数位DP
概念:
数位DP是与数字相关的一类计数问题。在这类题目中,一般给定一些限制条件,求满足限制条件的第K小的数是多少,或者求在区间[L, R]内有多少个满足限制条件的数。这类题先用动态规划进行预处理,在基于拼凑思想,用“试填法”求出最终的答案。
Acwing 1081.度的数量

网上一些题解说的是看成一个树形结构,然后分成二叉树的形式来分情况讨论,但我觉得其实不用看成这么麻烦。
我来说说我的想法:求给定区间[X, Y]中满足下列条件的整数个数:这个数恰好等于 K 个互不相等的 B 的整数次幂之和。我们把每个数(十进制)转化成一个B进制的数,满足条件的数的B进制是有K个1,除了1之外的位都为0。
这样说比较抽象,看看样例来理解,15 ~ 20的2进制表示(因为b = 2):
15 = 01111
16 = 10000
17 = 10001
18 = 10010
19 = 10011
20 = 10100
我们在后续的计算中需要用到在i个位置选j个位置去填1,所以我们要先初始化f[i][j],组合数的公式:f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i - 1][j - 1];我们要计算在[X, Y]中有多少数满足条件,利用前缀和的思想,我们要计算出前n个数中有多少个数满足条件,最后输出dp(y) - dp(x - 1)即可。
现在来分情况讨论,假设现在要计算dp(n)的值,先把n转成b进制数,然后再从第一位遍历到最后一位,假设遍历到的数为x,如果x大于1,在它以及它后面的位中选k - tot个位置“放1”即可(tot是x前面的位中已经放了几个1);如果x == 1,假设在x所在的位置是0,所以在它后面的位中选k - tot个位置“放1”,然后tot++(后续ans累加的都是x所在的位置放1的情况)。最后判断到最后一位的时候,k是否等于tot,如果刚好成立,说明这一种情况也要算在内。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 30;
int f[N][N], k, b;
void u(){
for(int i = 0; i <= N - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++){
if(!j) f[i][j] = 1;
else f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
int dp(int n){
int ans = 0, tot = 0;
vector<int> a;
while(n){
a.push_back(n % b);
n = n / b;
}
for(int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = a[i];
if(x){
if(x > 1){
if(k - tot >= 1) ans += f[i + 1][k - tot]; //从0到i的后面一位总共有i位
break;
}
if(x == 1){
ans += f[i][k - tot];
tot++;
if(tot > k) break;
}
}
if(!i && k == tot) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int x, y;
u();
cin >> x >> y >> k >> b;
cout << dp(y) - dp(x - 1) << endl;
return 0;
}
Acwing 1082、数字游戏
数位dp跟普通的dp不一样,它的dp是在预处理的时候。
典型的数位dp可以看成有一棵树,然后每一层代表的是每一位,假设要进行dp的数中的某一位为x,左边的分支是0 ~ x - 1,右边的分支是x。

