利用DCGAN-生成对抗网络和CNN-卷积神经网络对图像进行训练和分类
总体流程步骤
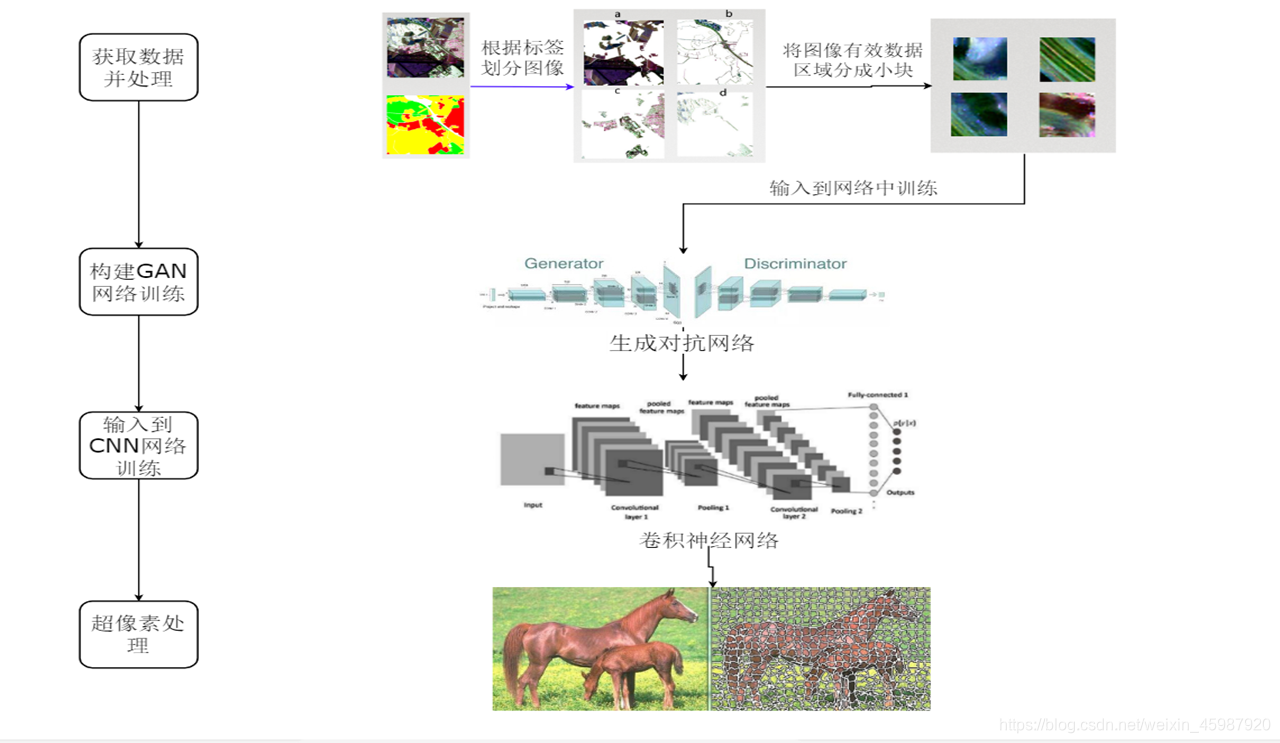

