reinterpret_cast
C++ 强制类型转换运算符的用法如下:
强制类型转换运算符 <要转换到的类型> (待转换的表达式)
reinterpret_cast < type> (expressoin):
reinterpret_cast 运算符把某种指针改为其他类型的指针。它可以把一个指针转换为一个整数,也可以把一个整数转换为一个指针。转换时,执行的是逐个比特复制的操作。
它会产生一个新的值,这个值会有与原始参数(expressoin)有完全相同的比特位。
例如:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int i;
int j;
A(int n):i(n),j(n) { }
};
int main()
{
A a(100);
int &r = reinterpret_cast<int&>(a); //强行让 r 引用 a
r = 200; //把 a.i 变成了 200
cout << a.i << "," << a.j << endl; // 输出 200,100
int n = 300;
A *pa = reinterpret_cast<A*> ( & n); //强行让 pa 指向 n
pa->i = 400; // n 变成 400
pa->j = 500; //此条语句不安全,很可能导致程序崩溃
cout << n << endl; // 输出 400
long long la = 0x12345678abcdLL;
pa = reinterpret_cast<A*>(la); //la太长,只取低32位0x5678abcd拷贝给pa
unsigned int u = reinterpret_cast<unsigned int>(pa);//pa逐个比特拷贝到u
cout << hex << u << endl; //输出 5678abcd
typedef void (* PF1) (int);
typedef int (* PF2) (int,char *);
PF1 pf1; PF2 pf2;
pf2 = reinterpret_cast<PF2>(pf1); //两个不同类型的函数指针之间可以互相转换
}
程序的输出结果是:
200, 100
400
5678abed
第 19 行的代码不安全,因为在编译器看来,pa->j 的存放位置就是 n 后面的 4 个字节。 本条语句会向这 4 个字节中写入 500。但这 4 个字节不知道是用来存放什么的,贸然向其中写入可能会导致程序错误甚至崩溃。
reinterpret_cast体现了 C++ 语言的设计思想:用户可以做任何操作,但要为自己的行为负责。
来自:C++强制类型转换运算符
typedef
typedef int (*MYFUN)(int, int);
这种用法一般用在给函数定义别名的时候
上面的例子定义MYFUN 是一个函数指针, 函数类型是带两个int 参数, 返回一个int
在分析这种形式的定义的时候可以用下面的方法:
先去掉typedef 和别名, 剩下的就是原变量的类型.
去掉typedef和MYFUN以后就剩:
int (*)(int, int)
typedef int (*PFunc)(int);
分析:
去掉typedef ,得到正常变量声明=> int (*PFunc)(int);
变量PFunc的类型为一个函数指针,指向的返回值类型为int,参数类型为int的函数原型;
=> "typedef int (*PFunc)(int)"中PFunc是函数指针类型(该指针类型指向返回值类型为int,参数类型为int的函数)的一个typedef-name。
PFunc fptr; <=> fptr是一个pointer to function with one int parameter, returning int
1 #include "iostream"
2
3 using namespace std;
4
5 int add(int a,int b){
6 return (a+b);
7 }
8
9 typedef int (* func)(int ,int ) ;
10
11 void main(){
12 func f = add;
13 int n = f(1,2);
14 cout << n << endl;
15 }
源码分析:
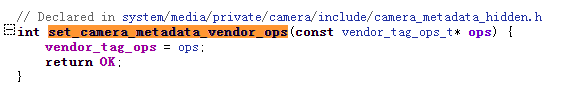
typedef int (*set_camera_metadata_vendor_ops)(const vendor_tag_ops_t *query_ops);
status = reinterpret_cast<set_camera_metadata_vendor_ops>(pfnEntry)(ops);
将pfnEntry转换为set_camera_metadata_vendor_ops类型
reinterpret_cast<set_camera_metadata_vendor_ops>(pfnEntry)这里就看成一体,(ops)就是参数,
例
mtk camera配置中,经常会看到**ppCamcalList的配置,这里简化了一下,帮助理解,如下:
#include<string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned int (*cam_cal_cmd_func) (unsigned int addr, unsigned char *data, unsigned int size);
struct stCAM_CAL_LIST_STRUCT {
unsigned int sensorID;
unsigned int slaveID;
cam_cal_cmd_func readCamCalData;
cam_cal_cmd_func writeCamCalData;
unsigned int maxEepromSize;
};
unsigned int Common_read_region(unsigned int addr,
unsigned char *data, unsigned int size)
{
strcpy(data,"wrt");
printf("read的地址是 %x,size is %d\n", addr,size);
return 0;
}
struct stCAM_CAL_LIST_STRUCT g_camCalList[] = {
{0x36, 0xA0, Common_read_region},
{0x37, 0xA0, Common_read_region},
{0, 0, 0}
};
unsigned int cam_cal_get_sensor_list(
struct stCAM_CAL_LIST_STRUCT **ppCamcalList)
{
if (ppCamcalList == NULL)
return 1;
*ppCamcalList = &g_camCalList[0];
return 0;
}
int main ()
{
int ret=1;
char *p=(char *)malloc(10);
struct stCAM_CAL_LIST_STRUCT *pCamCalList = NULL;
cam_cal_get_sensor_list(&pCamCalList);
printf("pCamCalList 0的id是 %x\n", pCamCalList->sensorID);
printf("pCamCalList 1的id是 %x\n", pCamCalList[1].sensorID);
ret=pCamCalList[1].readCamCalData(pCamCalList[1].slaveID,p,50);
printf("g_camCalList 1的id是 %x\n", g_camCalList[1].sensorID);
printf("buff是 %s\n", p);
return 0;
}
输出:
pCamCalList 0的id是 36
pCamCalList 1的id是 37
read的地址是 a0,size is 50
g_camCalList 1的id是 37
buff是 wrt
cam_cal_cmd_func是一个函数指针,
g_camCalList是需要我们配置的地方,下面通过
cam_cal_get_sensor_list(&pCamCalList)拿到结构体,
cam_cal_get_sensor_list函数的参数是个**ppCamcalList类型的
所以,参数要传一个*ppCamcalList的地址,即&pCamCalList。
cam_cal_get_sensor_list函数中,ppCamcalList就是**ppCamcalList的指向,要做的工作,就是将ppCamcalList指向g_camCalList结构体数组,而&g_camCalList[0]就是数组的首地址,也就是
*ppCamcalList = &g_camCalList[0];
因为是数组的首地址,所以 &g_camCalList[0];与g_camCalList是等价的。






















 860
860











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