这道题是求一个区间内的不降数,我们可以先预处理前i个数的不降数个数,类似于前缀和的思想,最后dp(b) - dp(a - 1)即为所求。
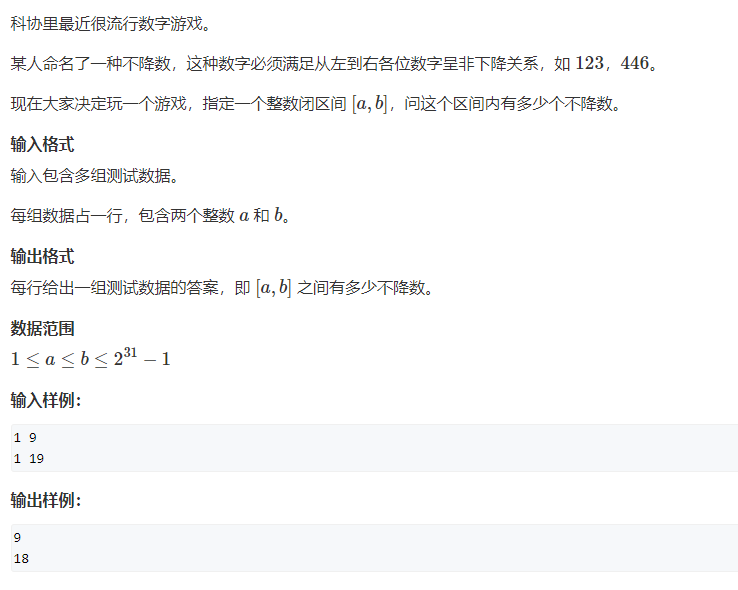
首先进行预处理,定义f[i][j],代表如果有一个数,它是i位数,最左边位的数是j,从0到这个数的不降数是f[i][j]。
预处理之后对题目提供的区间端点,分别求数值比他们小的不降数,假设是求0 ~ n之间的不降数,用个vector把每一位数存进去,然后就按照前面画的树来计算,要用一个last来保存前面的一位(即每一层的右分支),每一层所计算的方案数,都是建立在前一位数为last的前提下,如果某一位的最大数比last小,结束循环。注意,如果最后遍历到最后一位数x也满足条件(本身这个数就满足条件),ans++。
这样说比较抽象,举个例子:一个数368,求0 ~ 368之间的下降数,首先求出百位是0 ~ 2时的不下降数(第一层左分支),接着计算百位是3(第一层右分支),十位是0 ~ 5的不下降数(第二层左分支),最后计算百位是3,十位是6,个位是0 ~ 7的不下降数(第三层左分支),最后第三层右分支(个位数是8)也满足条件,ans++。如果一个数是958,首先计算的是百位是0 ~ 8的不下降数,然后计算百位是9的不下降数(此时发现十位只能是0 ~ 5),发现找不到,直接break。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 15;
int f[N][N];
void init(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) f[1][i] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++){
for(int k = j; k <= 9; k++){
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][k];
}
}
}
}
int dp(int n){
if(!n) return 1;
int ans = 0;
int last = 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n){
nums.push_back(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = nums[i];
if(x < last) break;
for(int j = last; j < x; j++){
ans += f[i + 1][j];
}
last = x;
if(!i) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int a, b;
init();
while(cin >> a >> b){
debug(dp(b)), debug(dp(a - 1));
cout << dp(b) - dp(a - 1) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
P2657 [SCOI2009] windy数

这道题跟上一道题的思路一样,假设我们当前枚举到第i位(设共有n位),且第i位上的数字为x,那么对于答案中第i位数字j来说,有两类:
1、0 ~ x - 1
(如果第i位是最高位,这里是1 ~ x - 1)用last记录上一位的数字,然后枚举j,如果abs(j - last) >= 2 就累加答案,ans += f[i + 1][j];
2、x
不需要枚举j,last = x,再枚举之后的数位即可。
上述做完之后,由于上面的答案都是n位的,对于数位个数低于n的,再累加到答案中就行了。f数组的处理:f[i][j] 表示一共有i位,且最高位数字为j的满足windy数定义的数的个数。
状态转移: 因为第i位是j已经确定,考虑第i - 1位,设第i - 1位数字为k,那么根据windy数定义只要abs(k - j)>= 2就可以转移过来:
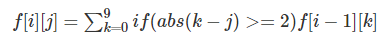
关于前导0:
上面提到了枚举的第i位是最高位,那么不能填0,这里解释一下,如果我们填0,那么答案就会加上f[i+1][0],举个例子,对于数字13,他是满足windy数定义的,那么加上前导0之后的013就不会被f[3][0]加进去,原因就是abs(0 - 1) < 2,这样就导致答案漏掉。
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 11;
int f[N][10];
void init(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) f[1][i] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++){
for(int k = 0; k <= 9; k++){
if(abs(j - k) >= 2) f[i][j] += f[i - 1][k];
}
}
}
}
int dp(int n){
if(!n) return 0;
int last = -2;
int ans = 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n){
nums.push_back(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = nums[i];
for(int j = 0; j < x; j++){ //不能有前导0
if(abs(last - j) >= 2) ans += f[i + 1][j];
}
if(abs(x - last) < 2) break;
else last = x;
if(!i) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int a, b;
init();
cin >> a >> b;
cout << dp(b) - dp(a - 1) << '\n';
return 0;
}
AcWing 1084. 数字游戏 II

