借助堆栈以非递归(循环)方式求解汉诺塔的问题(n, a, b, c),即将N个盘子从起始柱(标记为“a”)通过借助柱(标记为“b”)移动到目标柱(标记为“c”),并保证每个移动符合汉诺塔问题的要求。
输入格式:
输入为一个正整数N,即起始柱上的盘数。
输出格式:
每个操作(移动)占一行,按柱1 -> 柱2的格式输出。
输入样例:
3
输出样例:
a -> c
a -> b
c -> b
a -> c
b -> a
b -> c
a -> c
理解一下首先我写了下递归的情况,这里讲下思路:
其实最终移盘子可以看做是:
1.将0到n-1个盘子借助c从a移到b;
2.将第n个盘子借助b从a移动到c;
3.最后把0到n-1个盘子借助a移动到c;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void move(char A, char C)
{
printf("%c -> %c\n",A,C);
}
void hanoi(int n, char A, char B, char C);
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
char A = 'a', B = 'b', C = 'c';
hanoi(n,A,B,C);
return 0;
}
void hanoi( int n, char A, char B, char C )
{
if(n == 1)
{
move(A,C);
}
else
{
hanoi(n-1,A,C,B);
move(A,C);
hanoi(n-1,B,A,C);
}
}
这个憨批题目也不会检测你递归是错的,难点在非递归,这里得用堆栈的思想;
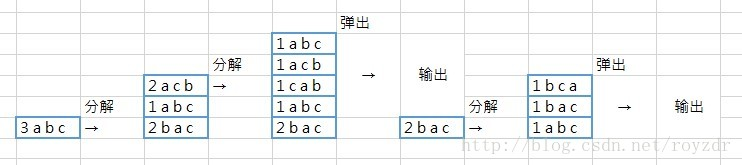
借用一下图https://blog.csdn.net/royzdr/article/details/79032032 出处是这里;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define STACKSIZE 100
typedef struct{
char a;
char b;
char c;
int n;
}ElementType;
typedef struct node *PtrToSnode;
struct node{
ElementType *data;
int top;
int maxsize;
};
typedef PtrToSnode mystack;
mystack creatstack(int maxsize)
{
mystack ms = (mystack)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
ms->data = (ElementType *)malloc(maxsize * sizeof(ElementType));
ms->top = -1;
ms->maxsize = maxsize;
return ms;
}
void pushdata( mystack ms, ElementType x )
{
if( ms->top == ms->maxsize - 1)
{
printf("Stack is Full!\n");
}
else
{
ms->data[++(ms->top)] = x;
}
}
ElementType popdata( mystack ms )
{
if(ms->top == -1)
{
printf("Stack is Empty!\n");
}
else
{
return ms->data[ms->top--];
}
}
void hanoi( int n )
{
mystack ms = creatstack(STACKSIZE);
ElementType tmp,topush;
tmp.a = 'a';
tmp.b = 'b';
tmp.c = 'c';
tmp.n = n;
pushdata(ms, tmp);
while(ms->top != -1)
{
tmp = popdata(ms);
if(tmp.n == 1)
{
printf("%c -> %c\n",tmp.a,tmp.c);
}
else
{
topush.a = tmp.b;
topush.b = tmp.a;
topush.c = tmp.c;
topush.n = tmp.n - 1;
pushdata(ms, topush);
topush.a = tmp.a;
topush.b = tmp.b;
topush.c = tmp.c;
topush.n = 1;
pushdata(ms, topush);
topush.a = tmp.a;
topush.b = tmp.c;
topush.c = tmp.b;
topush.n = tmp.n-1;
pushdata(ms, topush);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
hanoi(n);
return 0;
}
这里用到了结构体,堆栈以及结构数组,这里有一个点容易遗忘,当用malloc为指针类型变量申请空间的时候,格式是(ElementType *)malloc(n * sizeof(ElementType));这里的ElementType是你申请的变量的名称,本题这里是一个结构体数组,所以申请的是一个指向结构体的指针的空间,data数组存储的是一堆指针,其余的都是小操作,花了很多时间这道题,做了两次以后还得好好温习!!!
奥力给!
奥力给!
奥力给!

























 1645
1645











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








