1.最长不含重复字符的子字符串
请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。
示例 1:
输入: "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: "bbbbb"
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: "pwwkew"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,"pwke" 是一个子序列,不是子串。
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
int i = -1, res = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < s.length(); j++) {
if(dic.containsKey(s.charAt(j)))
i = Math.max(i, dic.get(s.charAt(j))); // 更新左指针 i
dic.put(s.charAt(j), j); // 哈希表记录
res = Math.max(res, j - i); // 更新结果
}
return res;
}
}
2. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回锯齿形层序遍历如下:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
class Solution {
//锯齿遍历
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
traversal(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res, int level) {
if (root == null) return;
if (res.size() == level) res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
if ((level & 1) == 1){//奇偶判断
res.get(level).add(0, root.val);//为奇数就正向放
} else {
res.get(level).add(root.val);
}
traversal(root.left, res, level + 1);
traversal(root.right, res, level + 1);
}
}
3. 数组中的第K个最大元素
TOP K问题
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
输出: 5
示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4
输出: 4
class Solution {
//TOP K
Random random = new Random();
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
return quickSelect(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length - k);
}
public int quickSelect(int[] a, int l, int r, int index) {
int q = randomPartition(a, l, r);
if (q == index) {
return a[q];
} else {
return q < index ? quickSelect(a, q + 1, r, index) : quickSelect(a, l, q - 1,index);
}
}
public int randomPartition(int[] a, int l, int r) {
int i = random.nextInt(r - l + 1) + l;
swap(a, i, r);
return partition(a, l, r);
}
public int partition(int[] a, int l, int r) {
int x = a[r], i = l - 1;
for (int j = l; j < r; ++j) {
if (a[j] <= x) {
swap(a, ++i, j);
}
}
swap(a, i + 1, r);
return i + 1;
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
4. 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null; //前指针节点
ListNode curr = head; //当前指针节点
//每次循环,都将当前节点指向它前面的节点,然后当前节点和前节点后移
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next; //临时节点,暂存当前节点的下一节点,用于后移
curr.next = prev; //将当前节点指向它前面的节点
prev = curr; //前指针后移
curr = nextTemp; //当前指针后移
}
return prev;
}
}
5. LRU 缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
class LRUCache {
int capacity;
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
cache = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity, 0.75f, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return cache.size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
return cache.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
}
6.三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 *a,b,c ,*使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
**注意:**答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
7. 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
输出:0
解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length <= 1) return 0;
int min = prices[0], max = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - min);
min = Math.min(min, prices[i]);
}
return max;
}
}
8. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例 2:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1
class Solution {
//公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left!= null && right != null) return root;
if(left == null) return right;
if(right == null) return left;
return null;
}
}
9. 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode head1 = headA;
ListNode head2 = headB;
while (head1 != head2) {
if (head1 != null) {
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
head1 = headB;
}
if (head2 != null) {
head2 = head2.next;
} else {
head2 = headA;
}
}
return head1;
}
}
10. 搜索旋转排序数组
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
输出:4
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1], target = 0
输出:-1
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int len = nums.length;
int left = 0, right = len-1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if(nums[mid] < nums[right]){
if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right])
left = mid+1;
else
right = mid-1;
}
else{
if(nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid])
right = mid-1;
else
left = mid+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
11. 接雨水
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] leftMax = new int[n];
leftMax[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], height[i]);
}
int[] rightMax = new int[n];
rightMax[n - 1] = height[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i + 1], height[i]);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans += Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]) - height[i];
}
return ans;
}
}
12. 螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:

输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:
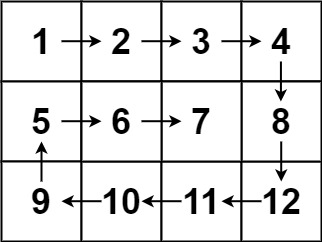
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0)
return list;
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int i = 0;
//统计矩阵从外向内的层数,如果矩阵非空,那么它的层数至少为1层
int count = (Math.min(m, n)+1)/2;
//从外部向内部遍历,逐层打印数据
while(i < count) {
for (int j = i; j < n-i; j++) {
list.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
for (int j = i+1; j < m-i; j++) {
list.add(matrix[j][(n-1)-i]);
}
for (int j = (n-1)-(i+1); j >= i && (m-1-i != i); j--) {
list.add(matrix[(m-1)-i][j]);
}
for (int j = (m-1)-(i+1); j >= i+1 && (n-1-i) != i; j--) {
list.add(matrix[j][i]);
}
i++;
}
return list;
}
13. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
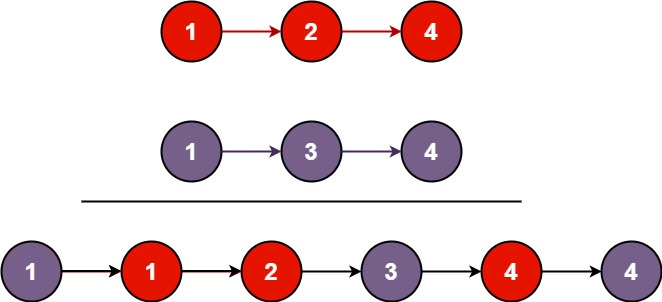
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
} else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
14. 合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) return lists[left];
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
ListNode l1 = merge(lists, left, mid);
ListNode l2 = merge(lists, mid + 1, right);
return mergeTwoLists(l1, l2);
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
15. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
注意:
你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1);
}
int pre = 0;
int in = 0;
private TreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, long stop) {
if(pre == preorder.length){
return null;
}
if (inorder[in] == stop) {
in++;
return null;
}
int root_val = preorder[pre++];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
root.left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, root_val);
root.right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, stop);
return root;
}
}
16. 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,
将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
示例 2:
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<ListNode>();
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
list.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
int i = 0, j = list.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
list.get(i).next = list.get(j);
i++;
if (i == j) {
break;
}
list.get(j).next = list.get(i);
j--;
}
list.get(i).next = null;
}
}
17.数值的整数次方
实现 pow(x, n) ,即计算 x 的 n 次幂函数(即,xn)。不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
示例 1:
输入:x = 2.00000, n = 10
输出:1024.00000
示例 2:
输入:x = 2.10000, n = 3
输出:9.26100
示例 3:
输入:x = 2.00000, n = -2
输出:0.25000
解释:2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
//好像要用快速幂
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return x;
if(n == -1) return 1 / x;
double half = myPow(x, n / 2);
double mod = myPow(x, n % 2);//判断奇偶数
return half * half * mod;
}
}
18. 全排列
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
class Solution {
//全排列
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visited = new int[nums.length];
backtrack(res, nums, new ArrayList<Integer>(), visited);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int[] nums, ArrayList<Integer> tmp, int[] visited) {
if (tmp.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 1) continue;
visited[i] = 1;
tmp.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(res, nums, tmp, visited);
visited[i] = 0;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
19. 岛屿数量
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int islandNum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
infect(grid, i, j);
islandNum++;
}
}
}
return islandNum;
}
//感染函数
public void infect(char[][] grid, int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length ||
j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] != '1'){
return;
}
grid[i][j] = '2';
infect(grid, i + 1, j);
infect(grid, i - 1, j);
infect(grid, i, j + 1);
infect(grid, i, j - 1);
}
}
20. 反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
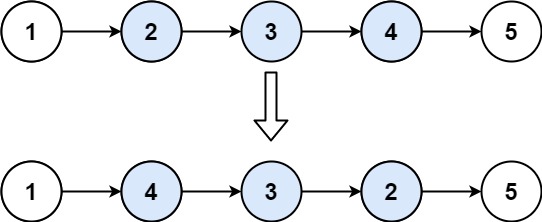
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
head = pre.next;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++){
ListNode nex = head.next;
head.next = nex.next;
nex.next = pre.next;
pre.next = nex;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
21.最长递增子序列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
子序列是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
输出:4
解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3]
输出:4
示例 3:
输入:nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7]
输出:1
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int[] tails = new int[nums.length];
int res = 0;
for(int num : nums) {
int i = 0, j = res;
while(i < j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(tails[m] < num) i = m + 1;
else j = m;
}
tails[i] = num;
if(res == j) res++;
}
return res;
}
}
22. K 个一组翻转链表
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
- 你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
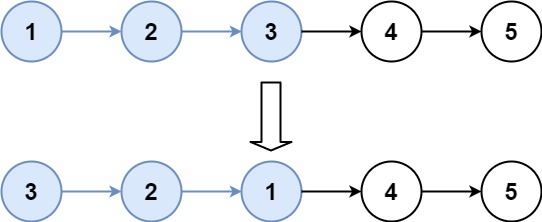
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode end = dummy;
while (end.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) end = end.next;
if (end == null) break;
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(start);
start.next = next;
pre = start;
end = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
23. 最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x)—— 将元素 x 推入栈中。pop()—— 删除栈顶的元素。top()—— 获取栈顶元素。getMin()—— 检索栈中的最小元素。
输入:
["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
[[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
输出:
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
解释:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
class MinStack {
Deque<Integer> xStack;
Deque<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
xStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
xStack.push(x);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
xStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return xStack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
24. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> hashtable = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (hashtable.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{hashtable.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
hashtable.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
25. 合并区间
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间。
示例 1:
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
示例 2:
输入:intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]]
输出:[[1,5]]
解释:区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
//不排序,直接遍历列表
for (int[] i : intervals) {
for (int j = 0; j < res.size(); j++) {
//将每一个结果集中的区间 re 与当前区间 i 进行比较,区间连续就合并 re 到当前区间 i
int[] re = res.get(j);
//三种相交的情况:
//i=[1,3],re=[2,4] 包括 i=[1,4],re=[2,3] 这种情况
//i=[2,4],re=[1,3]
//i=[2,3],re=[1,4]
if (re[0] <= i[1] && re[0] >= i[0]) {
i[1] = re[1] > i[1] ? re[1] : i[1];
} else if (re[1] <= i[1] && re[1] >= i[0]) {
i[0] = re[0];
} else if (re[1] > i[1] && re[0] < i[0]) {
i = re;
} else {
//当前区间与结果集不连续
continue;
}
//当前区间 i 与结果集区间 re 连续 -> 结果集的区间 re 已经被合并到当前区间 i ,从结果集中删除 re
res.remove(re);
j--;
}
//将当前区间添加到结果集
res.add(i);
}
return res.toArray(new int[0][]);
}
}






















 6831
6831











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