一、图像处理部分
如下图,分别是由SAR卫星获取的极化SAR图像及其标签图

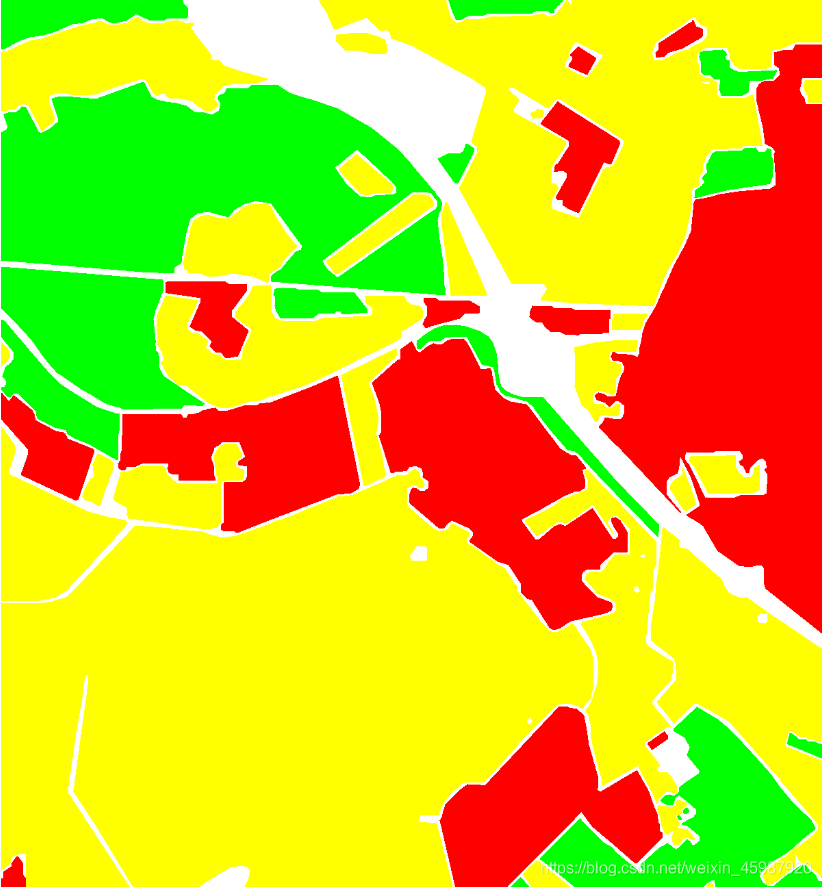
根据不同的颜色标签(红、绿、黄、白)可以将原图分为四个部分(下图只有三部分,白色区域图片没有展示)
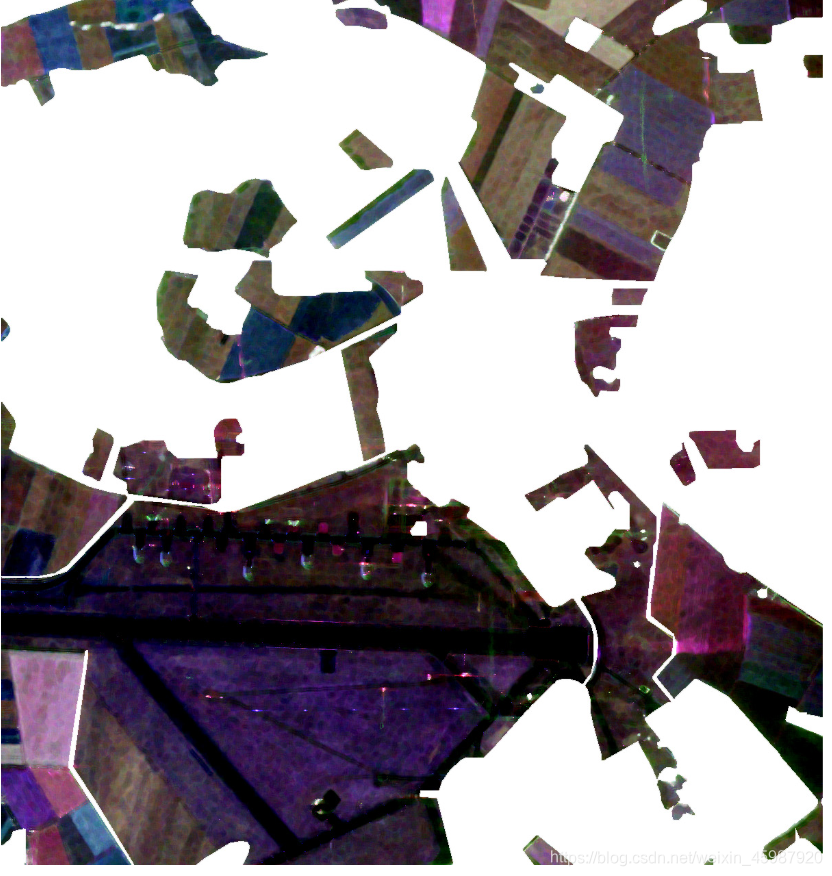
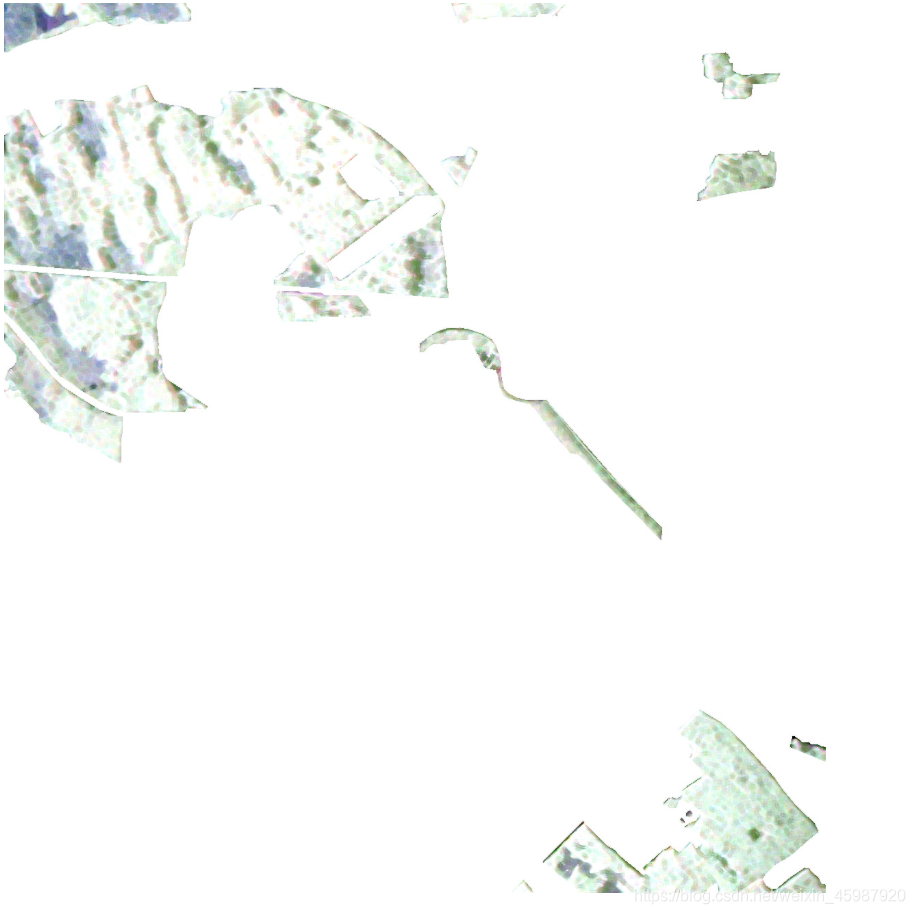