在几道数位dp题目练习过后,这类题目重点在于找到左边那一类如何直接计算。
对于这一题来说,假设我们当前枚举到的第i位,且第i位上的数字是x,那么对于答案中的第i位数字j来说,可以填两类数:
1、0 ~ x - 1
我们用last表示到当前为止,前面数位上的数字之和,对此,当前第i位数字为j,前面数字之和为last,那么后i位(包括j这一位)数字之和sum与last的关系就是(last + sum) % N == 0,那么sum % N的结果等价于(-last) % N,所以ans += f[i + 1][j][(-last % N)];
2、x
如果j填x,那么不用枚举了,last += x,再枚举下一位即可。
f数组的处理:f[i][j][k] 表示一共有i位,且最高位数字是j,且所有位数字和模N结果为k的数的个数。
状态转移:因为第i位已经是j,且所有数字之和模N为k,所以我们考虑第i - 1位,假设第i - 1位数字是x,由于j已经知道,那么剩下的i - 1位数字之和模N的结果就是(k - j)%N,那么状态转移方程就是:
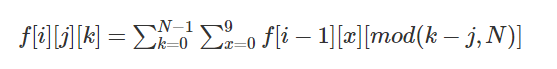
具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 11, M = 110;
int f[N][10][M]; //f[i][j][k] 表示一共有i位,且最高位数字是j,且所有位数字和模p位k的数字个数
int p;
int mod(int x, int y){
return (x % y + y) % y; //c++的 % 会得到负数,需要处理成正数
}
void init(){
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) f[1][i][i % p] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < p; k++){
for(int x = 0; x <= 9; x++){
f[i][j][k] += f[i - 1][x][mod(k - j, p)];
}
}
}
}
}
int dp(int n){
if(!n) return 1;
int last = 0;
int ans = 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n){
nums.push_back(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = nums[i];
for(int j = 0; j < x; j++){ //第i位放0 ~ x - 1
ans += f[i + 1][j][mod(-last, p)]; //0 ~ i位,所以一共有i + 1位
}
last += x;
if(!i && mod(last, p) == 0) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int a, b;
while(cin >> a >> b >> p){
init();
cout << dp(b) - dp(a - 1) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Acwing 1085、不要62
(题意跟杭电一样,但数据范围不同,纯暴力过不了)

还是相同的套路,假设数字num当前枚举到第i位,且第i位数字是x,那么对于答案的第i位来说,假设是j,有两种填法:
1、0 ~ x - 1
我们用last表示num中第i位的高一位数字,那么根据题意,j不能是4且当last是6的时候j不能为2,这两种情况在枚举的时候特判一下即可。然后,累加到答案中,ans += f[i+1][j]。
2.x
那么这一位就不用处理了,更新一下last即可,last = x。
f数组的处理:f[i][j]表示一共有i位,且最高位是j的满足新的士牌照定义的数的个数。
转态转移:第i位是j已知,那么考虑第i - 1位,假设为k,根据牌照定义,j为6时k不为2且k不能等于4。
具体的代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 35;
int f[N][10];
void init(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++){
if(i != 4) f[1][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++){
if(j == 4) continue;
for(int k = 0; k <= 9; k++){
if(k == 4 || j == 6 && k == 2) continue;
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][k];
}
}
}
}
int dp(int n){
if(!n) return 1;
vector<int> nums;
int ans = 0;
int last = 0;
while(n){
nums.push_back(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = nums[i];
for(int j = 0; j < x; j++){
if(j == 4 || last == 6 && j == 2) continue;
ans += f[i + 1][j];
}
if(x == 4 || last == 6 && x == 2) break;
last = x;
if(!i) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int a, b;
init();
while(cin >> a >> b, a || b){
cout << dp(b) - dp(a - 1) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
AcWing 1086. 恨7不成妻

