job9/pc.c
题目
使用信号量解决生产者、计算者、消费者问题
功能与 job8/pc.c 相同
运行
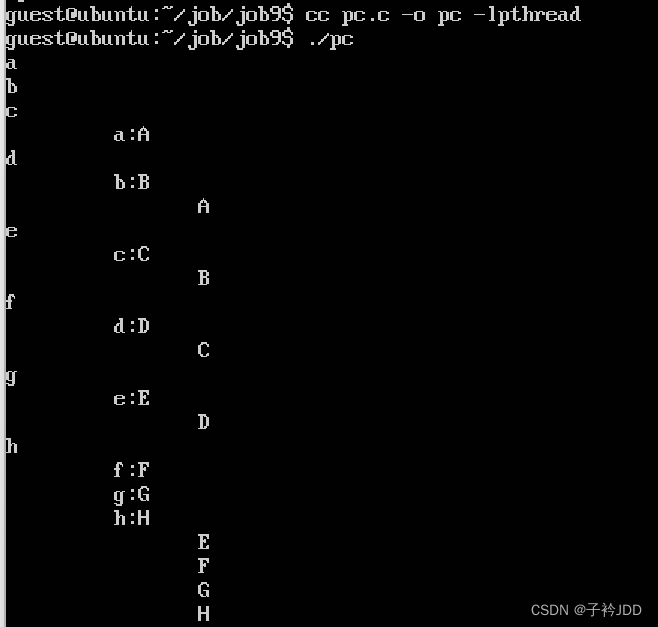
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define CAPACITY 4
int buffer1[CAPACITY],buffer2[CAPACITY];
int in1,in2;
int out1,out2;
int buffer1_is_empty()
{
return in1==out1;
}
int buffer1_is_full()
{
return (in1+1)%CAPACITY==out1;
}
int get_item1()
{
int item;
item = buffer1[out1];
out1 = (out1+1)%CAPACITY;
return item;
}
void put_item1(int item)
{
buffer1[in1] = item;
in1 = (in1+1)%CAPACITY;
}
int buffer2_is_empty()
{
return in2==out2;
}
int buffer2_is_full()
{
return (in2+1)%CAPACITY==out2;
}
int get_item2()
{
int item;
item = buffer2[out2];
out2 = (out2+1)%CAPACITY;
return item;
}
void put_item2(int item)
{
buffer2[in2] = item;
in2 = (in2+1)%CAPACITY;
}
typedef struct{
int value;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
} sema_t;
void sema_init(sema_t *sema,int value)
{
sema->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&sema->mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&sema->cond,NULL);
}
void sema_wait(sema_t *sema)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&sema->mutex);
while(sema->value<=0)
pthread_cond_wait(&sema->cond,&sema->mutex);
sema->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sema->mutex);
}
void sema_signal(sema_t *sema)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&sema->mutex);
++sema->value;
pthread_cond_signal(&sema->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sema->mutex);
}
sema_t mutex1_sema;
sema_t mutex2_sema;
sema_t empty_buffer1_sema;
sema_t empty_buffer2_sema;
sema_t full_buffer1_sema;
sema_t full_buffer2_sema;
#define ITEM_COUNT (CAPACITY * 2)
void *produce(void *arg)
{
int i;
int item;
for(i=0;i<ITEM_COUNT;i++)
{
sema_wait(&empty_buffer1_sema);
sema_wait(&mutex1_sema);
item = i+'a';
put_item1(item);
printf("%c\n",item);
sema_signal(&mutex1_sema);
sema_signal(&full_buffer1_sema);
}
return NULL;
}
void *commpute(void *arg)
{
int i;
int item;
int ITEM;
for(i=0;i<ITEM_COUNT;i++)
{
sema_wait(&full_buffer1_sema);
sema_wait(&mutex1_sema);
item = get_item1();
ITEM = item+'A'-'a';
// printf("commpute:%c\n",item);
printf("\t %c:%c\n",item,ITEM);
sema_signal(&mutex1_sema);
sema_signal(&empty_buffer1_sema);
sema_wait(&empty_buffer2_sema);
sema_wait(&mutex2_sema);
put_item2(ITEM);
sema_signal(&mutex2_sema);
sema_signal(&full_buffer2_sema);
}
return NULL;
}
void *consume(void *arg)
{
int i;
int item;
for(i=0;i<ITEM_COUNT;i++)
{