对于图片中有效区域进行裁切分割,按照类型分别存储在不同的文件夹中作为训练数据。
二、训练GAN网络生成模拟图像
每次运行该程序选择某一文件夹的所有图片进行训练得到效果图,直到将所有类型图片都训练完成一遍
# 生成对抗网络模型,训练模型生成仿真图片。
import argparse
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.utils as vutils
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
from random import randint
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class NetG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngf, nz):
super(NetG, self).__init__()
# layer1输入的是一个100x1x1的随机噪声, 输出尺寸(ngf*8)x4x4
# Sequential是一个时序容器modules会以他们传入时的顺序添加到容器中
# ConvTranspose2d是二维卷积转置操作,将普通卷积的输出作为转置卷积的输入
# BatchNorm2d是一个批标准化操作,对每一个小批量中计算各维度的均值和标准差
# inplace=True代表的对源数据进行原地操作
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# 参数分别有:输入通道数,输出通道数,卷积核大小,计算步长大小,补充0的层数,偏置
nn.ConvTranspose2d(nz, ngf * 8, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# layer2输出尺寸(ngf*4)x8x8
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# layer3输出尺寸(ngf*2)x16x16
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# layer4输出尺寸(ngf)x32x32
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# layer5输出尺寸 3x96x96
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf, 3, 5, 3, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
)
# 定义NetG的前向传播
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = self.layer3(out)
out = self.layer4(out)
out = self.layer5(out)
return out
# 定义鉴别器网络D
class NetD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ndf):
super(NetD, self).__init__()
# layer1 输入 3 x 96 x 96, 输出 (ndf) x 32 x 32
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, ndf, kernel_size=5, stride=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
)
# layer2 输出 (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
)
# layer3 输出 (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
)
# layer4 输出 (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
)
# layer5 输出一个数(概率)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# 定义NetD的前向传播
def forward(self,x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = self.layer3(out)
out = self.layer4(out)
out = self.layer5(out)
return out
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--batchSize', type=int, default=64) # 每次处理的图片数量
parser.add_argument('--imageSize', type=int, default=96) # 图片像素大小
parser.add_argument('--nz', type=int, default=100, help='size of the latent z vector') # 图片信息维度
parser.add_argument('--ngf', type=int, default=64)
parser.add_argument('--ndf', type=int, default=64)
parser.add_argument('--epoch', type=int, default=4000, help='number of epochs to train for')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0002, help='learning rate, default=0.0002')
parser.add_argument('--beta1', type=float







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 271
271

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








