Arithmetic Circuits
Hadd
Create a half adder. A half adder adds two bits (with no carry-in) and produces a sum and carry-out.
//成功代码
module top_module(
input a, b,
output cout, sum );
assign sum = a+b;
assign cout = a&b;
endmodule
Fadd
Create a full adder. A full adder adds three bits (including carry-in) and produces a sum and carry-out.
//成功代码
module top_module(
input a, b, cin,
output cout, sum );
assign sum = a^b^cin;
assign cout = a&b | b&cin | a&cin;
endmodule
波形
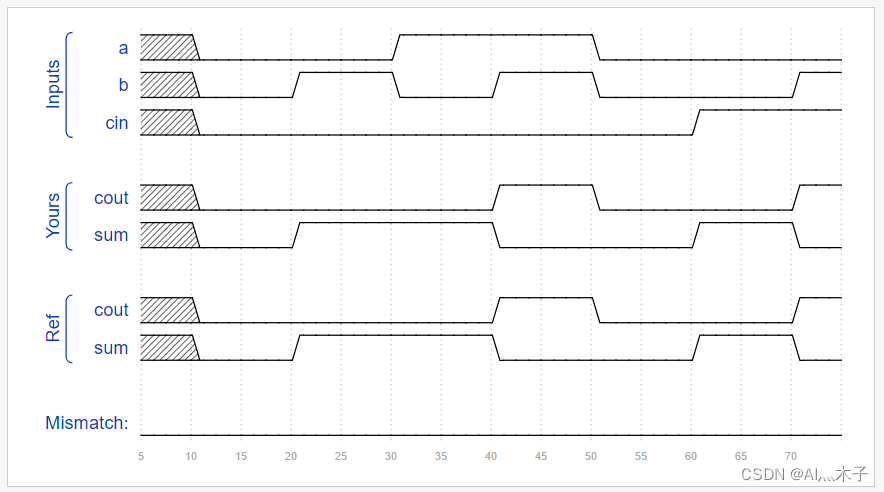
Adder3
Now that you know how to build a full adder, make 3 instances of it to create a 3-bit binary ripple-carry adder. The adder adds two 3-bit numbers and a carry-in to produce a 3-bit sum and carry out. To encourage you to actually instantiate full adders, also output the carry-out from each full adder in the ripple-carry adder. cout[2] is the final carry-out from the last full adder, and is the carry-out you usually see.
//成功代码
module top_module(
input [2:0] a, b,
input cin,
output [2:0] cout,
output [2:0] sum );
full_add (.a(a[0]),.b(b[0]),.cin(cin),.cout(cout[0]),.sum(sum[0]));
full_add (.a(a[1]),.b(b[1]),.cin(cout[0]),.cout(cout[1]),.sum(sum[1]));
full_add (.a(a[2]),.b(b[2]),.cin(cout[1]),.cout(cout[2]),.sum(sum[2]));
endmodule
module full_add(
input a,b,
input cin,
output cout,sum);
assign cout = a&b | a&cin | b&cin;
assign sum = a^b^cin;
endmodule
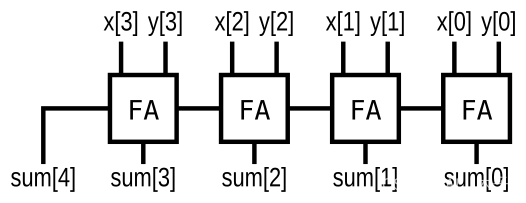
Exams/m2014 q4j
Implement the following circuit:(“FA” is a full adder)
//虽然它成功了但是不得不说这个代码很垃圾
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum);
wire [2:0] cout;
wire cin;
assign cin = 0;
FA(.a(x[0]),.b(y[0]),.cin(cin),.cout(cout[0]),.sum(sum[0]));
FA(.a(x[1]),.b(y[1]),.cin(cout[0]),.cout(cout[1]),.sum(sum[1]));
FA(.a(x[2]),.b(y[2]),.cin(cout[1]),.cout(cout[2]),.sum(sum[2]));
FA(.a(x[3]),.b(y[3]),.cin(cout[2]),.cout(sum[4]),.sum(sum[3]));
endmodule
module FA(
input a,b,
input cin,
output cout ,sum);
assign cout = a&b | a&cin | b&cin;
assign sum = a^b^cin;
endmodule
//这才是真理
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum
);
assign sum = x+y;
endmodule
Exams/ece241 2014 q1c
Assume that you have two 8-bit 2’s complement numbers, a[7:0] and b[7:0]. These numbers are added to produce s[7:0]. Also compute whether a (signed) overflow has occurred.
