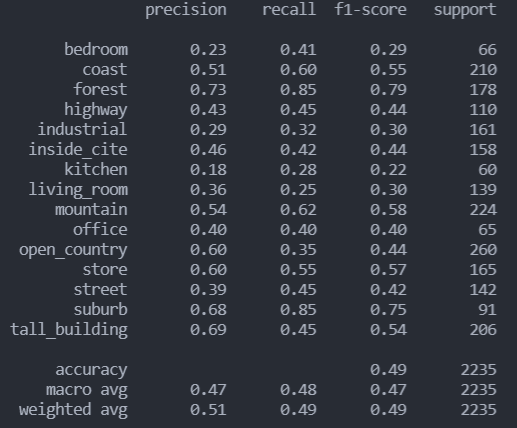
混淆矩阵

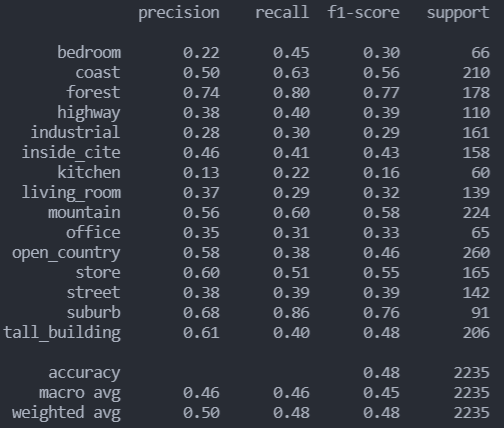
- 重新选用线性核函数,调整惩罚因子,效果相比直接使用LinearSVC同样有了不小的提升
linear分类报告
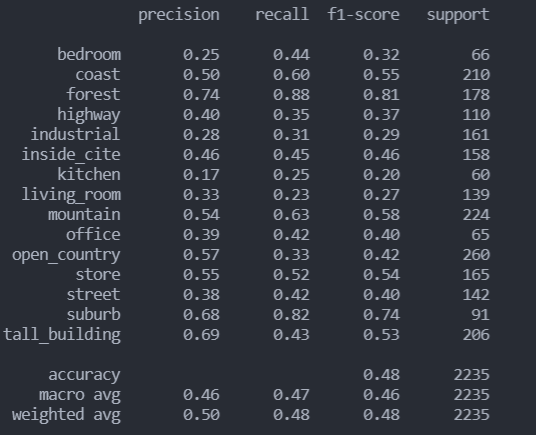
- 改用poly核函数后分类效果极差
poly分类报告
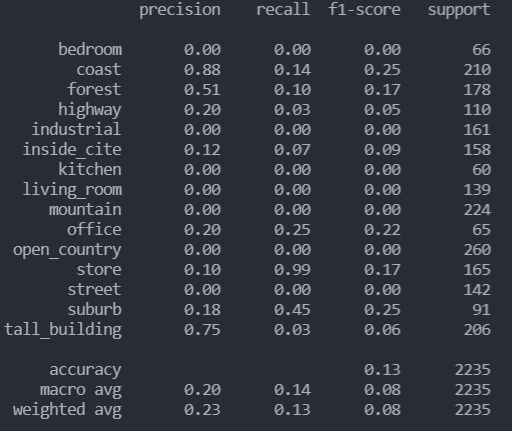
- sigmoid核函数与线性核函数分类效果差不多
sigmoid分类报告
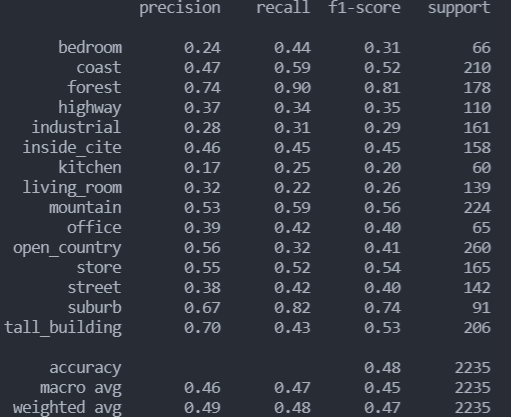
- 调整高斯核函数的gamma为10,结果并未提升
gamma为10的rbf分类报告
4.3 总结
综上,在本次实验中,设置svm的核函数为rbf,惩罚因子为1000,有着最优的表现,但是相较示例结果仍有一定差距,猜测是在数据处理方面的改进,值得继续研究。
























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








