Java 学习 Day07
一、this关键字的使用
-
this可以用来修饰、调用:属性、方法、构造器
-
this修饰属性和方法:
this理解为:当前对象 或 当前正在创建的对象
(1)在类的方法中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用当前对象属性或方法。但是,通常情况下,我们都选择省略"this."。特殊情况下,如果方法的形参和类的属性同名时,我们必须显式的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。
(2) 在类的构造器中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用当前正在创建的对象属性或方法。但是,通常情况下,我们都选择省略 “this.”。特殊情况下,如果构造器的形参和类的属性同名时,我们必须显式的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。 -
this调用构造器
① 我们在类的构造器中,可以显式的使用"this(形参列表)"方式,调用本类中指定的其他构造器
② 构造器中不能通过"this(形参列表)“方式调用自己
③ 如果一个类中有n个构造器,则最多有 n - 1构造器中使用了"this(形参列表)”
④ 规定:"this(形参列表)“必须声明在当前构造器的首行
⑤ 构造器内部,最多只能声明一个"this(形参列表)”,用来调用其他的构造器 -
例1:

public class Boy {
private String name;
private int age;
public Boy() {
}
public Boy(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Boy(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age=age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void marry(Girl girl) {
System.out.println("我想娶" + girl.getName());
}
public void shout() {
if(this.age>=22) {
System.out.println("你可以去合法登记结婚了!");
}else {
System.out.println("先多谈谈恋爱~~");
}
}
}
public class Girl {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girl() {
}
public Girl(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void marry(Boy boy){
System.out.println("我想嫁给" + boy.getName());
boy.marry(this);
}
/**
*
* @Description 比较两个对象的大小
* @param girl
* @return 正数:当前对象大; 负数:当前对象小 ; 0:当前对象与形参对象相等
*/
public int compare(Girl girl){
// if(this.age > girl.age){
// return 1;
// }else if(this.age < girl.age){
// return -1;
// }else{
// return 0;
// }
return this.age - girl.age;
}
}
public class BoyGirlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy = new Boy("罗密欧", 21);
boy.shout();
Girl girl = new Girl("朱丽叶", 18);
girl.marry(boy);
Girl girl1 = new Girl("祝英台",19);
int compare = girl.compare(girl1);
if(compare > 0){
System.out.println(girl.getName() + "大");
}else if(compare < 0){
System.out.println(girl1.getName() + "大");
}else{
System.out.println("一样大");
}
}
}
例2:

public class Account {
private int id;//账号
private double balance;//余额
private double annualInterestRate;//年利率
public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
//在提款方法withdraw中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示
public void withdraw(double amount) {//取钱
if(balance<amount ) {
System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");
}else {
balance-=amount;
System.out.println("成功取出:" + amount);
}
}
public void deposit (double amount){//存钱
if(amount > 0){
balance += amount;
System.out.println("成功存入:" + amount);
}
}
}
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String f,String l){
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
}
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer cust=new Customer("Jane", "Smith");
Account acct=new Account(1000, 2000, 0.0123);
cust.setAccount(acct);//建立账户跟顾客的关系,把acct赋给形参,此时赋的是地址值,指向了1000, 2000, 0.0123
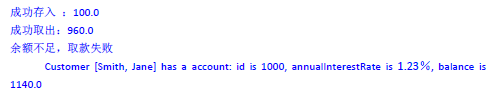
cust.getAccount().deposit(100);//先get到账户,然后再存,调用了两个类中的两个方法
cust.getAccount().withdraw(960);
cust.getAccount().withdraw(2000);
System.out.println("Customer[" + cust.getLastName() + "," + cust.getFirstName() +
"] has a account: id is " + cust.getAccount().getId() + ",annualInterestRate is "+
cust.getAccount().getAnnualInterestRate() * 100 + "% ,balance is " + cust.getAccount().getBalance());
}
}
例3:


public class Account {
private double balance;
public Account(double init_balance){
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public double getBalance(){
return balance;
}
//存钱操作
public void deposit(double amt){
if(amt > 0){
balance += amt;
System.out.println("存钱成功");
}
}
//取钱操作
public void withdraw(double amt){
if(balance >= amt){
balance -= amt;
System.out.println("取钱成功");
}else{
System.out.println("余额不足");
}
}
}
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String f, String l) {
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
public class Bank {
private Customer[] customers;// 存放多个客户的数组
private int numberOfCustomers;// 记录客户的个数
public Bank() {
customers = new Customer[10];//初始化数组
}
// 添加客户
public void addCustomer(String f, String l) {
Customer cust = new Customer(f, l);
// customers[numberOfCustomers] = cust;
// numberOfCustomers++;
// 或
customers[numberOfCustomers++] = cust;
}
// 获取客户的个数
public int getNumOfCustomers() {
return numberOfCustomers;
}
// 获取指定位置上的客户
public Customer getCustomer(int index) {
// return customers[index];//可能报异常
if (index >= 0 && index < numberOfCustomers) {
return customers[index];
}
return null;
}
}
public class BankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank bank = new Bank();
bank.addCustomer("Jane", "Smith");
//连续操作
bank.getCustomer(0).setAccount(new Account(2000));//在顾客中建立一个账户
bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().withdraw(500);//在顾客的账户中取钱
double balance = bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().getBalance();//得到顾客的账户余额
System.out.println("客户:" + bank.getCustomer(0).getFirstName() + "的账户余额为:" + balance);
System.out.println("***********************");
bank.addCustomer("万里", "杨");
System.out.println("银行客户的个数为:" + bank.getNumOfCustomers());
}
}
二、package关键字的使用
- 为了更好的实现项目中类的管理,提供包的概念
- 使用package声明类或接口所属的包,声明在源文件的首行
- 包,属于标识符,遵循标识符的命名规则、规范(xxxyyyzzz)、“见名知意”
- 每“.”一次,就代表一层文件目录。
- 补充:
(1)同一个包下,不能命名同名接口、类
(2)不同的包下,可以命名同名的接口、类


三、import关键字的使用
- import:导入
- 在源文件中显式的使用import结构导入指定包下的类、接口
- 声明在包的声明和类的声明之间
- 如果需要导入多个结构,则并列写出即可
- 可以使用"xxx.*"的方式,表示可以导入xxx包下的所有结构
- 如果使用的类或接口是java.lang包定义一下的,则可以省略import结构
- 如果使用的接口是本包下定义的,则可以省略import结构
- 如果源文件中,使用了不同包下的同名的类,则必须至少有一个类需要以全类名的方式显示
- 如果使用"xxx.*"方式表明可以调用xxx包下的所有结构,但是如果使用的是xxx子包下的结构,则仍需要显式导入
- import static:导入指定类或接口中的静态结构:属性或方法。
例:
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class PackageImportTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String info = Arrays.toString(new int[]{1,2,3});
Bank bank = new Bank();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Scanner s = null;
System.out.println("hello!");
Person p = new Person();
Account acct = new Account(1000);
//全类名的方式显示
com.atguigu.exer3.Account acct1 = new com.atguigu.exer3.Account(1000,2000,0.0123);
Date date = new Date();
java.sql.Date date1 = new java.sql.Date(5243523532535L);
Dog dog = new Dog();
Field field = null;
out.println("hello");
long num = round(123.434);
}
}






















 394
394











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