这道题也是求某个区间里边满足某种性质的数的个数,但这道题的性质比较复杂:
1、每一位的数不能是7。
2、每一位加起来的和不能是7的整数倍。
3、这个数本身不能是7的倍数。
其实我们在dp的同时考虑三个性质就可以了,难点在于这道题不是求个数,而是求满足性质的数的平方和。
这道题的预处理太恶心了,反正状态表示和转移都是那样,懒得说了,大概的思路见下图(网上的):

具体的实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void debug_out(){
cerr << endl;
}
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T){
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef local
#define debug(...) cerr<<"["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]:",debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 55
#endif
#define m_p make_pair
const int N = 20, p = 1e9 + 7;
struct F{
int s0, s1, s2;
}f[N][10][7][7];
int mod(LL x, int y){
return (x % y + y) % y;
}
int power7[N], power9[N];
void init(){
for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++){
if(i == 7) continue;
auto &v = f[1][i][i % 7][i % 7];
v.s0++;
v.s1 += i;
v.s2 += i * i;
}
LL power = 10;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++, power *= 10){
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; j++){
if(j == 7) continue;
for(int a = 0; a < 7; a++){
for(int b = 0; b < 7; b++){
for(int k = 0; k <= 9; k++){
if(k == 7) continue;
auto &v1 = f[i][j][a][b], &v2 = f[i - 1][k][mod(a - j * power, 7)][mod(b - j, 7)];
v1.s0 = mod(v1.s0 + v2.s0, p);
v1.s1 = mod(v1.s1 + v2.s1 + j * (power % p) % p * v2.s0, p);
v1.s2 = mod(v1.s2 + j * j * (power % p) % p * (power % p) % p * v2.s0 + v2.s2 + 2 * j * power % p * v2.s1, p);
}
}
}
}
}
power7[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
power7[i] = power7[i - 1] * 10 % 7;
}
power9[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
power9[i] = power9[i - 1] * 10ll % p;
}
}
F get(int i, int j, int a, int b){
int s0 = 0, s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
for(int x = 0; x < 7; x++){
for(int y = 0; y < 7; y++){
if(x != a && y != b){
auto v = f[i][j][x][y];
s0 = (s0 + v.s0) % p;
s1 = (s1 + v.s1) % p;
s2 = (s2 + v.s2) % p;
}
}
}
return {s0, s1, s2};
}
int dp(LL n){
if(!n) return 0;
LL backup_n = n % p;
int ans = 0;
LL last_a = 0, last_b = 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n){
nums.push_back(n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int x = nums[i];
for(int j = 0; j < x; j++){
if(j == 7) continue;
int a = mod(-last_a * power7[i + 1], 7);
int b = mod(-last_b, 7);
auto v = get(i + 1, j, a, b);
ans = mod(ans + (last_a % p) * (last_a % p) % p * power9[i + 1] % p * power9[i + 1] % p * v.s0 % p + v.s2 + 2 * last_a % p * power9[i + 1] % p * v.s1, p);
}
if(x == 7) break;
last_a = last_a * 10 + x;
last_b += x;
if(!i && last_a % 7 && last_b % 7) ans = (ans + backup_n * backup_n) % p;
}
debug(ans);
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T;
init();
cin >> T;
while(T--){
LL a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << mod(dp(b) - dp(a - 1), p) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}





















 1670
1670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