Hint:A signed overflow occurs when adding two positive numbers produces a negative result, or adding two negative numbers produces a positive result. There are several methods to detect overflow: It could be computed by comparing the signs of the input and output numbers, or derived from the carry-out of bit n and n-1.
//成功代码
module top_module (
input [7:0] a,
input [7:0] b,
output [7:0] s,
output overflow
);
assign s = a+b;
assign overflow = (s[7]==a[7] || s[7]==b[7])?0:1;
endmodule
波形
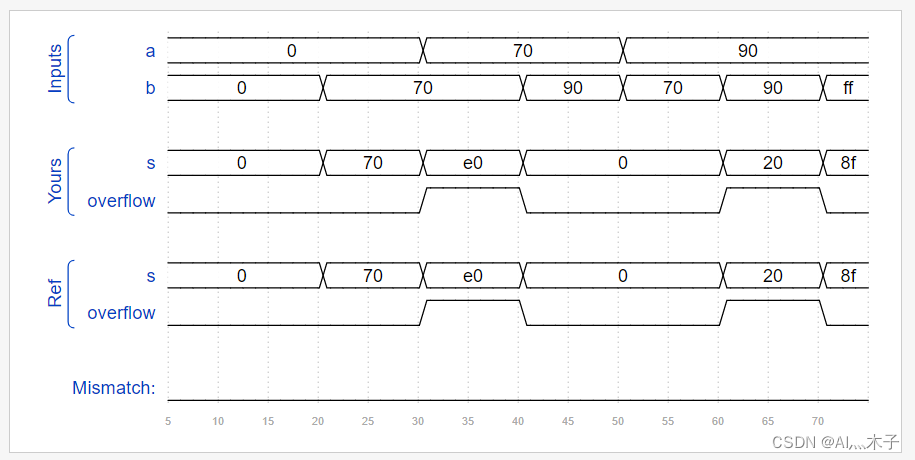
Adder100
Create a 100-bit binary adder. The adder adds two 100-bit numbers and a carry-in to produce a 100-bit sum and carry out.
Hint:There are too many full adders to instantiate, but behavioural code works well here. Also see the solution to Adder.
//成功代码
module top_module(
input [99:0] a,b,
input cin,
output [99:0] cout,
output [99:0] sum
);
assign {cout,sum} = a + b + cin;//拼接,多出来的进位就是最后cout的数值。
endmodule
Bcdadd4
You are provided with a BCD (binary-coded decimal) one-digit adder named bcd_fadd that adds two BCD digits and carry-in, and produces a sum and carry-out.
module bcd_fadd (
input [3:0] a,
input [3:0] b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [3:0] sum );
Instantiate 4 copies of bcd_fadd to create a 4-digit BCD ripple-carry adder. Your adder should add two 4-digit BCD numbers (packed into 16-bit vectors) and a carry-in to produce a 4-digit sum and carry out.
Hint:The BCD representation for the 5-digit decimal number 12345 is 20’h12345. This is not the same as 14’d12345 (which is 14’h3039).
The circuit is structured just like a binary ripple-carry adder, except the adders are base-10 rather than base-2.
//最暴力的解法
module top_module (
input [15:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [15:0] sum );
wire [2:0] cout_tmp;
bcd_fadd (.a(a[3:0]),.b(b[3:0]),.cin(cin),.cout(cout_tmp[0]),.sum(sum[3:0]));
bcd_fadd (.a(a[7:4]),.b(b[7:4]),.cin(cout_tmp[0]),.cout(cout_tmp[1]),.sum(sum[7:4]));
bcd_fadd (.a(a[11:8]),.b(b[11:8]),.cin(cout_tmp[1]),.cout(cout_tmp[2]),.sum(sum[11:8]));
bcd_fadd (.a(a[15:12]),.b(b[15:12]),.cin(cout_tmp[2]),.cout(cout),.sum(sum[15:12]));
endmodule
//简单一些的代码
module top_module (
input [15:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [15:0] sum );
wire [3:0] cout_tmp;
genvar i;
generate
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
begin:bad_fadd
if(i==0)
bcd_fadd (.a(a[i+3:i]),.b(b[i+3:i]),.cin(cin),.cout(cout_tmp[i]),.sum(sum[i+3:i]));
else
bcd_fadd(.a(a[i*4+3:i*4]),.b(b[i*4+3:i*4]),.cin(cout_tmp[i-1]),.cout(cout_tmp[i]),.sum(sum[i*4+3:i*4]));
end
assign cout = cout_tmp[3];
endgenerate
endmodule






















 307
307











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










