第1章 Pandas基础
基本数据结构
1. Series
(a)创建一个Series
对于一个Series,其中最常用的属性为值(values),索引(index),名字(name),类型(dtype)
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'],name='这是一个Series',dtype='float64')
s
a 1.049740
b -0.037450
c 0.892020
d -0.194631
e 0.006840
Name: 这是一个Series, dtype: float64
(b)访问Series属性
s.values
array([ 1.04974037, -0.03745004, 0.8920197 , -0.19463146, 0.00683963])
s.name
‘这是一个Series’
'这是一个Series'
Index([‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’], dtype=‘object’)
s.dtype
dtype(‘float64’)
c)取出某一个元素
s['a']
1.0497403654768036
d)调用方法
s.mean()
0.34330364010357356
0.34330364010357356

2. DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1':list('abcde'),'col2':range(5,10),'col3':[1.3,2.5,3.6,4.6,5.8]},#col:列
index=list('一二三四五'))#index:索引
df
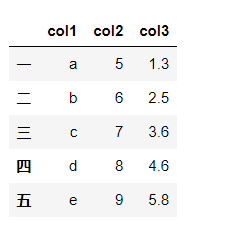
df['col1']

type(df)
pandas.core.frame.DataFrame
type(df['col1'])
pandas.core.series.Series
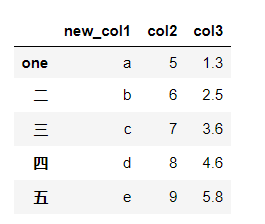
修改行或列名
df.rename(index={'一':'one'},columns={'col1':'new_col1'})
调用属性和方法
df.index
Index([‘一’, ‘二’, ‘三’, ‘四’, ‘五’], dtype=‘object’)
df.columns
Index([‘col1’, ‘col2’, ‘col3’], dtype=‘object’)
df.values#矩阵
array([[‘a’, 5, 1.3],
[‘b’, 6, 2.5],
[‘c’, 7, 3.6],
[‘d’, 8, 4.6],
[‘e’, 9, 5.8]], dtype=object)
df.shape
(5, 3)
df.mean() #本质上是一种Aggregation操作
col2 7.00
col3 3.56
dtype: float64
索引对齐特性
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A':[1,2,3]},index=[1,2,3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A':[1,2,3]},index=[3,1,2])
print('df1: ')
print(df1)
print('')
print('df2: ')
print(df2)
df1-df2 #由于索引对齐,因此结果不是0

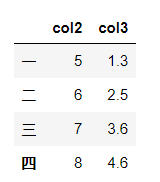
列的删除与添加
df.drop(index='五',columns='col1')
#设置inplace=True后会直接在原DataFrame中改动
df['col1']=[1,2,3,4,5]#不明白
del df['col1']
df
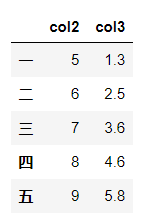
pop方法直接在原来的DataFrame上操作,且返回被删除的列,与python中的pop函数类似
df['col1']=[1,2,3,4,5]
df.pop('col1')
一 1
二 2
三 3
四 4
五 5
Name: col1, dtype: int64
df
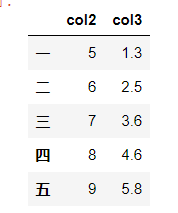
可以直接增加新的列,也可以使用assign方法
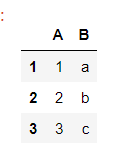
df1['B']=list('abc')
df1

df1.assign(C=pd.Series(list('def')))#索引的对齐性
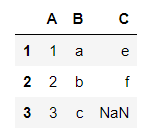
但assign方法不会对原DataFrame做修改
df1
根据类型选择列
df.select_dtypes(include=['number']).head()
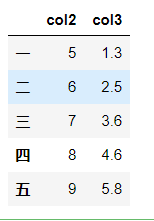
df
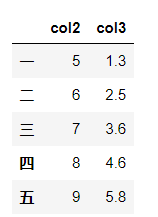
df.select_dtypes(include=['float']).head()
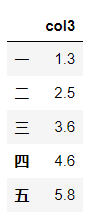
将Series转换为DataFrame
s = df.mean()
s.name='to_DataFrame'
s
col2 7.00
col3 3.56
Name: to_DataFrame, dtype: float64
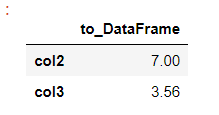
s.to_frame()
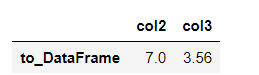
s.to_frame().T
三、常用基本函数
df = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\de\Desktop\table.csv')
df.head()
#默认读取前五行,用来检查数据是否导入正确。

df.tail()

df.head(3)