sema_wait(&full_buffer2_sema);
sema_wait(&mutex2_sema);
item = get_item2();
printf("\t\t%c\n",item);
sema_signal(&mutex2_sema);
sema_signal(&empty_buffer2_sema);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t commpute_tid;
pthread_t consume_tid;
sema_init(&mutex1_sema,1);
sema_init(&mutex2_sema,1);
sema_init(&empty_buffer1_sema,CAPACITY-1);
sema_init(&full_buffer1_sema,0);
sema_init(&empty_buffer2_sema,CAPACITY-1);
sema_init(&full_buffer2_sema,0);
pthread_create(&commpute_tid,NULL,commpute,NULL);
pthread_create(&consume_tid,NULL,consume,NULL);
produce(NULL);
pthread_join(commpute_tid,NULL);
pthread_join(consume_tid,NULL);
return 0;
}
job9/pp.c
题目
使用信号量实现 ping-pong 问题
功能与 job8/pp.c 相同
运行
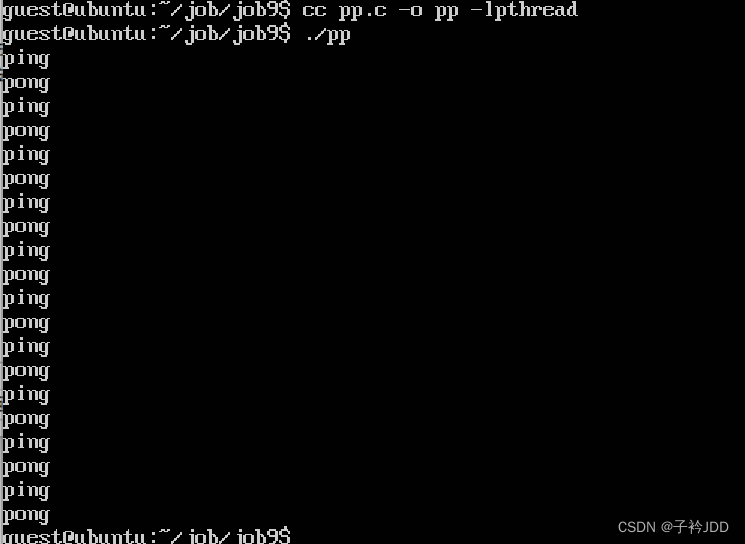
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
typedef struct{
int value;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}sema_t;
void sema_init(sema_t *sema,int value)
{
sema->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&sema->mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&sema->cond,NULL);
}
void sema_wait(sema_t *sema)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&sema->mutex);
while(sema->value<=0)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&sema->cond,&sema->mutex);
}
sema->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sema->mutex);
}
void sema_signal(sema_t *sema)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&sema->mutex);
++sema->value;
pthread_cond_signal(&sema->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sema->mutex);
}
sema_t mutex;
sema_t wait_ping_print;
sema_t wait_pong_print;
int p = 1;
void *ping(void *arg)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sema_wait(&wait_pong_print);
printf("ping\n");
sema_signal(&wait_ping_print);
}
return NULL;
}
void *pong(void *arg)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sema_wait(&wait_ping_print);
printf("pong\n");
sema_signal(&wait_pong_print);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t ping_tid;
pthread_t pong_tid;
sema_init(&wait_ping_print,0);
sema_init(&wait_pong_print,1);
pthread_create(&ping_tid,NULL,ping,NULL);
pthread_create(&pong_tid,NULL,pong,NULL);
pthread_join(ping_tid,NULL);
pthread_join(pong_tid,NULL);
return 0;
}
感想
- 所谓信号量实现线程同步,我感觉就是在代码中将线程同步用函数分装起来,看起来是信号量
- 使用时直接使用sema_wait(),sema_signal()等。
- 线程同步没有value计数,信号量有value可以控制资源数量






















 783
783











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








