(二)二维数组
定义方式:
数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]
数据类型 数组名[行数][列数] = { {数据1,数据2},{数据三,数据4},···}
数据类型 数组名[行数][列数] = {数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4}
数据类型 数组名[ ][列数] = {数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4}
数组名用处:
可以查看占用空间内存大小
可以查看首地址
六、函数
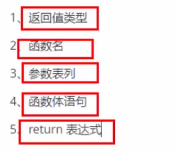
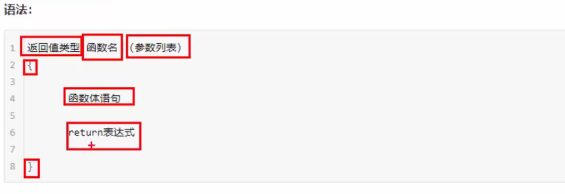
(一)定义
函数的定义的步骤:

(二)函数调用
函数定义的参数列表为形参,传入的值为实参
(三)值传递
如果函数不需要返回值,那么声明的时候直接void
void swap(int num1,int num2)
{
int temp =num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
形参改变 实参无影响
(四)函数的常见形式
无参无返
有参无返
无参有返
有参有返
(五)函数的声明
作用:告诉编译器函数名称以及如何调用参数
函数的声明可以多次,但是定义只能有一次
只需要 返回值类型 函数名(参数列表)
int max(int a, int b)
(六)函数的分文件编写
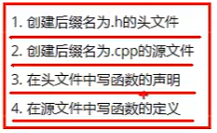
include“xxxxx.h”
七、指针
(一)定义
语法:数据类型 *指针变量名
int * p ;
p = &a;
p记录了变量a的地址
通过*p去操作指针变量指向的内存
在32位操作系统下:指针占用4个字节
在64位操作系统下:指针占用8个字节
(二)空指针和野指针
空指针:指针变量指向内存中编号为0的空间
用途:初始化指针变量
注意:空指针指向的内存是不可以访问的
int *p = NULL;
野指针:指针变量指向的非法的内存空间
(三)const修饰指针
const修饰指针有三种情况:
const修饰指针 --常量指针
const int *p = &a;
指针的指向可以改,但是指针指向的值不可以改
*p = 20 错误 p = &b 正确
const修饰常量 --指针常量
int * const p = &a
指针的指向不可以改,指针的值可以改
const既修饰指针又修饰常量
const int * const p = &a
(四)指针和数组
int arr[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int *p = arr;
通过数组名来得到数组的地址,然后访问整个数组。
(五)指数和函数
地址传递
int a = 20;
int b = 10;
int swap(int *p1, int *p2)
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
swap( &a, &b);
地址传递可以改变实参
(六)指针、函数、数组
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int* arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0;i < len - 1;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i;j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 1,8,3,564,6,36,75,8,97,4510 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, 10);
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}八、结构体
(一)概念 定义 使用
用户自定义的数据类型,允许存储不同的数据类型
语法: struct 结构体名 {结构体成员列表}
创建方式:
struct 结构体名 变量名
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
struct Student s1;
s1.name = "张三阿萨十阿松大";
s1.score = 100;
cout << s1.name << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}struct 结构体名 变量名 = {成员1值,成员2值....}
struct Student s2 = {"占山",15,65}定义结构体时顺便创建变量
s3.age = 20;
s3.score = 15;
s3.name = "啊水水"
(二)结构体数组
struct 结构体名 数组名[元素个数] = { {},{},····}
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
struct Student arr[3]=
{
{"掌声",15,25},
{"阿松大",651,65}
};
system("pause");
return 0;
}(三)结构体指针
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
struct Student s1;
s1.name = "张三阿萨十阿松大";
s1.score = 100;
s1.age = 15;
student *p = &s1;
//通过箭头访问数据
cout<<p->name<<endl;
cout << s1.name << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}(四)结构体嵌套结构体
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct
int main()
{
struct Student s1;
s1.name = "张三阿萨十阿松大";
s1.score = 100;
struct Teacher t1;
t1.name = "阿松大";
t1.age = 100;
t1.stu = s1;
cout << t1.stu.name << endl;
cout << s1.name << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}(五)结构体作为函数参数
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
void print1(Student s)
{
cout << s.age << " " << s.name << endl;
}
void print2(Student * s)
{
cout << s->age << " " << s->name << endl;
}
int main()
{
struct Student s1;
s1.name = "张三阿萨十阿松大";
s1.score = 100;
s1.age = 5;
print1(s1);
print2(&s1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}(六)结构体中const使用
函数参数传指针会节省很多空间
void print1(const Student *s)
只可以看不可以改参数值
例子:

#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
string name;
int score;
};
struct Teacher
{
string name;
Student stu[5];
};
void cin_print1(Teacher t[], int len)
{
string names = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++)
{
t[i].name = "Teacher";
t[i].name += names[i];
cout << t[i].name << endl;
for (int j = 0;j < 5;j++)
{
t[i].stu[j].name = "Student";
t[i].stu[j].name += names[j];
t[i].stu[j].score = 60+5*j;
cout << t[i].stu[j].name << " " << t[i].stu[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
struct Teacher tarray[3];
int len = sizeof(tarray) / sizeof(tarray[0]);
cin_print1(tarray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}





















 1049
1049

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