nunique显示有多少个唯一值
df['Physics'].nunique()
7
df['Physics'].unique()#显示所有唯一值
array([‘A+’, ‘B+’, ‘B-’, ‘A-’, ‘B’, ‘A’, ‘C’], dtype=object)
count返回非缺失值元素个数
df['Physics'].count()
35
value_counts返回每个元素有多少个
df['Physics'].value_counts()
B+ 9
B 8
B- 6
A 4
A- 3
A+ 3
C 2
Name: Physics, dtype: int64
info函数返回有哪些列、有多少非缺失值、每列的类型
df.info()
<class ‘pandas.core.frame.DataFrame’>
RangeIndex: 35 entries, 0 to 34
Data columns (total 9 columns):
School 35 non-null object
Class 35 non-null object
ID 35 non-null int64
Gender 35 non-null object
Address 35 non-null object
Height 35 non-null int64
Weight 35 non-null int64
Math 35 non-null float64
Physics 35 non-null object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(3), object(5)
memory usage: 2.5+ KB
describe默认统计数值型数据的各个统计量
df.describe()#mean均值 std标准差

df.describe(percentiles=[.05, .25, .75, .95])

df['Physics'].describe()
count 35
unique 7
top B+
freq 9
Name: Physics, dtype: object
idxmax函数返回最大值,在某些情况下特别适用,idxmin功能类似
df['Math'].idxmax()#返回标签
5
nlargest函数返回前几个大的元素值,nsmallest功能类似
df['Math'].nlargest(3)
5 97.0
28 95.5
11 87.7
Name: Math, dtype: float64
clip和replace
clip和replace是两类替换函数
clip是对超过或者低于某些值的数进行截断
df['Math'].head()
0 34.0
1 32.5
2 87.2
3 80.4
4 84.8
Name: Math, dtype: float64
df['Math'].clip(33,80).head()#大于第一个数的值都变成第一个数;中间值不动;小于第二个数的值都变成第二个数。
0 34.0
1 33.0
2 80.0
3 80.0
4 80.0
Name: Math, dtype: float64
df['Math'].mad()
16.924244897959188
replace是对某些值进行替换
df['Address'].head()
0 street_1
1 street_2
2 street_2
3 street_2
4 street_4
Name: Address, dtype: object
df['Address'].replace(['street_1','street_2'],['one','two']).head()
0 one
1 two
2 two
3 two
4 street_4
Name: Address, dtype: object
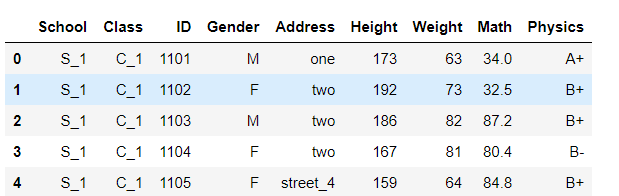
通过字典,可以直接在表中修改
df.replace({'Address':{'street_1':'one','street_2':'two'}}).head()
apply函数
apply是一个自由度很高的函数,在第3章我们还要提到
对于Series,它可以迭代每一列的值操作:
df['Math'].apply(lambda x:str(x)+'!').head() #可以使用lambda表达式,也可以使用函数
df[‘Math’].apply(lambda x:str(x)+’!’).head() #可以使用lambda表达式,也可以使用函数
1
df[‘Math’].apply(lambda x:str(x)+’!’).head() #可以使用lambda表达式,也可以使用函数
0 34.0!
1 32.5!
2 87.2!
3 80.4!
4 84.8!
Name: Math, dtype: object
df.apply(lambda x:x.apply(lambda x:str(x)+'!')).head() #这是一个稍显复杂的例子,有利于理解apply的功能

四、排序
- 索引排序
`df.set_index('Math').head()`

df.set_index('Math').sort_index().head()#默认升序

2. 值排序
df.sort_values(by='Class').head()
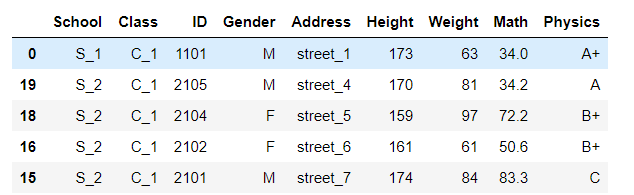
多个值排序,即先对第一层排,在第一层相同的情况下对第二层排序
df.sort_values(by=['Address','Height']).head()

问题

练习一、
df = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\de\Desktop\Game_of_Thrones_Script.csv')
df.head()

df['Name'].nunique()
564
df['Name'].value_counts().index[0]
‘tyrion lannister’
df_words = df.assign(Words=df['Sentence'].apply(lambda x:len(x.split()))).sort_values(by='Name')
df_words.head()

L_count = []
N_words = list(zip(df_words['Name'],df_words['Words']))
for i in N_words:
if i == N_words[0]:
L_count.append(i[1])
last = i[0]
else:
L_count.append(L_count[-1]+i[1] if i[0]==last else i[1])
last = i[0]
df_words['Count']=L_count
df_words['Name'][df_words['Count'].idxmax()]
‘tyrion lannister’
练习二、
df = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\de\Desktop\Kobe_data.csv',index_col='shot_id')
df.head()

pd.Series(list(zip(df['action_type'],df['combined_shot_type']))).value_counts().index[0]
(‘Jump Shot’, ‘Jump Shot’)
pd.Series(list(list(zip(*(pd.Series(list(zip(df['game_id'],df['opponent'])))
.unique()).tolist()))[1])).value_counts().index[0]
‘SAS’





















 398
398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








