前言
本节学习梯度下降法
- 基于搜索的最优化方法
- 用来最小化损失函数
1、梯度下降法的原理与简单实现

看图理解
- 计算梯度
- 每次根据学习率进行梯度下降
- 最终得到最优解
学习率的取值影响最优解的速度
- 太小则收敛太慢
- 太大则可能不收敛
- 需要调整学习率和初始点
实现如下
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""模拟梯度下降法"""
# 以一个二次函数为损失函数
plot_x = np.linspace(-1., 6., 141)
plot_y = (plot_x-2.5)**2 - 1
# 损失函数
def J(theta):
try:
return (theta-2.5)**2 - 1.
except:
return float('inf')
# 导数
def dJ(theta):
return 2 * (theta - 2.5)
"""
# 梯度下降法
eta = 0.1 #学习率
theta = 0.0 #起始点
epsilon = 1e-8 #判断
theta_history = [theta]
while True:
gradient = dJ(theta) #梯度
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient #梯度下降移一步
theta_history.append(theta)
if (abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):
break
plt.plot(plot_x, J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history), J(np.array(theta_history)), color="r", marker='+')
plt.show()
print(theta)
print(J(theta))"""
# 梯度下降法函数封装
theta_history = []
def gradient_descent(initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e4,epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
theta_history.append(initial_theta)
i_iter = 0
while i_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
theta_history.append(theta)
if (abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):
break
i_iter += 1
return
def plot_theta_history():
plt.plot(plot_x, J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history), J(np.array(theta_history)), color="r", marker='+')
plt.show()
eta = 0.01
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0, eta)
plot_theta_history()2、线性回归中的梯度下降法

公式如下

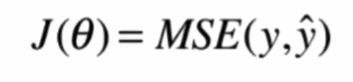
实现如下
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""线性回归中的梯度下降"""
# 为了可视化,搞个一维数组
np.random.seed(666) #随机种子
x = 2 * np.random.random(size=100)
y = x * 3. + 4. + np.random.normal(size=100)
X = x.reshape(-1, 1)
# 损失函数
def J(theta, X_b, y):
try:
return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta))**2) / len(X_b)
except:
return float('inf')
# 梯度
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
res = np.empty(len(theta))
res[0] = np.sum(X_b.<







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 9282
9282











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








